Cell Theory and Scientists
... He saw what appeared to be thousands of tiny empty chambers. He called these chambers cells... and the term is still used today. 1674 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water - and revealed a world of tiny living organisms. He drew illustrations of organisms he fou ...
... He saw what appeared to be thousands of tiny empty chambers. He called these chambers cells... and the term is still used today. 1674 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water - and revealed a world of tiny living organisms. He drew illustrations of organisms he fou ...
Research Scientist, Molecular and Cell Biology
... biologist to join the team. The successful candidate will join active drug discovery programmes and can expect to be involved with a broad range of different activities but particularly: ...
... biologist to join the team. The successful candidate will join active drug discovery programmes and can expect to be involved with a broad range of different activities but particularly: ...
File
... If breathed in affect cell metabolism Carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin as well as oxygen doesaffects cellular respiration- then the person dies ...
... If breathed in affect cell metabolism Carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin as well as oxygen doesaffects cellular respiration- then the person dies ...
Click Here For Review Sheet
... 2. They perform thousands of different _____________________ in the life forms of Earth. ...
... 2. They perform thousands of different _____________________ in the life forms of Earth. ...
animal tissues and organ systems
... work together to perform a common task or function Organs system is composed of two or more organs that work together to perform a common task or function. Function to of all 11 systems is to maintain homeostasis. ...
... work together to perform a common task or function Organs system is composed of two or more organs that work together to perform a common task or function. Function to of all 11 systems is to maintain homeostasis. ...
Cytoplasm is where all the chemical reactions take
... CELLS 1. All living things are made of cells which are either unicellular eg bacteria and yeast or multicellular organisms. 2. Microscopes are used to study cells, light microscopes can magnify about 1500 times and an electron microscope magnifies 40,000 to 500,000 times. ...
... CELLS 1. All living things are made of cells which are either unicellular eg bacteria and yeast or multicellular organisms. 2. Microscopes are used to study cells, light microscopes can magnify about 1500 times and an electron microscope magnifies 40,000 to 500,000 times. ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... I’ve been called a storage tank by those with little taste. I’m a sac filled with water, food, enzymes, or waste. What am I? ...
... I’ve been called a storage tank by those with little taste. I’m a sac filled with water, food, enzymes, or waste. What am I? ...
disc cells. ability.
... 50 km radius of Perth. Fourteen sites were sampled using banana and fermenting wheat bran baits. At eight of the sites D. nitidithorax was recorded, usually at low density, but commonly at Quinn's Rock (40 km N. of Perth, on the coast). Banana bait proved attractive to this species, but it has been ...
... 50 km radius of Perth. Fourteen sites were sampled using banana and fermenting wheat bran baits. At eight of the sites D. nitidithorax was recorded, usually at low density, but commonly at Quinn's Rock (40 km N. of Perth, on the coast). Banana bait proved attractive to this species, but it has been ...
1 Unit 1: The Body as a Whole
... Certain important molecules or ions are not brought into cell by transport processes, but by receptor-mediated endocytosis III. Homeostasis Cell survival depends upon some basic requirements, such as consumption of oxygen, release of carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste, breakdown down of nutrients, ...
... Certain important molecules or ions are not brought into cell by transport processes, but by receptor-mediated endocytosis III. Homeostasis Cell survival depends upon some basic requirements, such as consumption of oxygen, release of carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste, breakdown down of nutrients, ...
Organization of Living Things
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If the organism is only a single cell, it is called a ...
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If the organism is only a single cell, it is called a ...
10 E all qs
... Q1: What is active transport? A1: The movement of molecules from an area of low to high concentration with the help of energy and channel protein. Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is ...
... Q1: What is active transport? A1: The movement of molecules from an area of low to high concentration with the help of energy and channel protein. Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of water ...
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of water ...
Note taking guide
... Have rounded bodies and are 800-1000 nm in diameter. Number varies depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...
... Have rounded bodies and are 800-1000 nm in diameter. Number varies depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...
CELL TYPES EPITHELIA CONNECTIVE TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE
... Absorptive cells have numerous hairlike projections called microvilli on their free surface to increase the area for absorption. ...
... Absorptive cells have numerous hairlike projections called microvilli on their free surface to increase the area for absorption. ...
2.2 – Prokaryotic Cells
... Cytoplasm - The region where metabolic reaction occur which are essential for life. Mesosome - Permeable boundary that allows for entry and exit of nutrients and waste, and may play a role in DNA replication. Cell/ Plasma Membrane - This is a barrier across which all nutrients and waste products mus ...
... Cytoplasm - The region where metabolic reaction occur which are essential for life. Mesosome - Permeable boundary that allows for entry and exit of nutrients and waste, and may play a role in DNA replication. Cell/ Plasma Membrane - This is a barrier across which all nutrients and waste products mus ...
Cell Organelles
... Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids ...
... Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids ...
Passive Vs. Active Transport
... • Active Transport: When an input of energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane. (this could occur because the molecule is too large or because it is moving against the concentration gradient) ...
... • Active Transport: When an input of energy is required to move materials through a cell membrane. (this could occur because the molecule is too large or because it is moving against the concentration gradient) ...
Mitosis and Cancer - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
doc 3.2.1.1 eukaryotes checklist
... In complex multicellular organisms, eukaryotic cells become specialised for specific functions. Specialised cells are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems. Students should be able to apply their knowledge of these features in explaining adaptations of eukaryotic cells. ...
... In complex multicellular organisms, eukaryotic cells become specialised for specific functions. Specialised cells are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into systems. Students should be able to apply their knowledge of these features in explaining adaptations of eukaryotic cells. ...
The Organization of Living Things
... As multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate (change & separate) and form levels of organization Why it Matters: so Humans (we are multicellular) can have different kinds of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems ...
... As multicellular organisms develop, their cells differentiate (change & separate) and form levels of organization Why it Matters: so Humans (we are multicellular) can have different kinds of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems ...
Sci_Ch_1_Notes
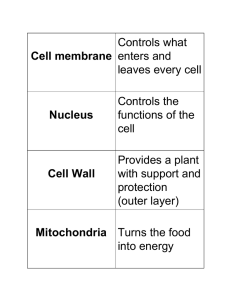
... Cell Wall – the cell wall is stiff and provides strength and support. It is outside the cell membrane. Vacuole – Plant cells usually have one large, central vacuole. It stores extra water to the plant does not dry out. Chloroplast – Makes food for the plant. Plants are green because the chloroplast ...
... Cell Wall – the cell wall is stiff and provides strength and support. It is outside the cell membrane. Vacuole – Plant cells usually have one large, central vacuole. It stores extra water to the plant does not dry out. Chloroplast – Makes food for the plant. Plants are green because the chloroplast ...