Quiz D - exam Q`s
... A. Chitin B. Glucose C. Cellulose D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Tra ...
... A. Chitin B. Glucose C. Cellulose D. Glycogen 2. mRNA is A. A double-stranded molecule B. Found only in eukaryotic cells C. Found exclusively in the nucleus D. Formed during transcription of DNA 3. Lipids are A. Used as an energy source B. Involved in active transport C. Part of glycoproteins D. Tra ...
Mitosis and Cancer - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
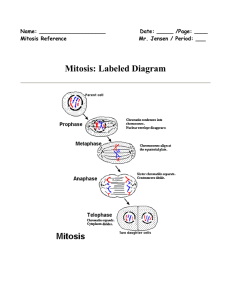
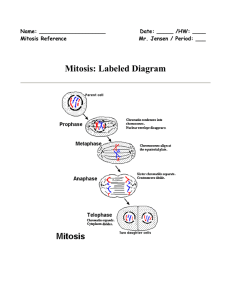
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
cells-study-guide
... Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
... Understand how these relate to each other Organism > Organ System > Organ > Tissue > Cell ...
Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
sgCh1Cell
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
... Name _______________________________Date______________ Block ______________ Science Chapter 1 (Study Guide) Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek obs ...
science chapter 1 questions
... of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes themto other parts of the cell. 2b. the endoplasmic reticulum carry proteins form one part to another 2c. the ...
... of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes themto other parts of the cell. 2b. the endoplasmic reticulum carry proteins form one part to another 2c. the ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
Document
... • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm • Animals – cleavage furrow • Plants – Cell plate ...
... • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm • Animals – cleavage furrow • Plants – Cell plate ...
The Cell Theory
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. Why didn’t anyone know about cells before the late 17th century? __________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 9/10 Short Answer questions
... 1. Lab Question: A slide of dividing cells in an onion root tip is a “snapshot” in time. Each cell is stopped at the particular point in tis cell cycle when the slide was made. A biology student examined such a slide under a microscope. Out of 100 cells she caught in the act of dividing, 38 were in ...
... 1. Lab Question: A slide of dividing cells in an onion root tip is a “snapshot” in time. Each cell is stopped at the particular point in tis cell cycle when the slide was made. A biology student examined such a slide under a microscope. Out of 100 cells she caught in the act of dividing, 38 were in ...
Matching Cell Parts WS File
... ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane breaking loose; stores substances ____8. Sites for photosynthesis; found only in plant cells; contains chlorophyll ____9. Locomotive structures; ...
... ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane breaking loose; stores substances ____8. Sites for photosynthesis; found only in plant cells; contains chlorophyll ____9. Locomotive structures; ...
Cells - biologybi
... Plasm- contains organelles. Vacuoles- storage areas for food, minerals, and waste. Mitochondria- releases energy for functions. Chloro Plasts- contains chlorophyll used for photosynthesis. (Plant cells only) Ribosome- helps make proteins. ...
... Plasm- contains organelles. Vacuoles- storage areas for food, minerals, and waste. Mitochondria- releases energy for functions. Chloro Plasts- contains chlorophyll used for photosynthesis. (Plant cells only) Ribosome- helps make proteins. ...
Get a PDF of this story
... the cell remains in an uncontrolled state. By principles governing differentiation pinpointing this noise and its “off” switch, in complex animals.” ...
... the cell remains in an uncontrolled state. By principles governing differentiation pinpointing this noise and its “off” switch, in complex animals.” ...
l2 biology: topics covered on the midterm exam and what to study
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
Chapter 7 Review Questions
... chambers within cork and named them “cells”? 2. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells are produced from existing cells. 6. Looking at a cell und ...
... chambers within cork and named them “cells”? 2. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells are able to reproduce. d. All cells are produced from existing cells. 6. Looking at a cell und ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...