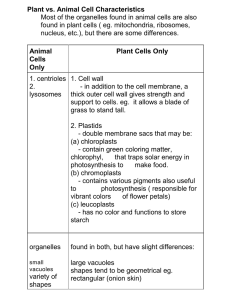
Plant vs. Animal Cell Characteristics Most of the organelles found in
... Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
... Most of the organelles found in animal cells are also found in plant cells ( eg. mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, etc.), but there are some differences. Animal Cells Only ...
Ch.7.4 Homeostasis Notes
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
11-14-02
... Discovery of the Cell Invention of the microscope seventeenth century Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
... Discovery of the Cell Invention of the microscope seventeenth century Robert Hooke , Looked at cork Saw little boxes that reminded him of cells in a monastery; Coined the word cell Anton von Leeuwenhoek observed the first living cell ...
cell_assignment
... Purpose: To describe the differences between animal and plant cells. Materials and Methods: ...
... Purpose: To describe the differences between animal and plant cells. Materials and Methods: ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
cells_can_you
... Describe and draw the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine, and a palisade mesophyll cell from a plant, as seen with a light microscope. Recall that eukaryotic cells have organelles, including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, roug ...
... Describe and draw the structure of an epithelial cell from the small intestine, and a palisade mesophyll cell from a plant, as seen with a light microscope. Recall that eukaryotic cells have organelles, including the cell wall, the cell membrane, the nucleus, the mitochondrion, the chloroplast, roug ...
Cellular Processes
... Getting materials in and out of cells • Food needs to get into the cell, wastes need to get out, and water is constantly moving back and forth. • Substances that can easily pass through the semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of ...
... Getting materials in and out of cells • Food needs to get into the cell, wastes need to get out, and water is constantly moving back and forth. • Substances that can easily pass through the semi-permeable cell membrane do so by passive transport Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
Cell Size Limitations
... Most cells are between 2µm and 200µm A micrometer is 1 millionth of a meter! Too small to be seen with naked eye ...
... Most cells are between 2µm and 200µm A micrometer is 1 millionth of a meter! Too small to be seen with naked eye ...
Name______________________________________
... The structure labeled I in Figure 7-1 is a thin, flexible barrier around a cell. It is called the: ...
... The structure labeled I in Figure 7-1 is a thin, flexible barrier around a cell. It is called the: ...
Mechanobiology of tumour
... Integrative cell and tissue dynamics group Group leader: Xavier Trepat ...
... Integrative cell and tissue dynamics group Group leader: Xavier Trepat ...
Slide 1
... 7. Some organelles have their own DNA that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This is true of which organelle? A cell wall B mitochondrion C plasma membrane D vacuole ...
... 7. Some organelles have their own DNA that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This is true of which organelle? A cell wall B mitochondrion C plasma membrane D vacuole ...
Slide 1
... • Working genes which are incorporated into the cell then produce their protein products, correcting the cell’s malfunction • So cells will continue to create copies of inserted DNA, new gene needs to integrate into cell’s DNA – Altered retroviruses (disease-causing genetic material removed) integra ...
... • Working genes which are incorporated into the cell then produce their protein products, correcting the cell’s malfunction • So cells will continue to create copies of inserted DNA, new gene needs to integrate into cell’s DNA – Altered retroviruses (disease-causing genetic material removed) integra ...
CELL PARTS
... 10. Chloroplast --Converts light energy to carbohydrates --Has stacks of thylakoids --Has its own DNA ...
... 10. Chloroplast --Converts light energy to carbohydrates --Has stacks of thylakoids --Has its own DNA ...
Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... plant), what their function is, and a real life example of each(analogy): cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cel ...
... plant), what their function is, and a real life example of each(analogy): cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. b. What are the differences between an animal cel ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...
... NAME: ___________________________ Text Book Reading Questions…The Cell!!! (See chapter 7 in your book to answer these questions) 1. The size of a typical cell is _______________. 2. Who was the first person to observe “cells”? 3. The cell theory states: (3 parts) 4. What is the timeline for the hist ...