Animal Cell Structure
... The lack of a rigid cell wall allowed animals to develop a greater diversity of cell types, tissues, and organs. Specialized cells that formed nerves and muscles -- tissues impossible for plants to evolve -- gave these organisms mobility. The ability to move about by the use of specialized muscle ti ...
... The lack of a rigid cell wall allowed animals to develop a greater diversity of cell types, tissues, and organs. Specialized cells that formed nerves and muscles -- tissues impossible for plants to evolve -- gave these organisms mobility. The ability to move about by the use of specialized muscle ti ...
Spirogyra - Biology Resources
... Spirogyra Spirogyra is a member of the Algae. These are simple plants ranging from single-celled organisms (Chlamydomonas, Euglena) to complex seaweeds. They contain chlorophyll and make their food by photosynthesis. Spirogyra is a filamentous alga. Its cells form long, thin strands that, in vast nu ...
... Spirogyra Spirogyra is a member of the Algae. These are simple plants ranging from single-celled organisms (Chlamydomonas, Euglena) to complex seaweeds. They contain chlorophyll and make their food by photosynthesis. Spirogyra is a filamentous alga. Its cells form long, thin strands that, in vast nu ...
Cell Structure
... related to function at all levels of biological organization from molecules to organisms. Lesson Essential Questions: What are the major structures and functions of a typical cell? What are the parts and function of the endomembrane system? How do surface structures of cells help them survive? ...
... related to function at all levels of biological organization from molecules to organisms. Lesson Essential Questions: What are the major structures and functions of a typical cell? What are the parts and function of the endomembrane system? How do surface structures of cells help them survive? ...
Cell structure and function
... • The icons on the slides are designed to help you remember the function of each cell part. ...
... • The icons on the slides are designed to help you remember the function of each cell part. ...
pbioch3quiz frisci blog
... 14. Use the following words to complete the paragraph. Endoplasmic Reticulum, DNA, Golgi complex, amino acids, ribosome. In order to make a protein, _______ that is found in the nucleus is copied. RNA is then taken to a ______________, which are small organelles found on the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... 14. Use the following words to complete the paragraph. Endoplasmic Reticulum, DNA, Golgi complex, amino acids, ribosome. In order to make a protein, _______ that is found in the nucleus is copied. RNA is then taken to a ______________, which are small organelles found on the endoplasmic reticulum. ...
pogil 9
... mitochondria or chloroplasts. In the nucleus you find two circular chromosomes. Propose a series of events that led to evolution of this organism. ...
... mitochondria or chloroplasts. In the nucleus you find two circular chromosomes. Propose a series of events that led to evolution of this organism. ...
Biology 109: Biology Today Laboratory 2 A literature review of cells
... Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
... Have a full understanding of the (many) events involved in a typical cell life cycle. Have extra help to study for Exam One!! ...
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
... D. Chromatin and Chromosomes 1. DNA bound to protein 2. Chromatin is the Stringy material seen in ...
... D. Chromatin and Chromosomes 1. DNA bound to protein 2. Chromatin is the Stringy material seen in ...
Part B: Cell Organelles Structure and Function
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
Cell Structures (chapter 7-1, 7-2)
... What is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? nucleus What is the cells boundary from its environment? cell membrane What contains DNA, is the control center, and is found in eukaryotes? nucleus What type of cells has chloroplasts? plants What organelle is responsible for digesting and recycli ...
... What is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? nucleus What is the cells boundary from its environment? cell membrane What contains DNA, is the control center, and is found in eukaryotes? nucleus What type of cells has chloroplasts? plants What organelle is responsible for digesting and recycli ...
Cell Theory
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All livings are composed of cells. Unicellular & multicellular. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell ...
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All livings are composed of cells. Unicellular & multicellular. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell ...
The Cell
... • A protective covering • Made up of polysaccharides • Keep the bacterium from drying out & to protect it ...
... • A protective covering • Made up of polysaccharides • Keep the bacterium from drying out & to protect it ...
cells - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... Organelle - specialized structures within a cell with a specific function, separated by a membrane. ...
... Organelle - specialized structures within a cell with a specific function, separated by a membrane. ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is the function of the nucleus? Where DNA and RNA are made 10. Lysosomes ar ...
... Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is the function of the nucleus? Where DNA and RNA are made 10. Lysosomes ar ...
Cell Biology - rci.rutgers.edu
... a. Cytosol—fluid in which other components are suspended b. Organelles (see below) c. Inclusions—non-functioning chemicals substances that may be unique to a given cell type B. Ribosomes—site of protein synthesis 1. Complexes of RNA and protein 2. Free in cytosol a. Suspended in the cytosol ...
... a. Cytosol—fluid in which other components are suspended b. Organelles (see below) c. Inclusions—non-functioning chemicals substances that may be unique to a given cell type B. Ribosomes—site of protein synthesis 1. Complexes of RNA and protein 2. Free in cytosol a. Suspended in the cytosol ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... ______________ are made of ____________________and have unique _______________________ (size, ____________, acidity) Since _______________ carry out critical functions, they __________ to be made __________________ ...
... ______________ are made of ____________________and have unique _______________________ (size, ____________, acidity) Since _______________ carry out critical functions, they __________ to be made __________________ ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...
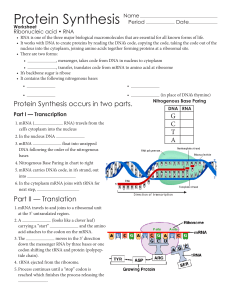
Protein Synthesis
... , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It contains the following nitrogenous bases ...
... , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It contains the following nitrogenous bases ...
Cell Division
... In order for the parent cell to produce two new identical daughter cells, the genetic material from the parent cell nucleus must be passed on to the nuclei of the daughter cells. Cell division occurs in a series of phases. Phase 1: Chromosomes are copied (Interphase) A. Chromosomes are duplicated. B ...
... In order for the parent cell to produce two new identical daughter cells, the genetic material from the parent cell nucleus must be passed on to the nuclei of the daughter cells. Cell division occurs in a series of phases. Phase 1: Chromosomes are copied (Interphase) A. Chromosomes are duplicated. B ...
biology terms cells mixed
... characteristics of life; has an orderly structure, produces offspring, grows, develops, and adjusts to changes in the environment. 2. A ___________________________ is a unicellular organism such as bacteria which is composed of a prokaryotic cell that lack internal membrane-bound structures. 3. ____ ...
... characteristics of life; has an orderly structure, produces offspring, grows, develops, and adjusts to changes in the environment. 2. A ___________________________ is a unicellular organism such as bacteria which is composed of a prokaryotic cell that lack internal membrane-bound structures. 3. ____ ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.