2nd Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide - Mr. Barger
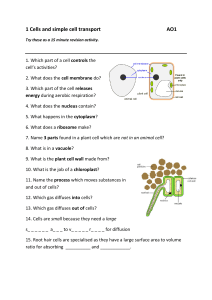
... 6. Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called _________________. 7. Vertical rows of the periodic table are called ___________________. 8. Isotopes are atoms of the same element who have a different number of _____________________. 9. Radioactive isotopes have ________________ nuclei and will ...
... 6. Horizontal rows of the periodic table are called _________________. 7. Vertical rows of the periodic table are called ___________________. 8. Isotopes are atoms of the same element who have a different number of _____________________. 9. Radioactive isotopes have ________________ nuclei and will ...
Diapositiva 1
... Cancer is characterized by abnormal, unrelated cell proliferation Cancer invades healthy tissues and compete with normal cells for oxygen, nutrients, and space Abnormal cells reproduce in the same way as normal cells, but they do not have the regulatory mechanisms to control growth The abnor ...
... Cancer is characterized by abnormal, unrelated cell proliferation Cancer invades healthy tissues and compete with normal cells for oxygen, nutrients, and space Abnormal cells reproduce in the same way as normal cells, but they do not have the regulatory mechanisms to control growth The abnor ...
Malayer research
... organisms are the result of specific expression of subsets of genes present in the genome. The processes that establish and maintain these patterns of expression begin in the earliest developmental stages. We are interested in the combinatorial diversity of the molecular interactions that control ce ...
... organisms are the result of specific expression of subsets of genes present in the genome. The processes that establish and maintain these patterns of expression begin in the earliest developmental stages. We are interested in the combinatorial diversity of the molecular interactions that control ce ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
... Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
Honors Biology
... Infects plants, animals, bacteria (all life) Lytic (short) vs. Lysogenic (long) – Cell dies Retrovirus (RNA DNA) Reverse transcription No treatment(antibiotics), vaccines prevent Bacteriophage – infect bacteria only ...
... Infects plants, animals, bacteria (all life) Lytic (short) vs. Lysogenic (long) – Cell dies Retrovirus (RNA DNA) Reverse transcription No treatment(antibiotics), vaccines prevent Bacteriophage – infect bacteria only ...
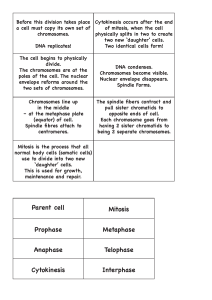
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. Cell Theory A. Discovered since 1600 by
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
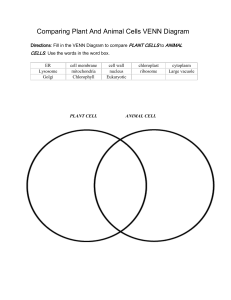
... Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1.2 Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell ...
... Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1.2 Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell ...
Organelles – Who Am I?
... 1. I surround the nucleus and protect it. 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and supports organelles. 4. I am a series of tubes found throughout the cell. I transport proteins ...
... 1. I surround the nucleus and protect it. 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and supports organelles. 4. I am a series of tubes found throughout the cell. I transport proteins ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 5. How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells alike? A.K.A. How are cells alike? ...
... 5. How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells alike? A.K.A. How are cells alike? ...
Cell anatomy and cell division
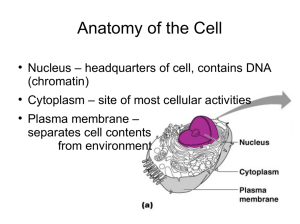
... Nucleus – headquarters of cell, contains DNA (chromatin) Cytoplasm – site of most cellular activities Plasma membrane – separates cell contents from environment ...
... Nucleus – headquarters of cell, contains DNA (chromatin) Cytoplasm – site of most cellular activities Plasma membrane – separates cell contents from environment ...
Tour of the Cell Chapter 6
... of cells. Curriculum prepares individuals to work in clinical laboratory settings. Students learn basic science principles and complete a clinical practicum. Training is focused on detecting abnormalities at the cellular level using microscopic evaluation methods. Successful individuals will possess ...
... of cells. Curriculum prepares individuals to work in clinical laboratory settings. Students learn basic science principles and complete a clinical practicum. Training is focused on detecting abnormalities at the cellular level using microscopic evaluation methods. Successful individuals will possess ...
Chapter 6 Exam – Part II
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
Abbreviation Protein Name Function AKT3 AKT serine/threonine
... nucleotide exchange on RanGTP, and also binds directly to nuclear pore complexes ...
... nucleotide exchange on RanGTP, and also binds directly to nuclear pore complexes ...
First Grade Portfolio
... common. (Nucleus, Mitochondria, Membrane) Nucleus-the “brain” of the cell. -Contains genetic information - controls the cell’s activity by directing protein synthesis -( a combination or mixture) Mitochondria- carries out cellular respiration in eurakaryotic cells -Converts nutrients into energy in ...
... common. (Nucleus, Mitochondria, Membrane) Nucleus-the “brain” of the cell. -Contains genetic information - controls the cell’s activity by directing protein synthesis -( a combination or mixture) Mitochondria- carries out cellular respiration in eurakaryotic cells -Converts nutrients into energy in ...