Cell Structures Quick Check
... contains green pigment in plant cells to make glucose e. ribosome builds proteins f. cytoskeleton microtubules that help provide shape in animal cells g. cytoplasm fluid that holds the cell’s organelles in place h. Golgi complex lipids that modify & package proteins before being transported out of t ...
... contains green pigment in plant cells to make glucose e. ribosome builds proteins f. cytoskeleton microtubules that help provide shape in animal cells g. cytoplasm fluid that holds the cell’s organelles in place h. Golgi complex lipids that modify & package proteins before being transported out of t ...
29 - Alamo Colleges
... chromatin Gene-containing control center of the cell Contains the blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized ...
... chromatin Gene-containing control center of the cell Contains the blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized ...
Cells
... a) necessary due to the lack of a 3. Associated Structures A) (“little shaggy hairs”) – fingerlike projections that increase the surface area of the plasma membrane B) Membrane junctions ...
... a) necessary due to the lack of a 3. Associated Structures A) (“little shaggy hairs”) – fingerlike projections that increase the surface area of the plasma membrane B) Membrane junctions ...
Cell division File
... Why are there two types: mitosis and meiosis? How are they different? How does meiosis produce new combinations of genes? ...
... Why are there two types: mitosis and meiosis? How are they different? How does meiosis produce new combinations of genes? ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... pores and ribosomes • Cell reproduction starts here • Protein synthesis starts here: message from DNA to ribosomes ...
... pores and ribosomes • Cell reproduction starts here • Protein synthesis starts here: message from DNA to ribosomes ...
Chemistry of Macromolecules
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
Paste or tape this function sheet to the back of your labeled animal
... RER near the nucleus and free-floating in the cytoplasm extends from the nucleus and is covered with ribosomes; responsible for helping with the synthesis, packaging, and transporting of proteins in within the cell has no ribosomes; acts as a storage area for protein that will later be exported out ...
... RER near the nucleus and free-floating in the cytoplasm extends from the nucleus and is covered with ribosomes; responsible for helping with the synthesis, packaging, and transporting of proteins in within the cell has no ribosomes; acts as a storage area for protein that will later be exported out ...
cells - RIScienceTeachers
... • Cell membrane: the outer boundary • Nucleus: the control center • Cytoplasm: the space in between membrane and nucleus ...
... • Cell membrane: the outer boundary • Nucleus: the control center • Cytoplasm: the space in between membrane and nucleus ...
4-2: Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell
... Function: transporting molecules through lipid bilayer Two types: ...
... Function: transporting molecules through lipid bilayer Two types: ...
Mitosis
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
... • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) ...
Cell Structure and Function: Review
... 6. Infectious diseases (infections) are caused by? (Lesson 3 pg. 216-218) A. white blood cells B. no vitamins C. old age D. harmful microorganisms 7. In chloroplasts, energy from the sun is used to make food in a process called? (pg. 200-203) A. photosynthesis B. mitosis C. respiration D. inflammati ...
... 6. Infectious diseases (infections) are caused by? (Lesson 3 pg. 216-218) A. white blood cells B. no vitamins C. old age D. harmful microorganisms 7. In chloroplasts, energy from the sun is used to make food in a process called? (pg. 200-203) A. photosynthesis B. mitosis C. respiration D. inflammati ...
Cellular Biology Crossword
... organelles called ribosomes to produce proteins from amino acids. 14 - Protein packaging plant -Sends vesicles of macromolecules to destination in cell. ...
... organelles called ribosomes to produce proteins from amino acids. 14 - Protein packaging plant -Sends vesicles of macromolecules to destination in cell. ...
Cell Organelle Riddles
... Read each description below and then identify the correct cell structure. Write your answer in the line provided using only 10 of the following words: ...
... Read each description below and then identify the correct cell structure. Write your answer in the line provided using only 10 of the following words: ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... • Whereas prokaryotic cells contain no organelles and smaller (70S) ribosomes • Most prokaryotes have a rigid external cell wall that contains peptidoglycan a polymer of aminoacids and sugars as its unique structural component. • Eukaryotes do not contain peptidoglycan . They are bounded by a flexib ...
... • Whereas prokaryotic cells contain no organelles and smaller (70S) ribosomes • Most prokaryotes have a rigid external cell wall that contains peptidoglycan a polymer of aminoacids and sugars as its unique structural component. • Eukaryotes do not contain peptidoglycan . They are bounded by a flexib ...
Cells Study Guide
... 6. Relate cell parts/organelles to their function: ALL organelles we discussed ...
... 6. Relate cell parts/organelles to their function: ALL organelles we discussed ...
NAME OF ORGANELLE
... nucleolus ribosome rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus vacuole lysosome Mitochondria ...
... nucleolus ribosome rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus vacuole lysosome Mitochondria ...
Cell Theory and the Cell
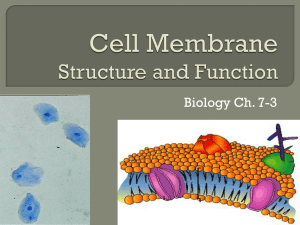
... • Physical & chemical boundary of all cells • A double layer called the phospholipid bilayer. – It is selectively permeable (semipermeable) meaning only certain things are let in and out • Gate-keeper of cell ...
... • Physical & chemical boundary of all cells • A double layer called the phospholipid bilayer. – It is selectively permeable (semipermeable) meaning only certain things are let in and out • Gate-keeper of cell ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
... bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
Notes-Organelles - Svetz-wiki
... --flattened stacks of membranes --functions in collection, packaging and distribution of molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi app ...
... --flattened stacks of membranes --functions in collection, packaging and distribution of molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi app ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.