Cell Theory`s 3 Main Ideas
... Cell Theory’s 3 Main Ideas 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms 3. All cells come from preexisting cells -a cell divides to form two identical cells ...
... Cell Theory’s 3 Main Ideas 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms 3. All cells come from preexisting cells -a cell divides to form two identical cells ...
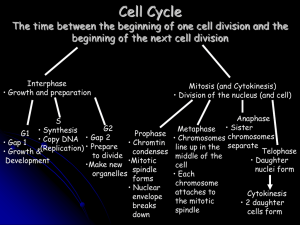
The Cell Cycle
... Hypothesis: The cell cycle is directed by specific signaling molecules present in the cytoplasm ...
... Hypothesis: The cell cycle is directed by specific signaling molecules present in the cytoplasm ...
Plasma Membranes - cellsinactionEDF4402
... increased surface area to maximise absorption of nutrients from the small intestine Disease conditions that damage villi cause malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies Plants have also adapted in this way (root systems) ...
... increased surface area to maximise absorption of nutrients from the small intestine Disease conditions that damage villi cause malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies Plants have also adapted in this way (root systems) ...
Chapter 38: Excretory System
... maintains the concentration gradient e. Distal Convoluted Tubule: tubular secretion of H ions, potassium, and certain drugs ...
... maintains the concentration gradient e. Distal Convoluted Tubule: tubular secretion of H ions, potassium, and certain drugs ...
Outline
... 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have interior membranes to separate ...
... 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have interior membranes to separate ...
People in Science Who am I
... I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. I found that microorganisms found in dirt that could enter the flask would cause the broth to spoil where air (which supposedly carried the “vital force”) did not cause it to spoil. My name is carried in a process to keep milk fresh. ...
... I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. I found that microorganisms found in dirt that could enter the flask would cause the broth to spoil where air (which supposedly carried the “vital force”) did not cause it to spoil. My name is carried in a process to keep milk fresh. ...
Cell Unit Test Study Guide
... a. collects and begins disposal of extracellular fluids 3. What are the main organs in the respiratory system? a. Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus ...
... a. collects and begins disposal of extracellular fluids 3. What are the main organs in the respiratory system? a. Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus ...
Name_________________________ KEY Ch 4 Quiz How is the
... 5. Name 2 of the 3 types of intercellular junctions and what function they serve (2) • Tight junctions can bind cells together into leakproof sheets • Anchoring junctions link animal cells into strong tissues • Gap junctions allow substances to flow from cell to cell 6. Which organelle works in conj ...
... 5. Name 2 of the 3 types of intercellular junctions and what function they serve (2) • Tight junctions can bind cells together into leakproof sheets • Anchoring junctions link animal cells into strong tissues • Gap junctions allow substances to flow from cell to cell 6. Which organelle works in conj ...
cells
... (and have more than one of them) – Flagella and cilia always have the 9 + 2 arrangement ...
... (and have more than one of them) – Flagella and cilia always have the 9 + 2 arrangement ...
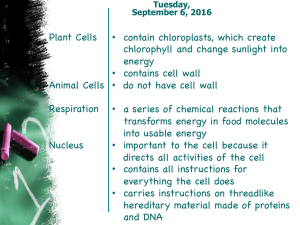
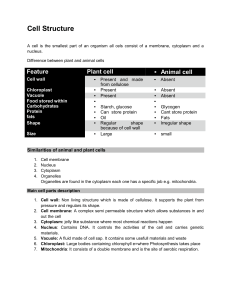
Plant Cells Animal Cells Respiration Nucleus • contain chloroplasts
... chlorophyll and change sunlight into energy ...
... chlorophyll and change sunlight into energy ...
Name: Per. _____ UNIT 4 – CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... 1. Reviewing your notes & worksheets based on the material listed here. 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
... 1. Reviewing your notes & worksheets based on the material listed here. 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
The Cell
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems make up the structure of multi-cellular organisms. ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems make up the structure of multi-cellular organisms. ...
Unit 03 - fixurscore
... 4. Guard cell (stomata): Allows O2 and CO2 to pass in and out the leaf. They can change their shape thus can open and close their holes. 5. Red blood cells: It transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. It has no nucleus, t has hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface are ...
... 4. Guard cell (stomata): Allows O2 and CO2 to pass in and out the leaf. They can change their shape thus can open and close their holes. 5. Red blood cells: It transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. It has no nucleus, t has hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface are ...
General Biology Bozeman Cell Membrane video 1. Describe what
... 9. Identify what characteristics a substance must have in order to move through the membrane, give 2 examples of these substances. ...
... 9. Identify what characteristics a substance must have in order to move through the membrane, give 2 examples of these substances. ...
Semester 1-13.5 Week Assessment
... 4. What are groups of one or more organs working together to perform functions for the organism? Organ system 5. What are the parts of the cell theory? All living things are made of cells; Cells are the smallest working units of all living things; Cells come from pre-existing cells through cell divi ...
... 4. What are groups of one or more organs working together to perform functions for the organism? Organ system 5. What are the parts of the cell theory? All living things are made of cells; Cells are the smallest working units of all living things; Cells come from pre-existing cells through cell divi ...
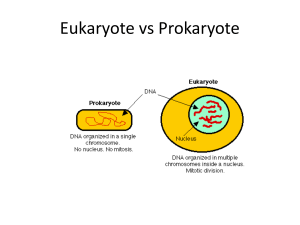
Eukaryote vs Prokaryote
... Schematic Diagrams Of The Two Bacteria Cell Wall Types A Gram Positive Bacteria Cell and a Gram Negative Bacteria Cell • A: Peptidoglycan layer Polymer of sugars and amino acids for structure and support. Note the difference in thickness between the two cells. This difference is what allows gram-po ...
... Schematic Diagrams Of The Two Bacteria Cell Wall Types A Gram Positive Bacteria Cell and a Gram Negative Bacteria Cell • A: Peptidoglycan layer Polymer of sugars and amino acids for structure and support. Note the difference in thickness between the two cells. This difference is what allows gram-po ...