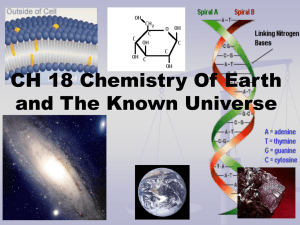
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Science
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relati ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. • Atoms of different elements have different properties. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. In a given compound, the relati ...
Chapter 2
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
... understanding of atomic structure. 5. Distinguish between each of the following pairs of terms: a. neutron and proton b. atomic number and mass number c. atomic weight and mass number 6. Explain how the atomic number and mass number of an atom can be used to determine the number of neutrons. 7. Expl ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
Periodic Table
... “placement” in the table. B. Atomic Radius and the Periodic Table = atom size 1. patterns: increases from top to bottom and right to left 2. explanations: top to bottom (adding energy levels increases atomic radius); right to left ...
... “placement” in the table. B. Atomic Radius and the Periodic Table = atom size 1. patterns: increases from top to bottom and right to left 2. explanations: top to bottom (adding energy levels increases atomic radius); right to left ...
2. NH3 - Huffman Chemistry Website!
... b. Write the symbol for this atom using subscripts to show the mass number and atomic number. ____________ ...
... b. Write the symbol for this atom using subscripts to show the mass number and atomic number. ____________ ...
answers
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
... c.) Rutherford – discovered positively charged nucleus d.) Bohr – solar system model of atoms, energy levels at increasing distance from nucleus ...
Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Every element consists of
... o Every element consists of tiny particles called ____________ o All atoms of a particular element have the same ____________________ o Different elements have different properties because their atoms are different o Atoms of different elements can combine in specific ways to form ____________ o Che ...
... o Every element consists of tiny particles called ____________ o All atoms of a particular element have the same ____________________ o Different elements have different properties because their atoms are different o Atoms of different elements can combine in specific ways to form ____________ o Che ...
Regents questions
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...
ch2_objectives
... 9. Define the terms energy and potential energy. Explain why electrons in the first electron shell have less potential energy than electrons in higher electron shells. 10. Distinguish among nonpolar covalent, polar covalent and ionic bonds. 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are b ...
... 9. Define the terms energy and potential energy. Explain why electrons in the first electron shell have less potential energy than electrons in higher electron shells. 10. Distinguish among nonpolar covalent, polar covalent and ionic bonds. 11. Explain why strong covalent bonds and weak bonds are b ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...
... Proton- P+ positive charged - in nucleus Number of P+ distinguishes one atom from another Made of 2 up quarks (+2/3 charge) and 1 down ...
Chapter 2—Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... middle, nonmetals on the right, metalloids in between them: look at the stairway in your book and know it. ...
... middle, nonmetals on the right, metalloids in between them: look at the stairway in your book and know it. ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...
SCH3U Course Review
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
Chapter 1 D Study Guide Answers
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
... 3. Electrons move around the nucleus in electron rings or shells or energy levels. 4. Atomic number is equal to the number of protons, and is unique to each element 5. The number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in a balanced atom, but not in an ION 6. The atomic mass (rounded off) is ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ element with an imbalance in the number of neutrons and protons ___ uncharged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ physica ...
... ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ element with an imbalance in the number of neutrons and protons ___ uncharged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ physica ...
Atom The smallest piece of matter that still has the properties of the
... Sub-atomic particle with negative charge; much smaller than protons and neutrons Located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties The number of protons in an atom. T ...
... Sub-atomic particle with negative charge; much smaller than protons and neutrons Located at the center of the atom. Consists of protons and neutrons. Electrons surround the nucleus. Electron found in outermost shell of an atom; determines atoms chemical properties The number of protons in an atom. T ...
Test Review Answers File
... 15. List all 4 parts to Dalton’s Atomic Theory. Which part is incorrect due to the discovery of subatomic particles? a. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. b. Atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can ...
... 15. List all 4 parts to Dalton’s Atomic Theory. Which part is incorrect due to the discovery of subatomic particles? a. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. b. Atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can ...
Atomic Structure PPT Notes Sheet
... 33. There are two basic types of bonds: ____________________ and ______________________. The reason that bonds occur is that atoms “want” to have __________ outer electron shells. An atom gets a full outer shell by getting ____________ in one of the two types of _____________. 34. Sharing one of mor ...
... 33. There are two basic types of bonds: ____________________ and ______________________. The reason that bonds occur is that atoms “want” to have __________ outer electron shells. An atom gets a full outer shell by getting ____________ in one of the two types of _____________. 34. Sharing one of mor ...
Setting up Programmable PRS Keypad as Fixed ID Keypads
... Parser06 example6
The identity of an element is determined by the number of…
Q
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
A molecule may consist of one atom.
Q
True
False
Molybdenum has atomic number 42. Its molar mass is 95.94 grams/mole. How many neutrons does
the most common isotope have?
Q
...
... Parser06 example
Chapter 4
... Metals: solid (except mercury), shiny, conductors of electricity and heat, ductile, malleable ...
... Metals: solid (except mercury), shiny, conductors of electricity and heat, ductile, malleable ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in compounds. ...
... everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in compounds. ...
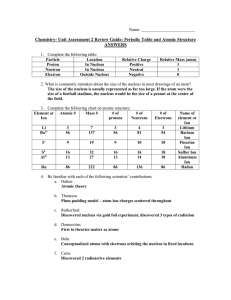
Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry OEQs
... Discuss how the model of the atom has changed from the model illustrated by the Ancient Greeks to the modern Bohr model. Do you believe that there are smaller subatomic particles than the ones that are currently believed to be the smallest? Explain. The Periodic Table of Elements is an organized ...
... Discuss how the model of the atom has changed from the model illustrated by the Ancient Greeks to the modern Bohr model. Do you believe that there are smaller subatomic particles than the ones that are currently believed to be the smallest? Explain. The Periodic Table of Elements is an organized ...
Group 1: The Alkali Metals
... All alkali metals have their own specific flame color. The colors are caused by the difference in energy among the valence shell of s and p orbitals, which corresponds to wavelengths of visible light. When the element is introduced into the flame, its outer electrons are excited and jump to a higher ...
... All alkali metals have their own specific flame color. The colors are caused by the difference in energy among the valence shell of s and p orbitals, which corresponds to wavelengths of visible light. When the element is introduced into the flame, its outer electrons are excited and jump to a higher ...