Sections 3
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
... 5. What are the 4 phases of mitosis? 6. What are the structures at the ends of the cell during prophase? 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 1 ...
pathway_cell_models
... - this enables one to simulate the change in concentrations of the components of the pathway over ...
... - this enables one to simulate the change in concentrations of the components of the pathway over ...
Microscopes allow us to see inside the cell
... important tool. • Cells are diverse (very different) • Plants & Animals have EUKARYOTIC cells. ...
... important tool. • Cells are diverse (very different) • Plants & Animals have EUKARYOTIC cells. ...
ws: Oodles of Organelles
... with the DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FUNCTIONS of the following organelles; NUMBER AND LETTER YOUR PAPER JUST AS THE LIST SHOWS BELOW. The numbers locate the organelles in an animal cell; the letters locate the organelles in a plant cell. ...
... with the DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FUNCTIONS of the following organelles; NUMBER AND LETTER YOUR PAPER JUST AS THE LIST SHOWS BELOW. The numbers locate the organelles in an animal cell; the letters locate the organelles in a plant cell. ...
CELL PROCESSES A selectively permeable cell membrane allows
... into usable, soluble particles that can be used by different cells. There are two types of digestion: mechanical - involving the physical breakdown of food into useable pieces and chemical - breaking down with enzymes the smaller pieces into usable nutrients. ...
... into usable, soluble particles that can be used by different cells. There are two types of digestion: mechanical - involving the physical breakdown of food into useable pieces and chemical - breaking down with enzymes the smaller pieces into usable nutrients. ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Cells that work together to perform a specific function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as ...
... • Cells that work together to perform a specific function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Cells that work together to perform a specific function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as ...
... • Cells that work together to perform a specific function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as ...
Cell Review
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
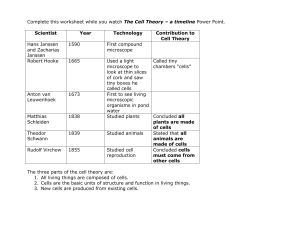
Life Science Preview Vocabulary Terms Vocabulary Quiz 1. Cells
... Life Science Preview Vocabulary Terms Vocabulary Quiz 1. Cells are the basic units of all living things. 2. The cell membrane regulates movement of stuff into & out of all cells. 3. The cell wall is the outer covering of plant cells. 4. The lysosome is a section of a cell in which waste removed. 5. ...
... Life Science Preview Vocabulary Terms Vocabulary Quiz 1. Cells are the basic units of all living things. 2. The cell membrane regulates movement of stuff into & out of all cells. 3. The cell wall is the outer covering of plant cells. 4. The lysosome is a section of a cell in which waste removed. 5. ...
End of Semester Exam Review Guide and Answers
... Independent variable – what is changed by the person doing the experiment **Can only change one variable at a time. ...
... Independent variable – what is changed by the person doing the experiment **Can only change one variable at a time. ...
BIOLOGY
... 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
... 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
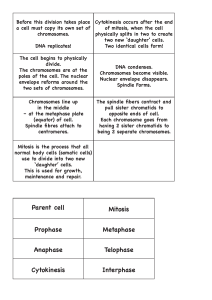
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
Vocabulary Flip Chart - Effingham County Schools
... symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ...
... symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ...
Objectives - Cengage Learning
... Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. Understand the essential structure and function of the cell membrane. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. Describe the organelles associated with ...
... Understand the basic tenets of the cell theory. Understand the essential structure and function of the cell membrane. Contrast the general features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. Describe the organelles associated with ...
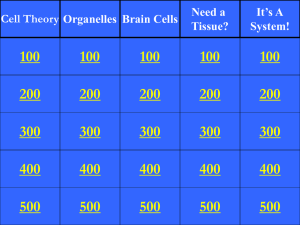
Cell Theory Organelles Brain Cells Need a Tissue?
... grow and develop…all of its genetic information? ...
... grow and develop…all of its genetic information? ...
Microscopy Lab: Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Study Guide Prokaryotes
... Please Note!!: These images are provided to assist your studying for the PostLab quiz since you are not able to bring a microscope home with you. However, you are also still responsible for the information about these cells contained in the Lab Sheets that you used to guide you through the lab AND t ...
... Please Note!!: These images are provided to assist your studying for the PostLab quiz since you are not able to bring a microscope home with you. However, you are also still responsible for the information about these cells contained in the Lab Sheets that you used to guide you through the lab AND t ...
Cell Structure Guided Notes
... 4. Which is largest, a plant cell, an animal cell, or a bacterial cell? 5. Cells in multicellular organisms often specialize or DIFFERENTIATE. What does this mean? ...
... 4. Which is largest, a plant cell, an animal cell, or a bacterial cell? 5. Cells in multicellular organisms often specialize or DIFFERENTIATE. What does this mean? ...