lesson_10
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
10-2 Cell Division lecture notes
... Each chromosomes makes__________________________________________________ Nucleolus _____________________ Nuclear envelope __________________________ Cell Cycle: a series of events that cells ________________________________________ ________________________________________ The cell grows, prepares to ...
... Each chromosomes makes__________________________________________________ Nucleolus _____________________ Nuclear envelope __________________________ Cell Cycle: a series of events that cells ________________________________________ ________________________________________ The cell grows, prepares to ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... Instructions: Review your notes, labs and homework to study for your test (chapter 3). A. Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a picture. nucleus cell membrane golgi bodies vacuoles ...
... Instructions: Review your notes, labs and homework to study for your test (chapter 3). A. Structures and Function of Cells- Know the function of each and be able to apply an analogy (Like your cell factory). Also be able to label a picture. nucleus cell membrane golgi bodies vacuoles ...
Cell Organelles Chart File
... -Contains genetic information (DNA) -Moves chromosomes during cell division ...
... -Contains genetic information (DNA) -Moves chromosomes during cell division ...
Week 9 CELL WALLS are found in plant cells. They are made up of
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
Chapter 6 Learning Targets 2016
... Explain the main ideas of the cell theory. Describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. Describe and distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Compare and contrast animal cells and plant cells. Describe the structure of cellular membranes Describe how passive transport occurs. Relate ...
... Explain the main ideas of the cell theory. Describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. Describe and distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Compare and contrast animal cells and plant cells. Describe the structure of cellular membranes Describe how passive transport occurs. Relate ...
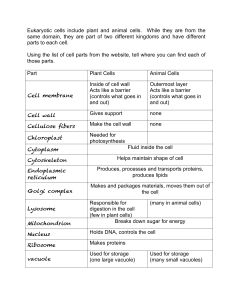
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
june 2 9h - 17h II Simpósio Temático DNA
... Glutamine metabolism and epigenetic control of cancer stem cell population ...
... Glutamine metabolism and epigenetic control of cancer stem cell population ...
Organic Compounds= most compounds containing carbon… make
... (ATP), can also offer structure and support (Cellulose & chitin) Cell walls, cytoskeleton ,mitochondr ia, chloroplasts primarily ...
... (ATP), can also offer structure and support (Cellulose & chitin) Cell walls, cytoskeleton ,mitochondr ia, chloroplasts primarily ...
Name - Humble ISD
... What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between active and passive transport? Describe the factors that determine potential osmotic pressure of electrolyte and non-electrolyte solutions. How does cell membrane permeability ...
... What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between active and passive transport? Describe the factors that determine potential osmotic pressure of electrolyte and non-electrolyte solutions. How does cell membrane permeability ...
Cell Specialization
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
Figure 1-21: Microtubules in a dividing cell.
... (A) A nerve cell from the cerebellum (a part of the brain that controls movement). This cell has a huge branching tree of processes, through which it receives signals from as many as 100,000 other nerve cells. (B) Paramecium. This protozoan swims by means of the beating cilia that cover its surface. ...
... (A) A nerve cell from the cerebellum (a part of the brain that controls movement). This cell has a huge branching tree of processes, through which it receives signals from as many as 100,000 other nerve cells. (B) Paramecium. This protozoan swims by means of the beating cilia that cover its surface. ...
Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... KEY QUESTION: What do all living things have in common? Looking Ahead Living things have several characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. All living things are made up of one or more cells. The compound microscope is an instrument used to see cells and can help us learn more abo ...
... KEY QUESTION: What do all living things have in common? Looking Ahead Living things have several characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things. All living things are made up of one or more cells. The compound microscope is an instrument used to see cells and can help us learn more abo ...
1b. The three statements that make up the cell theory
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure
... found in vesicles called lysosomes. • Known as the “garbage disposal” of the cell. ...
... found in vesicles called lysosomes. • Known as the “garbage disposal” of the cell. ...
By570PresAnimated
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
... – Identifying scientist who contributed to the Cell Theory – Defining important genetic terms (homozygous, dominant, etc) – Calculating genotypic and phenotypic percentages and ratios using a Punnett’s Square – Explaining relationships among DNA, genes & chromosomes – Relating genetic disorders and ...
Cell Division and Cancer Study Guide
... Metaphase – chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell ...
... Metaphase – chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell ...
biology exam review
... Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ systems and how each one interacts with at least one ...
... Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ systems and how each one interacts with at least one ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... 9. Briefly explain where proteins are made, modified, and packaged within a cell. 10. Explain what mitochondria do and what suggests that they may have descended from prokaryotic cells. ...
... 9. Briefly explain where proteins are made, modified, and packaged within a cell. 10. Explain what mitochondria do and what suggests that they may have descended from prokaryotic cells. ...
Unit_biology_2_Cells
... b) Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. Plant cells often have: ■ chloroplasts, which absorb light energy to make food ■ a permanent vacuole filled with cell sap. c) A bacterial cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall; ...
... b) Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell. Plant cells often have: ■ chloroplasts, which absorb light energy to make food ■ a permanent vacuole filled with cell sap. c) A bacterial cell consists of cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall; ...
Cells and Cell Organelle Test Review Sheet
... 3. If an element has 5 protons how many electrons will it have? 4. What are the major chemicals in the cell? C. H. N, O, P, S (SCHNOP) 5. Name the four properties of water. 6. What is adhesion? 7. What does heat capacity mean? 8. What is an enzyme? 9. What are the major molecules of life? 10. Which ...
... 3. If an element has 5 protons how many electrons will it have? 4. What are the major chemicals in the cell? C. H. N, O, P, S (SCHNOP) 5. Name the four properties of water. 6. What is adhesion? 7. What does heat capacity mean? 8. What is an enzyme? 9. What are the major molecules of life? 10. Which ...
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY
... b) Name the deficiency disease that results from lack of proteins in a persons diet 4. Two students were observing bacteria using two identical microscopes and identical slides. Students A saw 10 bacteria while student B saw 50 bacteria. a) Suggest a reason as to why they observed different numbers ...
... b) Name the deficiency disease that results from lack of proteins in a persons diet 4. Two students were observing bacteria using two identical microscopes and identical slides. Students A saw 10 bacteria while student B saw 50 bacteria. a) Suggest a reason as to why they observed different numbers ...
Ch 3 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Cell walls of algae are made of cellulose, proteins, agar, carrageenan, silicates, algin, calcium carbonate, or a combination of the aforementioned • ALL have cytoplasmic membrane ...
... • Cell walls of algae are made of cellulose, proteins, agar, carrageenan, silicates, algin, calcium carbonate, or a combination of the aforementioned • ALL have cytoplasmic membrane ...