2.9 Use the helium-4 isotope to define atomic number and mass
... 2.34 Give two examples of each of the following: (a) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (b) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of different elements, (c) polyatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (d) a polyatomic molecule containing atoms of different element ...
... 2.34 Give two examples of each of the following: (a) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (b) a diatomic molecule containing atoms of different elements, (c) polyatomic molecule containing atoms of the same element, (d) a polyatomic molecule containing atoms of different element ...
Atomic Structure
... Predict what ion is most likely to form from each element below. Write the symbol of that ion (example: Be2+). ...
... Predict what ion is most likely to form from each element below. Write the symbol of that ion (example: Be2+). ...
Periodic Table
... isotopes.The lighter isotope (Cu-63), with 29 protons and 34 neutrons, makes up 69.17% of copper atoms.The heavier isotope (Cu-65), with 29 protons and 36 neutrons, constitutes the remaining 30.83% of copper atoms. Calculate the atomic mass of Copper. ...
... isotopes.The lighter isotope (Cu-63), with 29 protons and 34 neutrons, makes up 69.17% of copper atoms.The heavier isotope (Cu-65), with 29 protons and 36 neutrons, constitutes the remaining 30.83% of copper atoms. Calculate the atomic mass of Copper. ...
Chapters 3
... Chapters 3 - 4 How It All Fits Together Developing a model of the atom in order to explain, predict and perform chemical reactions and chemical properties. ...
... Chapters 3 - 4 How It All Fits Together Developing a model of the atom in order to explain, predict and perform chemical reactions and chemical properties. ...
Chemistry of life
... • Many of our everyday experiences depend upon chemistry. – For example: Making kool aid or sweet tea. ...
... • Many of our everyday experiences depend upon chemistry. – For example: Making kool aid or sweet tea. ...
The Atom and how it is organized - Cashmere
... central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
... central nucleus with orbiting electrons. ◦ A nucleus is made up of positively charged PROTONS and neutral NEUTRONS. ◦ ELECTRONS are negatively charged and orbit around the nucleus. ...
1. Of the three major categories of elements (metals, non
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
... They are called groups or families. 12. What are the horizontal rows on the periodic table called? They are called periods. 13. Explain the relationship between elements in the same group. They have similar chemical and physical properties because each one has the same number of valence electrons. ...
History of the Atom and Periodic Table
... had a neutral charge and it is called the neutron. His discovery made us realize isotopes existed. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons. Proved Dalton’s Atomic theory was incorrect again by showing atoms of the same element can be different. ...
... had a neutral charge and it is called the neutron. His discovery made us realize isotopes existed. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons. Proved Dalton’s Atomic theory was incorrect again by showing atoms of the same element can be different. ...
What is Matter? Anything that can be smelled, tasted, touched… Has
... sharing electrons The first three periods of elements are the easiest to understand. The most eheld in the outer cloud of these elements is 8. In order to become more stable, elements will share e-. ...
... sharing electrons The first three periods of elements are the easiest to understand. The most eheld in the outer cloud of these elements is 8. In order to become more stable, elements will share e-. ...
BC1 Atoms Unit Standards
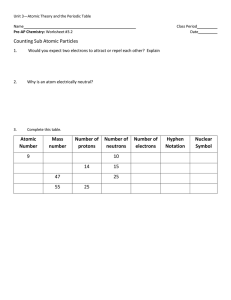
... Predict whether two charged objects will attract or repel each other, and explain why. Describe the relative amount, charges, masses, and locations of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element. 2a For a given element, determine the number of protons 2b When given a number of prot ...
... Predict whether two charged objects will attract or repel each other, and explain why. Describe the relative amount, charges, masses, and locations of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element. 2a For a given element, determine the number of protons 2b When given a number of prot ...
CH 5 Periodic Law
... - highly reactive metallic elements in group 1 - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
... - highly reactive metallic elements in group 1 - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
Intro to Atoms Clicker Questions 1. "atomos" means? 2. Atoms of one
... 2. Atoms of one kind of element _______ be changed into a different element with ordinary chemical means. (can, can’t) 3. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined how? 4. In Thompson's model of the atom, the negatively charged electrons were located how in the atom? 5. In R ...
... 2. Atoms of one kind of element _______ be changed into a different element with ordinary chemical means. (can, can’t) 3. Every compound is composed of atoms of different elements combined how? 4. In Thompson's model of the atom, the negatively charged electrons were located how in the atom? 5. In R ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain reaction (bomb) or controlled (energy plants) ...
... usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain reaction (bomb) or controlled (energy plants) ...
Periodic Table of Elements * Study Guide
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
File
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
CHAPTER6_MEET_THE_ELEMENTS
... as the coinage metals are located in the same group. Horizontal rows are called PERIODS. The atomic number of elements increases as you move from left to right across the table, starting with hydrogen (H) which has an atomic number of 1. Atomic Mass – is the mass of an average atom of an element. It ...
... as the coinage metals are located in the same group. Horizontal rows are called PERIODS. The atomic number of elements increases as you move from left to right across the table, starting with hydrogen (H) which has an atomic number of 1. Atomic Mass – is the mass of an average atom of an element. It ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
... 40. Draw the Lewis Dot structures for the following: Potassium, Carbon, Iodine and Xenon? 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and w ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Also on closer inspection of the different n levels, additional fine structure is observed within each n level and these are assigned different letters of the alphabet. According to the mathematics each s, p, d level can accommodate 2 electrons. There is one s level for each shelf, three equivalent ...
... Also on closer inspection of the different n levels, additional fine structure is observed within each n level and these are assigned different letters of the alphabet. According to the mathematics each s, p, d level can accommodate 2 electrons. There is one s level for each shelf, three equivalent ...
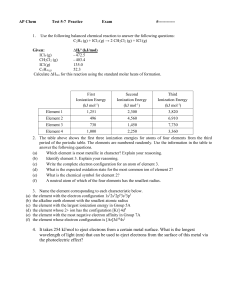
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in water is 44.4 kJ/mol. When a 13.9-g sample of NaOH dissolves in 250.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature change is _______. Assume that the solution has the same specific heat as liquid water, ...
... 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in water is 44.4 kJ/mol. When a 13.9-g sample of NaOH dissolves in 250.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature change is _______. Assume that the solution has the same specific heat as liquid water, ...
Atomic Size
... • The apparent discontinuities in this diagram reflect the difficulty of comparing the radii of atoms of metallic and nonmetallic bonding types. Radii of the noble gas elements are estimates from those of nearby elements. ...
... • The apparent discontinuities in this diagram reflect the difficulty of comparing the radii of atoms of metallic and nonmetallic bonding types. Radii of the noble gas elements are estimates from those of nearby elements. ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...