Worksheet - Rudds Classroom
... 18. A uranium atom can have an atomic mass of 235 or 238. Each atom is, therefore, a. a different isotope c. a different element b. negatively charged d. stable 19. Atoms that emit particles and energy from their nuclei are called a. contaminated b. stable c. heavy d. radioactive. 20. The electromag ...
... 18. A uranium atom can have an atomic mass of 235 or 238. Each atom is, therefore, a. a different isotope c. a different element b. negatively charged d. stable 19. Atoms that emit particles and energy from their nuclei are called a. contaminated b. stable c. heavy d. radioactive. 20. The electromag ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... Atoms, Molecules, Ions – fundamentals of elements o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an ...
... Atoms, Molecules, Ions – fundamentals of elements o Protons, electrons and neutrons make up an atom o Atoms make up molecules, all matter is made of atoms o Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are buzzing outside the nucleus around the nucleus in orbitals o # of protons defines an ...
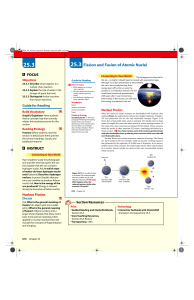
25.3 Fission and Fusion of Atomic Nuclei
... energy given off by the sun were the product of a combustion reaction, the sun would have burned out approximately 2000 years after it was formed, long before today. In this section, you will learn how energy is produced in the sun. ...
... energy given off by the sun were the product of a combustion reaction, the sun would have burned out approximately 2000 years after it was formed, long before today. In this section, you will learn how energy is produced in the sun. ...
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
... Vocabulary alpha particle - positively charged particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. (Helium nucleus) atomic mass number (A) - the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic mass unit - the unit of mass equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus; the atomic m ...
... Vocabulary alpha particle - positively charged particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. (Helium nucleus) atomic mass number (A) - the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic mass unit - the unit of mass equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus; the atomic m ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
... by Miller and Levine, © 2007. These images have been produced from the originals by permission of the publisher. These illustrations may not be reproduced in any format for any purpose without express written permission from the publisher. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. • No amount of neutrons can hold a nucleus together once it has more that 82 protons. All of the elements with an atomic number greater than 82 have only unstable isotopes. • Unstable atoms emit energy in the form of radiation when they bre ...
... many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. • No amount of neutrons can hold a nucleus together once it has more that 82 protons. All of the elements with an atomic number greater than 82 have only unstable isotopes. • Unstable atoms emit energy in the form of radiation when they bre ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... 1897, Mrs and Mr. P. & M. Curie discovered that the elements of 84Po and 88Ra have radioactive behaviors; 1899, and rays, 1900, rays; 1903, Rutherford found that ray is 2He++ and ray is ...
... 1897, Mrs and Mr. P. & M. Curie discovered that the elements of 84Po and 88Ra have radioactive behaviors; 1899, and rays, 1900, rays; 1903, Rutherford found that ray is 2He++ and ray is ...
AP Exam Questions: Nuclear
... 72. The nuclide 245Cm is radioactive and decays by the loss of one beta (-) particle. The product nuclide is (A) 245Pu (D) 250Cm (B) 95Am (E) 97Bk ...
... 72. The nuclide 245Cm is radioactive and decays by the loss of one beta (-) particle. The product nuclide is (A) 245Pu (D) 250Cm (B) 95Am (E) 97Bk ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
... ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... Episode 1 – The Discovery of Radioactivity 1. Nuclear radiation has been part of the human experience since ________________________. 2. In the mid-19th century, the scientist __________ ______________, experimented with a glass tube in which the air was excited by electricity. 3. Cathode rays are d ...
... Episode 1 – The Discovery of Radioactivity 1. Nuclear radiation has been part of the human experience since ________________________. 2. In the mid-19th century, the scientist __________ ______________, experimented with a glass tube in which the air was excited by electricity. 3. Cathode rays are d ...
Nuclear Final Exam
... hard once you understand the statistical view of the problem, I expect to see a derivation of the total probability here. (10 pt problem) 4. Lets say that you’re a nuclear physicsts who is working on determining the nuclear potential. You will have to determine the barrier for alpha decay. You then ...
... hard once you understand the statistical view of the problem, I expect to see a derivation of the total probability here. (10 pt problem) 4. Lets say that you’re a nuclear physicsts who is working on determining the nuclear potential. You will have to determine the barrier for alpha decay. You then ...
File - Ms M - EARL MARRIOTT SECONDARY
... The release of alpha particles is called alpha decay. Alpha particles are slow and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. ...
... The release of alpha particles is called alpha decay. Alpha particles are slow and penetrate materials much less than the other forms of radiation. A sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle. ...
Section 1 Review
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
... 5. Infer Sodium and potassium are in the same group on the periodic table. Name ...
Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons, but a different
... This process occur with neutron deficient or proton rich nuclei. Conversion of a proton into neutron + positron (β+ ) + v (neutrino). Positrons are emitted with a continuous energy spectrum. After β+ particle emission, the daughter nuclide has an atomic number that is one less than that of t ...
... This process occur with neutron deficient or proton rich nuclei. Conversion of a proton into neutron + positron (β+ ) + v (neutrino). Positrons are emitted with a continuous energy spectrum. After β+ particle emission, the daughter nuclide has an atomic number that is one less than that of t ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Duplin County Schools
... • Some of the elements that are essential for life have naturally occurring radioactive isotopes. • For example, about one out of every trillion carbon atoms is carbon-14, which emits a beta particle when it decays. • With each breath, you inhale about 3 million carbon-14 atoms. ...
... • Some of the elements that are essential for life have naturally occurring radioactive isotopes. • For example, about one out of every trillion carbon atoms is carbon-14, which emits a beta particle when it decays. • With each breath, you inhale about 3 million carbon-14 atoms. ...
Radioactivity
... • 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process • 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power • 7.6 describe the effec ...
... • 7.4 understand that alpha and beta particles and gamma rays are ionising radiations emitted from unstable nuclei in a random process • 7.5 describe the nature of alpha and beta particles and gamma rays and recall that they may be distinguished in terms of penetrating power • 7.6 describe the effec ...
Chapter 1
... • In nuclear chemistry, often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
... • In nuclear chemistry, often called a nuclide • This is not the only isotope of boron – boron-10 also exists – How many protons and neutrons does boron-10 have? • 5 protons, 5 neutrons ...
Flashcards - Chemistry - Muoio-Physical-Science-Wiki
... Element or compound that cannot be broken down into simpler components and maintain the properties of the original substance. ...
... Element or compound that cannot be broken down into simpler components and maintain the properties of the original substance. ...
12 · Nuclear Chemistry
... In a magnetic field, the alpha particle is bent a little (a lot, a little, not at all). In a magnetic field, the beta particle is bent a lot (a lot, a little, not at all). In a magnetic field, the gamma particle is bent not at all (a lot, a little, not at all). ...
... In a magnetic field, the alpha particle is bent a little (a lot, a little, not at all). In a magnetic field, the beta particle is bent a lot (a lot, a little, not at all). In a magnetic field, the gamma particle is bent not at all (a lot, a little, not at all). ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... In the first atomic bomb, the energy released was equivalent to about 30 kilotons of TNT, where a ton of TNT releases an energy of 4.0 × 109 J. The amount of mass converted into energy in this event is nearest to: (a) 1 μg, (b) 1 mg, (c) 1 g, ...
... In the first atomic bomb, the energy released was equivalent to about 30 kilotons of TNT, where a ton of TNT releases an energy of 4.0 × 109 J. The amount of mass converted into energy in this event is nearest to: (a) 1 μg, (b) 1 mg, (c) 1 g, ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circ ...
... All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circ ...
Chp 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay
... • Unlike all previously discovered chemical reactions, radioactivity sometimes results in the formation of completely new atoms. • Radioactivity results from having an unstable nucleus. • When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs. • Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleu ...
... • Unlike all previously discovered chemical reactions, radioactivity sometimes results in the formation of completely new atoms. • Radioactivity results from having an unstable nucleus. • When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs. • Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleu ...
Fusion or Fission
... nuclear waste products are created in the process. This is a problem, as many nuclear power plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in fusion reactions, the nuclei from atoms with low atomic weights combine to create heavier nuclei. ...
... nuclear waste products are created in the process. This is a problem, as many nuclear power plants use fission to produce energy, producing a lot of radioactive byproducts as a result. 4 Conversely, in fusion reactions, the nuclei from atoms with low atomic weights combine to create heavier nuclei. ...
AlBr3 E IO Ionic FU C O Cov Molec C IO Cov Molec Sn E N/A N/A
... old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...