Facts About Cells
... Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism All cells contain living material called cytoplasm All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that controls what enters & leaves the cell ...
... Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism All cells contain living material called cytoplasm All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that controls what enters & leaves the cell ...
Bill Nye: CELLS
... 1. Organisms have many different kinds of cells to do different _____________ 2. Why are humans more like animals than plants? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. _____________________ is when more cells are made than die off. 4. Bill says that ALL ...
... 1. Organisms have many different kinds of cells to do different _____________ 2. Why are humans more like animals than plants? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. _____________________ is when more cells are made than die off. 4. Bill says that ALL ...
CELLS UNIT 1 Learning Targets - Milton
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
Due to Weather Revised Oct 10-14
... Standard H.B.2: The student will demonstrate the understanding that the essential functions of life take place within cells or systems of cells. H.B.2A. Conceptual Understanding: The essential functions of a cell involve chemical reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (i ...
... Standard H.B.2: The student will demonstrate the understanding that the essential functions of life take place within cells or systems of cells. H.B.2A. Conceptual Understanding: The essential functions of a cell involve chemical reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (i ...
Grade 11 Biology DP Assignment 3 Cells
... This process of maintaining the cell’s environment is called homeostasis. Selective permeability is a process used to maintain homeostasis in which the plasma membrane allows some molecules into the cell while keeping others out. ...
... This process of maintaining the cell’s environment is called homeostasis. Selective permeability is a process used to maintain homeostasis in which the plasma membrane allows some molecules into the cell while keeping others out. ...
Year 9 Biological Principles Topic Checklist
... Accurately draw biological specimens, using thin clear lines, labelling the visible structures (e.g. nucleus, cell wall), stating the magnification. Calculate magnifications from an eyepiece and objective lens Estimate the size of a cell from a scale bar Describe how specialised cells are adapted to ...
... Accurately draw biological specimens, using thin clear lines, labelling the visible structures (e.g. nucleus, cell wall), stating the magnification. Calculate magnifications from an eyepiece and objective lens Estimate the size of a cell from a scale bar Describe how specialised cells are adapted to ...
Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life
... Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life Below you will find general questions covering the material we discussed from Chapter 4. You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please under ...
... Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life Below you will find general questions covering the material we discussed from Chapter 4. You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please under ...
Cells - Humble ISD
... Did you know?! The average human being is composed of around 100 trillion individual cells It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” The invention of the microscope enabled the discovery of cells. Humans were able to see microscopic structures that had neve ...
... Did you know?! The average human being is composed of around 100 trillion individual cells It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” The invention of the microscope enabled the discovery of cells. Humans were able to see microscopic structures that had neve ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: A non-living infectious particles composed of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. ...
... A: A non-living infectious particles composed of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. ...
Name - DiBiasioScience
... b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes _____ 8. Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus c. vacuole b. mitochondrion d. ribosome _____ 9. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion c. c ...
... b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes _____ 8. Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus c. vacuole b. mitochondrion d. ribosome _____ 9. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion c. c ...
Name Date Class
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The _______________________________________ controls the materials that enter and leave the cell. 2. Ribosomes make _______________________. 3. The ____________________ is a large structure that directs the cell’s activities. 4. The storage area of a ...
... Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 1. The _______________________________________ controls the materials that enter and leave the cell. 2. Ribosomes make _______________________. 3. The ____________________ is a large structure that directs the cell’s activities. 4. The storage area of a ...
Organism - FinklerScience
... As multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate (change & separate) and form levels of organization Why it Matters: so Humans (we are multicellular) can have different kinds of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems ...
... As multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate (change & separate) and form levels of organization Why it Matters: so Humans (we are multicellular) can have different kinds of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems ...
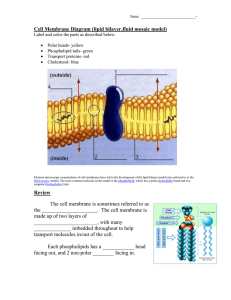
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
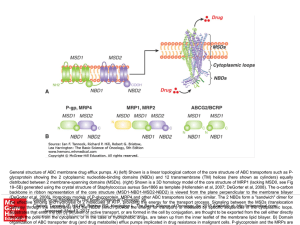
Analytical Approaches in Cell Biology
... A) Ion exchange - Charged resin on beads, e.g. DEAE dextran (+) 0r phosphocellulose (-) charged. Oppositely charged molecules bind, released by salt solution. B) Gel filtration - Retards smaller molecules that enter pores in gel beads, so larger molecules come thru 1st. C) Affinity chromatography - ...
... A) Ion exchange - Charged resin on beads, e.g. DEAE dextran (+) 0r phosphocellulose (-) charged. Oppositely charged molecules bind, released by salt solution. B) Gel filtration - Retards smaller molecules that enter pores in gel beads, so larger molecules come thru 1st. C) Affinity chromatography - ...
Discovery of Cells
... • He was the first person to discover bacteria AND determined cells were in both, plants and animals. ...
... • He was the first person to discover bacteria AND determined cells were in both, plants and animals. ...
Chapter 1 Cells Lesson 1 “What Are the Parts of a Cell?” Cell Theory
... react with oxygen. This process releases carbon dioxide, water, and LOTS of energy. Endoplasmic Reticulum-System of membranes and tubes. The membranes twist and turn through the cell, providing passages through which materials can pass. Endoplasmic reticulum can be rough or smooth. Rough ER helps ce ...
... react with oxygen. This process releases carbon dioxide, water, and LOTS of energy. Endoplasmic Reticulum-System of membranes and tubes. The membranes twist and turn through the cell, providing passages through which materials can pass. Endoplasmic reticulum can be rough or smooth. Rough ER helps ce ...
Cell Structures (chapter 7-1, 7-2)
... What type of macromolecule does not dissolve in water. It includes fats, oils, and waxes. Lipids What macromolecule has a primary function of providing energy? Carbohydrates What macromolecule builds muscle tissue, transports molecules, and regulates cell reactions? Proteins What macromolecule passe ...
... What type of macromolecule does not dissolve in water. It includes fats, oils, and waxes. Lipids What macromolecule has a primary function of providing energy? Carbohydrates What macromolecule builds muscle tissue, transports molecules, and regulates cell reactions? Proteins What macromolecule passe ...
Immune System: Practice Questions #1
... 5. Which statement does not describe an example of a feedback mechanism that maintains homeostasis? A. B. C. D. ...
... 5. Which statement does not describe an example of a feedback mechanism that maintains homeostasis? A. B. C. D. ...