Chapter 4.1
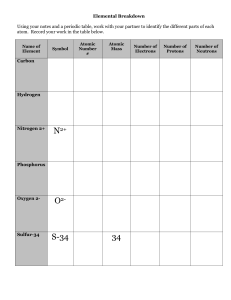
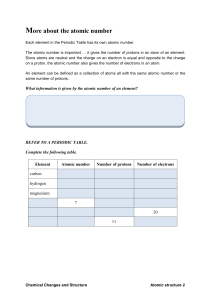
... -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
... -charge is +1 -# protons = atomic # 2. Electrons – negative particles on orbits around the nucleus -charge is -1 -# electons = # protons= atomic # 3. Neutrons – neutral particles in the nucleus -charge is 0 -#neutrons= mass-atomic # ...
Part A: Multiple Choice. Circle the letter
... 7. In general, which of the following properties does NOT increase across a row from left to right? a) atomic number b) atomic radius c) nuclear charge d) ionization energy e) electron affinity 8. Which of the following properties decreases from top to bottom in a column? a) ionization energy b) ato ...
... 7. In general, which of the following properties does NOT increase across a row from left to right? a) atomic number b) atomic radius c) nuclear charge d) ionization energy e) electron affinity 8. Which of the following properties decreases from top to bottom in a column? a) ionization energy b) ato ...
Chemical Change
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
Study Guide Answers
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus. 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? Explain. Positive char ...
CLASS TEST NAME Class IIB Date ______ 1 .Which atomic
... 21. The electrons ______________________________________________________ around the nucleus in shells. The first shell, which is _______________________________ the nucleus, can hold ________electrons, whereas the 2nd and 3rd shells can hold ...
... 21. The electrons ______________________________________________________ around the nucleus in shells. The first shell, which is _______________________________ the nucleus, can hold ________electrons, whereas the 2nd and 3rd shells can hold ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... Electrons move in specific layers (shells) Electrons move when atoms absorb or give off energy, moving from one shell to another ...
... Electrons move in specific layers (shells) Electrons move when atoms absorb or give off energy, moving from one shell to another ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
... Name the first 5 PREFIXES that we use to name molecular compounds. mono à one di à two tri à three tetra à four penta à five We usually refer to compounds containing HYDROGEN by their ...
Atomic Structure
... Electrons in the atom are to be found 90% of the time in 3D regions called orbitals THE BOHR ATOM When an electron transitions from the excited to the ground state, the atom loses energy When an electron transitions from the ground to the excited state, the atom absorbs energy Ground State Electron ...
... Electrons in the atom are to be found 90% of the time in 3D regions called orbitals THE BOHR ATOM When an electron transitions from the excited to the ground state, the atom loses energy When an electron transitions from the ground to the excited state, the atom absorbs energy Ground State Electron ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
... – Excited state when electrons is pushed into an orbit farther from the nucleus. • When electrons move from an excited state (higher energy level) to the ground state (lower energy level), the energy produced is given off often as light. • Worked well to explain the emision spectrum of hydrogen, but ...
World of
... Always us a CAPITAL letter for the first letter in element. Use lower case if there is a second letter. – Ex: Hydrogen = H – Gold = Au ...
... Always us a CAPITAL letter for the first letter in element. Use lower case if there is a second letter. – Ex: Hydrogen = H – Gold = Au ...
key - Greenslime.info
... Which of the following elements is most reactive: carbon, sodium, magnesium, boron? Most reactive is sodium, followed by magnesium, boron and then carbon. Why? Sodium only has one valence electron to lose in order to react. Magnesium has two valance electrons, boron has three, and carbon has four. T ...
... Which of the following elements is most reactive: carbon, sodium, magnesium, boron? Most reactive is sodium, followed by magnesium, boron and then carbon. Why? Sodium only has one valence electron to lose in order to react. Magnesium has two valance electrons, boron has three, and carbon has four. T ...
element - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
... • The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. – During Mendeleev’s time, this arrangement left several blanks, however, the table exhibited a regularly repeating pattern, which could be used to predict the properties of elements that had not been discovered yet. – He was proven right ...
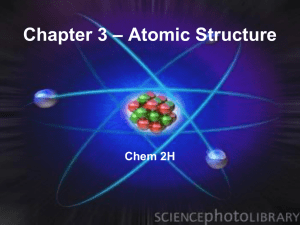
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
... • English schoolteacher John Dalton, 1803 – Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Each element is composed of tiny atoms • Atoms of an element are identical but differ from those of other elements. • Atoms are neither created nor destroyed. • A given compound always has the same relative numbers and kinds of ato ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds ...
... More distant an electron is from the nucleus, the greater the energy possible in the atom Different states of energy are called energy levels or electron shells o 1st shell is closest to the nucleus, has the lowest energy, and holds only 2 electrons o 2nd shell has a little more energy and holds ...
Science notes on Atoms, Periodic table
... The oxygen can be replaced with something that acts like oxygen, hence it does not necessary mean that it HAS to be oxygen, this is why its called the oxidizing agent. The fuel can be sugar, gas, oil etc …anything that can react with oxygen, usually it has a lot of carbon The heat is needed to get t ...
... The oxygen can be replaced with something that acts like oxygen, hence it does not necessary mean that it HAS to be oxygen, this is why its called the oxidizing agent. The fuel can be sugar, gas, oil etc …anything that can react with oxygen, usually it has a lot of carbon The heat is needed to get t ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
September 28th Notes
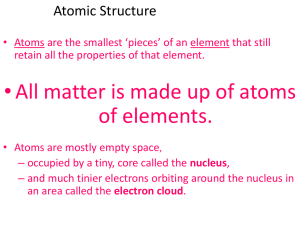
... Atomic Structure Element: matter that is composed of one type of atom. Elements are abbreviated in scientific shorthand- either a letter or a pair of letters called a chemical symbol. Ex- Aluminum =Al Copper=Cu Atom- smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of the element. Protons- pos ...
... Atomic Structure Element: matter that is composed of one type of atom. Elements are abbreviated in scientific shorthand- either a letter or a pair of letters called a chemical symbol. Ex- Aluminum =Al Copper=Cu Atom- smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of the element. Protons- pos ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, t ...
... Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass numbers of the isotopes of an element, as they occur naturally, t ...
CHEMISTRY
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
Chemistry I Lecture Notes – Atomic Structure
... Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms are simply just rearranged in chemical reactions. Law of Definite Proportions Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Law of Multiple Proportions Atoms of the same two (or mo ...
... Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Atoms are simply just rearranged in chemical reactions. Law of Definite Proportions Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Law of Multiple Proportions Atoms of the same two (or mo ...