* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
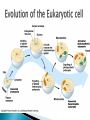
C10 EXISTING CELLS ARE THE PRODUCTS OF EVOLUTION People naturally question the origins of life General agreement that our planet is 4.5 billion years ago Atmosphere was water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, methane and ammonia gas Warmer temps/lost of volcanic activity Many electrical storms 1953- Stanley Miller- mixed the above gases and controlled temps as above and produced organic molecules ◦ Amino acids, nucleotides and ATP ◦ SOME SPONATNEOUSLY POLYMERISED AND /OR JOINED TOGETHER Other scientists later showed that when these molecules mixed in the presence of lipids some organisations/membranes formed Supports the idea that simple cellular structures capable of reproduction could have occurred Earliest form of life the Stromatolites- 3 billion years ago-fossilised remains of photosynthetic prokaryotes Found along coastlines- bacterial matsautotrophic- therefore produce oxygenadded this to the atmosphere Oldest eukaryotes-protists Two main groups: ◦ Protozoa ◦ Algae Many forms still exist today Live generally aquatic environments Widely believed that eukaryotic cells originated as a collection, community of prokaryotes Development to eukaryotes in involved two steps…. Infolding of the plasma membrane to form an endo- membrane system-formed the endoplasmic reticulum and most other organelles, i.e nucleus and golgi bodies 2nd- endosymbiosis- means that close organisms/living in close proximity were taken in or incorporated into other organisms The chloroplasts and mitochondria seem to have evolved from small prokaryotes that were engulfed by endosymbiosis into larger prokaryotes Thought to have been heterotrophic cells able to use oxygen in aerobic respiration-release energy CHLOROPLASTS: ◦ Evolved from autotrophic cells capable of using light energy to produce food and release oxygen Evidence to support these theories is that: ◦ Both mitochondria and chloroplast are similar to eubacteria which exists today ◦ Both have double membranes-originating from the original prokaryote and the host cell membrane ◦ Both have ribosomes, DNA and RNA- self replicating C11 Human beings culture cells for a variety of purposes C11.1- Understand techniques of cell culture and discuss some contemporary examples of their use ◦ Cells can be grown successfully in the lab ◦ These are referred to as cell cultures ◦ Variations are evident for plant or animal cells ◦ Following is a general procedure. 1. tissue of interest is dissected and cells of same type exposed 2.A protein digesting enzyme (proteolytic chemicals) are added to digest the intracellular matrix of the connective tissue and release the cells 3. the cells are then placed in a culture medium- with correct sugars and salts and sometimes antibiotics to prevent bacterial growth Culture is kept in a flat flask At the right/optimum temperature (37 for human cells) Cells grow quickly and can be easily removed for investigation/research They can only grow to about 40 generationsthe Hayflick Limit LAB or in-vitro techniques enable us to store cells for many years Shortens generation time for plant breeding/improves productivity Can be used to grow human tissue i.e for burns victims-and possibly organs in the future Bioethics is the term used when talking about peoples beliefs or arguments for and against such techniques ◦ the biggest controversy being IVF and keeping embryo's to research or discarding them and not implanting them all ◦ Or growing one in the lab completely/not in a uterus C12.1 Discuss possible benefits and/or harmful effects of chemicals that human beings use ◦ The four groups which affect humans either beneficially or detrimentally are: ◦ Drugs: Any chemical/substance that alters normal functioning Medical drugs treat disease or injury –antibiotics etc Non Medical: Nicotine and alcohol Both have deleterious effects on cells in high concentrations Alcohol- effects cell metabolism- leads to cirrhosis of the liver ◦ Cell death Illegal Drugs: ◦ Marihuana, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, ecstasy ◦ All effect cell activity- particularly nerve cells ◦ Interact with other chemicals in the body Recently new antiviral drugs- Zanamivir- for the flu Works b y blocking the active site of the enzyme neuraminidase –crucial to the replication of the virus Hoped to be available by a puffer-like asthma inhalers Not a trial and error drug- fits exactly More to come Blood pressure Pain Cholesterol levels etc All can have issues if not used as prescription states and if not us e by the rightful patient Overuse of antibiotics led to the multiresistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus Some are addictive or lead to psychological disorders Petrol, gas and coal When burnt with oxygen produce carbon dioxide or monoxide that accumulate in atmosphere If breathed in affect cell metabolism Carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin as well as oxygen doesaffects cellular respiration- then the person dies Inorganic fertilizers ◦ Boost crop production ◦ Detrimental effects occur as they are soluble in water and move through underground dams and would cause many issues- i.e increased dissolved salts in the soil= more algae growth or “blooms” in the rivers and sea Arsenic Cyanide ◦ Metabolic poisons ◦ Act as inhibitors of enzymes- block or compete for active sites Burning tobacco – greater number of harmful chemicals Insecticides- used to kill pests but overuse creates resistance as with bacteria Some last a long time in the soil and keep causing problems pg 105 RISK-need to clean up chemicals that pollute air/water etc. but how/ otherwise risk is high