File
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
... 1. How many electrons does the neutral atom contain? 2. The first 1 or 2 are placed into Energy Level #1 3. Energy Level 2 holds up to 8 electrons. 4. Energy Level 3 holds up to 8 electrons. 5. Energy Level 4 hold up to 8 electrons…etc. ...
Chapter 18
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
... • Dimitri Mendeleevarranged all the elements known in order of increasing atomic masses and discovered a pattern • Today’s Periodic Table— elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
... independently came to the same conclusion about how elements should be grouped in the periodic table. •Henry Moseley (1913) developed the concept of atomic numbers (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom) ...
Chapter 6 Notes
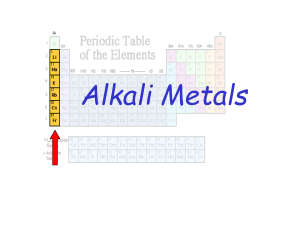
... NIB - Groups of elements and their Properties – Students should refer to Appendix A!!! Properties of families Group 1 - Alkali Metals - “alkali” comes from Arabic - means “ashes” - early chemists separated sodium and potassium compounds from ashes - the hydroxides of these compounds are strongly ba ...
... NIB - Groups of elements and their Properties – Students should refer to Appendix A!!! Properties of families Group 1 - Alkali Metals - “alkali” comes from Arabic - means “ashes” - early chemists separated sodium and potassium compounds from ashes - the hydroxides of these compounds are strongly ba ...
Metals
... • Although the Periodic Table is arranged by increasing atomic number, it is the arrangement of each element’s electrons that determines its properties • There are 7 possible energy levels for electrons and 7 periods (rows) on the periodic table • The periods go in order of increasing atomic # • Ele ...
... • Although the Periodic Table is arranged by increasing atomic number, it is the arrangement of each element’s electrons that determines its properties • There are 7 possible energy levels for electrons and 7 periods (rows) on the periodic table • The periods go in order of increasing atomic # • Ele ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 4. Using the Pauli Exclusion Principle, explain why an s-orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons? There is only one s-orbital in each shell. Adding a third electron would mean that two of the three would have the same set of four quantum numbers. 5. Balance the following: C6H14 (l) + O2 (g) ...
... 4. Using the Pauli Exclusion Principle, explain why an s-orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons? There is only one s-orbital in each shell. Adding a third electron would mean that two of the three would have the same set of four quantum numbers. 5. Balance the following: C6H14 (l) + O2 (g) ...
Chapter 5: The Periodic Law
... • The most abundant is Argon and it was the first be discovered (1894). However, it does not form any compounds (argon means “lazy one” in Greek). Now… a whole new, previously unknown and not predicted group of element has been discovered, too. Soon after the other noble gases were found and added t ...
... • The most abundant is Argon and it was the first be discovered (1894). However, it does not form any compounds (argon means “lazy one” in Greek). Now… a whole new, previously unknown and not predicted group of element has been discovered, too. Soon after the other noble gases were found and added t ...
RAD 354 Chapt 3 Structure of Matter
... Chemical Compound • Is a NEW substance that is formed when two or more atoms of different elements combine – Covalent bond – sharing electrons in outer orbital shells – Ionic bonding – atoms attracted to each other because of opposite charges • Smallest particle of an element is an atom • Smallest ...
... Chemical Compound • Is a NEW substance that is formed when two or more atoms of different elements combine – Covalent bond – sharing electrons in outer orbital shells – Ionic bonding – atoms attracted to each other because of opposite charges • Smallest particle of an element is an atom • Smallest ...
Test 1 - UTC.edu
... E) atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's ma ...
... E) atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 14. Which one of the following statements about atoms and subatomic particles is correct? A) The proton and the neutron have identical masses. B) Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus by bombarding gold foil with electrons C) The neutron's ma ...
Matter_Quiz_Topics_2017
... Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass of the atom found? Where is most of the volume of an atom? How is the periodic table organized and what information can be gained from it? If the location of an element is d ...
... Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass of the atom found? Where is most of the volume of an atom? How is the periodic table organized and what information can be gained from it? If the location of an element is d ...
Atomic Theory- 1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...
... Atomic Theory1. Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. An element is composed of one type of atom. Properties of atoms are identical to each other. 3. A compound contains two or more different elements. The relative number of atoms of each element in a compound is the sam ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
The periodic table is the most significant tool that chemist use for
... in atoms are arranged in spherical shells around the nucleus. The idea of electron “shells” is useful in visualizing the atom. However, it is a poor descriptor of atomic structure. ...
... in atoms are arranged in spherical shells around the nucleus. The idea of electron “shells” is useful in visualizing the atom. However, it is a poor descriptor of atomic structure. ...
Elements Unit Test
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
... 9. A Dutch scientist by the name of Neils Bohr was the first scientist to figure out that electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom (sometimes called shells) can only hold a certain number of electrons. Which of the following sets of numbers describe the number of electrons in the first three shel ...
Comprehensive Science 3 Module 4 Practice Test
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
... Different elements are made up of different atoms Atoms of different elements combine to make different compounds 5. The elements listed at the far right side of the periodic table are _______. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Transitional Metals ...
Are You suprised ?
... and label it increasing, atomic radius). Explain WHY the trends are the way they are. a. Atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity ...
... and label it increasing, atomic radius). Explain WHY the trends are the way they are. a. Atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... (1869, Russian) • Organized elements by increasing atomic mass • Predicted the existence of undiscovered elements. ...
... (1869, Russian) • Organized elements by increasing atomic mass • Predicted the existence of undiscovered elements. ...
Chemistry
... Molecule – the smallest unit of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Chemical Formula – the chemical symbols and subscripts used to identify the number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound. The make-up of molecules is shown in a chemical formula. Atom – the smalles ...
... Molecule – the smallest unit of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Chemical Formula – the chemical symbols and subscripts used to identify the number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound. The make-up of molecules is shown in a chemical formula. Atom – the smalles ...
Atomic Theory Outline
... ii. Each shell can hold a number of electrons equal to 2n2, where n = the number of the level. iii. Lower level shells are closer to the nucleus and have less energy. iv. Electrons must fill in closer, low energy shells before the further, high energy shells can be filled. v. The goal of all atoms i ...
... ii. Each shell can hold a number of electrons equal to 2n2, where n = the number of the level. iii. Lower level shells are closer to the nucleus and have less energy. iv. Electrons must fill in closer, low energy shells before the further, high energy shells can be filled. v. The goal of all atoms i ...
Quiz: The Atom (Open Notes)
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
File
... size, mass, properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine to form chemical compounds ...
... size, mass, properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine to form chemical compounds ...
document
... Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature uncombined Inner Transition Metals – (listed below table) Lanthanide Series – elements with atomic # 58 – ...
... Alkaline Earth Metals – (Group 2) shiny, ductile and malleable; combine readily with other elements Transition Elements – (Group 3 – 12) most familiar metals because they often occur in nature uncombined Inner Transition Metals – (listed below table) Lanthanide Series – elements with atomic # 58 – ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Foundations
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...
... Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Nucleus atomic number (Z) = mass number (A) = element symbol (X) = Note: mass number= Therefore …. mass number = ……. A= Z + number of neutrons ….. Number of neutrons = A-Z Note: For any given element on the periodic table: Number of protons = In order to symbolically ...