Cell and Macromolecule review questions
... 4. Which macromolecule provides long-term energy storage for animals? 5. Which macromolecule would you eat if you wanted to grow strong nails? ...
... 4. Which macromolecule provides long-term energy storage for animals? 5. Which macromolecule would you eat if you wanted to grow strong nails? ...
General Biology lab
... – These cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis and they may also engulf food by phagocytosis when light not available ...
... – These cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis and they may also engulf food by phagocytosis when light not available ...
Cell Structures and Their Functions
... ___________________________________10. Small organelles that divide and migrate to each pole of the cell during cell division. Chromosomes move toward them during cell division. ___________________________________11. Series of membranes that extend from the outer nuclear membrane; ribosomes attached ...
... ___________________________________10. Small organelles that divide and migrate to each pole of the cell during cell division. Chromosomes move toward them during cell division. ___________________________________11. Series of membranes that extend from the outer nuclear membrane; ribosomes attached ...
Cell Structure Cloze - Science
... Cell Structures Cloze Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cells mitochondria plant ...
... Cell Structures Cloze Fill in the blanks with words from the box. cells mitochondria plant ...
Key Points on Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... to be stored would be stored using protein. c. However, two scientists named Hershey and Chase, were skeptical. They doubted this idea because no experiments had been done proving this. d. They decided to do two experiments. One to see if DNA were the instructions passed to a new cell and another to ...
... to be stored would be stored using protein. c. However, two scientists named Hershey and Chase, were skeptical. They doubted this idea because no experiments had been done proving this. d. They decided to do two experiments. One to see if DNA were the instructions passed to a new cell and another to ...
Cell basics & structure
... Structure = Clear, jelly-like fluid that fills the cell a) Mostly water ...
... Structure = Clear, jelly-like fluid that fills the cell a) Mostly water ...
SBI4U_1-1_Organelles 5744KB Oct 19 2016 11:56:53 AM
... Chloroplast Permits cells to conduct photosynthesis; Light is absorbed by the photosynthetic pigment ...
... Chloroplast Permits cells to conduct photosynthesis; Light is absorbed by the photosynthetic pigment ...
Ch. 7 Cells - dublin.k12.ca.us
... extra- = outside (extracellular matrix: the substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded) flagell - = whip (flagellum: a long whip-like cellular appendage that moves cells) glyco - = sweet (glycoprotein: a protein covalently bonded to a carbohydrate) lamin - = sheet/layer (nuclear lamina: a n ...
... extra- = outside (extracellular matrix: the substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded) flagell - = whip (flagellum: a long whip-like cellular appendage that moves cells) glyco - = sweet (glycoprotein: a protein covalently bonded to a carbohydrate) lamin - = sheet/layer (nuclear lamina: a n ...
Cell Powerpoint - stephanieccampbell.com
... The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
Animal Cell Coloring
... 1. Give the function of the nucleus. (pg. 79) 2. What makes up the cell membrane? (pg. 77) 3. Where does cellular respiration take place? (pg. 80 at top) 4. Where does protein synthesis (making of proteins) take place? (pg. 80 on bottom) 5. Where are ribosomes made? (pg. 80 on bottom) 6. Give three ...
... 1. Give the function of the nucleus. (pg. 79) 2. What makes up the cell membrane? (pg. 77) 3. Where does cellular respiration take place? (pg. 80 at top) 4. Where does protein synthesis (making of proteins) take place? (pg. 80 on bottom) 5. Where are ribosomes made? (pg. 80 on bottom) 6. Give three ...
DR_3.2_CellParts
... 7.A web of proteins in the cytoplasm is known as the___________ 8. What are the two functions of the cytoskeleton? NUCLEUS 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus?________ 10.The function of proteins in a cell is to 11.What is the nucleolus? RIBOSOMES 12. Organelles that mak ...
... 7.A web of proteins in the cytoplasm is known as the___________ 8. What are the two functions of the cytoskeleton? NUCLEUS 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus?________ 10.The function of proteins in a cell is to 11.What is the nucleolus? RIBOSOMES 12. Organelles that mak ...
Cell Organelles
... permits the passage or transport of certain materials into and out of the cell, and prevents transport of other materials. ...
... permits the passage or transport of certain materials into and out of the cell, and prevents transport of other materials. ...
cell structure review sheet
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
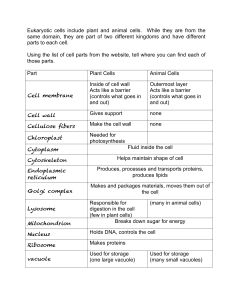
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... • What jobs do cells have to do? – Make proteins • proteins control every cell function ...
... • What jobs do cells have to do? – Make proteins • proteins control every cell function ...
DJ_Jeopardy
... This organelle functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell ...
... This organelle functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell ...
(Blanks)
... In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell; In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides twice to produce four genetically different daughter cells with one-half the number of chromosomes of a body cell, A C __ __ __ __ __ __ _ ...
... In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell; In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides twice to produce four genetically different daughter cells with one-half the number of chromosomes of a body cell, A C __ __ __ __ __ __ _ ...
Cells Test Review
... 1. What is the function of the nucleus? 2. What is the function of the cell wall? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. What is the function of the nucleus? 5. What is the function of the cell membrane? 6. What is the cell theory? ...
... 1. What is the function of the nucleus? 2. What is the function of the cell wall? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. What is the function of the nucleus? 5. What is the function of the cell membrane? 6. What is the cell theory? ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Cytoplasm – cell contents in thick fluid • Control center with DNA ...
... • Cytoplasm – cell contents in thick fluid • Control center with DNA ...
Biology: Cells and Organisms Notes
... More nuclear pores if highly active and connect outer and inner membranes of nuclear envelope (continuous). Pores are selective – RNA passes through. Long strands of DNA are covered in globular proteins – histones. DNA double wraps around histone to form a nucleosome. Histones are +ve, DNA –ve. A co ...
... More nuclear pores if highly active and connect outer and inner membranes of nuclear envelope (continuous). Pores are selective – RNA passes through. Long strands of DNA are covered in globular proteins – histones. DNA double wraps around histone to form a nucleosome. Histones are +ve, DNA –ve. A co ...
Lecture 4 - A tour through the cell
... the histone-DNA complex is called a nucleosome described by Roger Kornberg – Nobel Prize 2006 ...
... the histone-DNA complex is called a nucleosome described by Roger Kornberg – Nobel Prize 2006 ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.