Unit 2 Part 1: The Cell Test Review 1. What is the function of a cell`s
... 11. A compound is made of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Why is it a compound? 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a sec ...
... 11. A compound is made of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Why is it a compound? 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a sec ...
Cell Organelles - Bartlett High School
... Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
... Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Review Questions
... 3. Circle the letter of each structure that animals cell contain: a. Chloroplasts b. Lysosomes c. Mitochondria d. ER 4. Circle the letter of each structure that plant cells contain: a. Cell wall b. ER c. Lysosomes d. Chloroplasts 5. What is the function of the nucleus? ______________________________ ...
... 3. Circle the letter of each structure that animals cell contain: a. Chloroplasts b. Lysosomes c. Mitochondria d. ER 4. Circle the letter of each structure that plant cells contain: a. Cell wall b. ER c. Lysosomes d. Chloroplasts 5. What is the function of the nucleus? ______________________________ ...
Cell Vocabulary
... Cell wall- is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. Cell membrane- (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic)separates the interior of all cells from the ...
... Cell wall- is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. Cell membrane- (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic)separates the interior of all cells from the ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... DNA is the hereditary material. 2. 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organism. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. ...
... DNA is the hereditary material. 2. 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organism. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. ...
Procaryotic and Eucaryotic cell
... – Has a double membrane with pores – Contains nucleoli where ribosomal RNA is synthesized – Contains chromatin: DNA + histones (basic proteins) – Chromosomes divide by mitosis. ...
... – Has a double membrane with pores – Contains nucleoli where ribosomal RNA is synthesized – Contains chromatin: DNA + histones (basic proteins) – Chromosomes divide by mitosis. ...
Slide 1
... membranes throughout cytoplasm, arranged in tubes and sacs •Manufacture of molecules and transport throughout the cell •RER – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – bound ribosomes on the outside,produce proteins that go straight into the ER •SER – Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum – lacks ribosomes,builds lipid ...
... membranes throughout cytoplasm, arranged in tubes and sacs •Manufacture of molecules and transport throughout the cell •RER – Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – bound ribosomes on the outside,produce proteins that go straight into the ER •SER – Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum – lacks ribosomes,builds lipid ...
Cell organelles
... • Translate RNA (coming from the nucleus) into protein. (Protein synthesis) • Ribosomes attached to the Endoplasmic ...
... • Translate RNA (coming from the nucleus) into protein. (Protein synthesis) • Ribosomes attached to the Endoplasmic ...
PGS
... as ALL CELL TYPES, Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, have them so that all cells can make proteins and enzymes.) B. These are the site of Protein Synthesis. (These are like an actual “construction site” for a building, except they make proteins and not buildings.) 1. Normal proteins and enzymes are ALL ma ...
... as ALL CELL TYPES, Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, have them so that all cells can make proteins and enzymes.) B. These are the site of Protein Synthesis. (These are like an actual “construction site” for a building, except they make proteins and not buildings.) 1. Normal proteins and enzymes are ALL ma ...
Life Science Unit Test Review Key File
... 3. Describe a prokaryotic cell. They do not have a nucleus, and their DNA is scattered randomly throughout the cell. They don’t contain as many organelles as eukaryotic cells. They contain cytoplasm, a cell membrane, and ribosomes. They are less complicated and smaller that eukaryotes. All B ...
... 3. Describe a prokaryotic cell. They do not have a nucleus, and their DNA is scattered randomly throughout the cell. They don’t contain as many organelles as eukaryotic cells. They contain cytoplasm, a cell membrane, and ribosomes. They are less complicated and smaller that eukaryotes. All B ...
The Parts of A Cell - Lemoore Elementary School
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
Document
... 6. Within which organelle is water stored in a plant cell? 7. Glucose molecules are too large to enter the cell by themselves. Cells also usually like to “stockpile” sugar molecules for later. What process would the cell use to import glucose molecules? Explain why you think this way. ...
... 6. Within which organelle is water stored in a plant cell? 7. Glucose molecules are too large to enter the cell by themselves. Cells also usually like to “stockpile” sugar molecules for later. What process would the cell use to import glucose molecules? Explain why you think this way. ...
Meiosis & Mitosis Process
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
... The process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. Chromosomes make copies of themselves. Then line up in the middle of the cell side by side. Move to upset ends of the cell. Two new cells are formed. Line up in the center of the cell. Then the chromoso ...
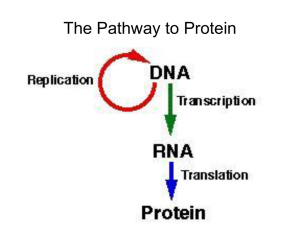
ProSyn
... – Ribose instead of deoxyribose – Shorter than DNA – Folds to form some double-stranded regions (A-U, C-G) ...
... – Ribose instead of deoxyribose – Shorter than DNA – Folds to form some double-stranded regions (A-U, C-G) ...
Biology 2201 Name: Organelle Assignment
... Be brief, point form is best You may only get a couple of organelles described per page! You must include the following organelles: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
... Be brief, point form is best You may only get a couple of organelles described per page! You must include the following organelles: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. ...
Cell Content Statement 1 Study Guide
... Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
... Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
Name Date Class
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The _______________________________________ controls the materials that enter and leave the cell. 2. Ribosomes make _______________________. 3. The ____________________ is a large structure that directs the cell’s activities. 4. The storage area of a ...
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The _______________________________________ controls the materials that enter and leave the cell. 2. Ribosomes make _______________________. 3. The ____________________ is a large structure that directs the cell’s activities. 4. The storage area of a ...
Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria Protists
... • Looked at animals & determined that animals were made of cells ...
... • Looked at animals & determined that animals were made of cells ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.