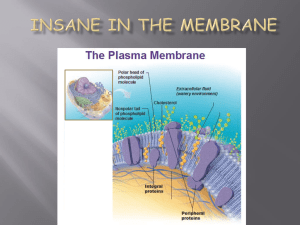
Questions
... Plant cells have cell walls that make their cells rigid. Plant cells keep their shape. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. The shape of animal cells can change. ...
... Plant cells have cell walls that make their cells rigid. Plant cells keep their shape. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. The shape of animal cells can change. ...
Body System Organization Overview
... oxygen and remove CO2 • Includes tubes that remove particles from incoming air & transport air into and out of the lungs • gas exchange between the atmosphere and body cells = respiration • Oxygen utilization and carbon dioxide production in the cells = cellular respiration ...
... oxygen and remove CO2 • Includes tubes that remove particles from incoming air & transport air into and out of the lungs • gas exchange between the atmosphere and body cells = respiration • Oxygen utilization and carbon dioxide production in the cells = cellular respiration ...
L3 I Have, Who Has? Cards
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
... Who has the basic unit of structure and function in all living things? ...
Name
... 7. What is the overall function of the CNS? ______________________________________________ 8. What organs makes up the PNS? _____________________ 9. What is the overall function of the PNS? _______________________________________________ 10. What are the three parts of the human brain and what do th ...
... 7. What is the overall function of the CNS? ______________________________________________ 8. What organs makes up the PNS? _____________________ 9. What is the overall function of the PNS? _______________________________________________ 10. What are the three parts of the human brain and what do th ...
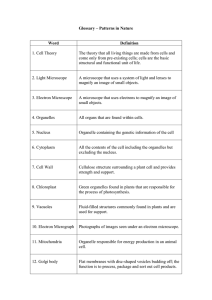
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... A group of organs working together to perform a similar function. ...
... A group of organs working together to perform a similar function. ...
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and need to consume other living things for nutrients. ...
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and need to consume other living things for nutrients. ...
Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7 “I can…” state discuss
... cell and the cell theory. identify similarities and differences between cells and viruses. construct a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. identify the cell organelles and state their functions. construct a cell model (i.e., form and function model, cell ana ...
... cell and the cell theory. identify similarities and differences between cells and viruses. construct a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. identify the cell organelles and state their functions. construct a cell model (i.e., form and function model, cell ana ...
Study Guide for Microscope and Cell Test
... compound has more than one lens and a simple contains 1 lens. ...
... compound has more than one lens and a simple contains 1 lens. ...
Tunneling nanotubes meso abstract
... and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell communication occurs between distant cells in the complex tumor microenvironment. We propose tunnel ...
... and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell communication occurs between distant cells in the complex tumor microenvironment. We propose tunnel ...
Levels of Organization of Life
... • Homeostasis: All living things maintain an internal balance known as homeostasis. ...
... • Homeostasis: All living things maintain an internal balance known as homeostasis. ...
Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant
... Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant Stem Cells We are seeking highly motivated candidates to investigate how stem cells in the root meristem sense and adapt to environmental changes. A specific focus will be on the epigenetic regulation of st ...
... Postdoctoral and PhD position in Epigenetic Regulation of Plant Stem Cells We are seeking highly motivated candidates to investigate how stem cells in the root meristem sense and adapt to environmental changes. A specific focus will be on the epigenetic regulation of st ...
Observing Specialized Cells
... Observing Specialized Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. All of the processes necessary for life occur in cells. In single-celled organisms, such as amoebas, all of the functions required by the organism take place within one cell. Multicell ...
... Observing Specialized Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. All of the processes necessary for life occur in cells. In single-celled organisms, such as amoebas, all of the functions required by the organism take place within one cell. Multicell ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
Chapter 1 Cells
... relationship between structure and function. Use alveoli as an example. Be sure to include more than one level of organization. The ...
... relationship between structure and function. Use alveoli as an example. Be sure to include more than one level of organization. The ...
The Cell School to Home LESSON 2 1.
... 1. Write a clue that could be used to describe each of the following cell structures. Then share your clues with your learning partner to see whether he or she can guess each answer. The first clue is provided as an example. ...
... 1. Write a clue that could be used to describe each of the following cell structures. Then share your clues with your learning partner to see whether he or she can guess each answer. The first clue is provided as an example. ...
Directed Reading A - Maples Elementary School
... 6. A structure that is made up of two or more tissues working together is ...
... 6. A structure that is made up of two or more tissues working together is ...
Cell Structure and Function
... All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Tissue - scienceathawthorn
... Muscle cells form the active contractile tissue of the body known as muscle tissue. Muscle tissue functions to produce force and cause motion, either locomotion or movement within internal organs. Muscle tissue is separated into three distinct categories: visceral or smooth muscle, which is found in ...
... Muscle cells form the active contractile tissue of the body known as muscle tissue. Muscle tissue functions to produce force and cause motion, either locomotion or movement within internal organs. Muscle tissue is separated into three distinct categories: visceral or smooth muscle, which is found in ...