Intensive Chemistry: the Structure of Matter
... Source: http://chem.illinois.edu/CLCwebsite/demos.html ...
... Source: http://chem.illinois.edu/CLCwebsite/demos.html ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
The Periodic Table - Mrs Molchany`s Webpage
... Electron affinity generally becomes increasingly negative moving from left to right. (exception: the addition of an electron to a noble gas would require the electron to reside in a new, higher-energy subshell. Occupying a higher-energy subshell is energetically unfavorable, so the electron affinity ...
... Electron affinity generally becomes increasingly negative moving from left to right. (exception: the addition of an electron to a noble gas would require the electron to reside in a new, higher-energy subshell. Occupying a higher-energy subshell is energetically unfavorable, so the electron affinity ...
Full Text PDF - Science and Education Publishing
... chemistry book. More interestingly, this communication shows that the latter question may be (simply) answered by making reference to the Bohr’s atomic model that, notwithstanding its well-known limits, allows teachers to demonstrate that (for a hydrogenoid atom) 137 is the highest possible value fo ...
... chemistry book. More interestingly, this communication shows that the latter question may be (simply) answered by making reference to the Bohr’s atomic model that, notwithstanding its well-known limits, allows teachers to demonstrate that (for a hydrogenoid atom) 137 is the highest possible value fo ...
(null): 096.AtomReview
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
... a. Each specific color tells us about the structure of specific electrons inside the atom b. Zinc spectrum s different from ANY other element (compare to sulfur and helium on same slide) E. Atomic structure basics (see AtomOverview.ppt) – what we’ve learned by seeing without seeing … 1. PROTONS: a. ...
Atomic Structure—Kitti, Noah, Derek
... isotopes are more stable than others, and the stable ratio of protons to neutrons depends on the size of the nucleus. In smaller nuclei the ratio is simply 1:1, for the large ones it’s about 1:1.5. Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon, which typically has 12 protons and 12 neutrons. Atomic m ...
... isotopes are more stable than others, and the stable ratio of protons to neutrons depends on the size of the nucleus. In smaller nuclei the ratio is simply 1:1, for the large ones it’s about 1:1.5. Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon, which typically has 12 protons and 12 neutrons. Atomic m ...
Early Chemistry Development of the Atomic Model
... 3- Chemical compounds are formed when elements combine. Compounds always have the same relative ratios 4- Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms. The atoms themselves are not changed in a chemical reaction. ...
... 3- Chemical compounds are formed when elements combine. Compounds always have the same relative ratios 4- Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms. The atoms themselves are not changed in a chemical reaction. ...
SNC1D0 Atomic History
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of isotopes were also discovered ...
... electrons orbiting around the nucleus. Later experiments showed that the positively charged particles, now called protons, have an equal but opposite charge to the electrons, and have a mass 1836 x greater! The neutron and the existence of isotopes were also discovered ...
Periodic Table Quiz
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
... 11. Which element is in Period 4, Group 13? a) Na b) Al c) Ga d) K 12. How many electrons does Sulfur contain? a) 15 b) 16 c) 17 d) 18 13. Which elements below are ALL nonmetals? a) K, Ca, Sc b) Be, Br, Kr c) V, Cr, Mn d) Ne, Cl, Br ...
Name
... 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atom of bromine-80? Write the symbol notation for this isotope. ...
... 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atom of bromine-80? Write the symbol notation for this isotope. ...
Ei otsikkoa
... ray diffraction). The bond determines whether the radius is covalent or metallic. ...
... ray diffraction). The bond determines whether the radius is covalent or metallic. ...
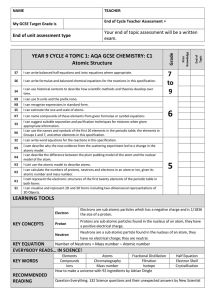
Cycle 4 Topic 1 C1 Atomic Structure Cycle Sheet
... Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this specification. I can write word equations for the reactions in this specification. ...
... Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this specification. I can write word equations for the reactions in this specification. ...
Honors Chemistry
... 4. Which of the following are found on the Periodic Table? For each, write what the value is for Argon: a. Atomic Number ...
... 4. Which of the following are found on the Periodic Table? For each, write what the value is for Argon: a. Atomic Number ...
Structure of the Atom
... • The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atoms can have different numbers of neutrons. • Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... • The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. • Atoms can have different numbers of neutrons. • Atoms that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Chapter 3 notes
... • Atomic number- the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • Atomic mass- the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. • Isotopes- any atoms having the same numbers of protons but a different number of neutrons. ...
... • Atomic number- the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • Atomic mass- the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. • Isotopes- any atoms having the same numbers of protons but a different number of neutrons. ...
1. Define each of the following terms: a.Alkaline earth metals
... Period 4, group 5 V (vanadium) a. Period 5, group 1 Rb (rubidium) b. Period 2, group 17 F (Fluorine) c. ...
... Period 4, group 5 V (vanadium) a. Period 5, group 1 Rb (rubidium) b. Period 2, group 17 F (Fluorine) c. ...
Atomic Structure AKS Correlation Use the modern atomic theory to
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
... formed by 2 or more atoms Describe the basic structure of the atom as protons, neutrons and electrons in specific arrangements. Identify the relative location, size and charge of subatomic particles. Define atom. What charge does an atom have? Fill in chart below proton neutron electron Location Nuc ...
1000 - Paint Valley Local Schools
... metals have only one valence electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements very easily. This makes them _______ _________ especially with group 17 because they have 7 valence electrons and when the two combine they make the ma ...
... metals have only one valence electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements very easily. This makes them _______ _________ especially with group 17 because they have 7 valence electrons and when the two combine they make the ma ...
1 - cloudfront.net
... All atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determi ...
... All atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determi ...
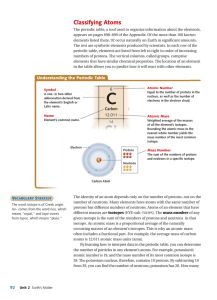
Classifying Atoms
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
... The periodic table, a tool used to organize information about the elements, appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the perio ...
The Periodic Table
... causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the group, reduces the electronelectron repulsions. A lower electron-nucleus attraction is thus counterbalanced by lower electron-electron repulsion ...
... causing the electron-nucleus attraction to decrease. The orbital that holds the outermost electron is increasingly spread out, however, proceeding down the group, reduces the electronelectron repulsions. A lower electron-nucleus attraction is thus counterbalanced by lower electron-electron repulsion ...
3-ELEMENTS AND THE ATOMIC MODEL. C4.8A Identify the
... Identify properties of common families of elements. Identify properties of common periods on the periodic table. Explain the history and organization of the periodic table. C4.8e Write the complete electron configuration of elements in the first three rows of the periodic table. C4.8g Predict oxidat ...
... Identify properties of common families of elements. Identify properties of common periods on the periodic table. Explain the history and organization of the periodic table. C4.8e Write the complete electron configuration of elements in the first three rows of the periodic table. C4.8g Predict oxidat ...
UNIT_6___ELECTRON___CONFIGURATIONS__NOTES
... - Non-metals will form covalent w/ other nonmetals Ionic bonds: -Chemical bonding where outershell e- are transferred from one atom to another in order to fulfill the octet rule. -Alkali and Alkaline earth metals only form ionic ...
... - Non-metals will form covalent w/ other nonmetals Ionic bonds: -Chemical bonding where outershell e- are transferred from one atom to another in order to fulfill the octet rule. -Alkali and Alkaline earth metals only form ionic ...