David Wang STS.092 Plutonium vs. Uranium: The Road Less
... works on the principal of starting an uncontrolled fission or fusion reaction. The types of which are varied, but generally involve using a chemical explosive of some sort to force a uranium or plutonium core to implode to critical mass (the state where the atoms of the radioactive material are so t ...
... works on the principal of starting an uncontrolled fission or fusion reaction. The types of which are varied, but generally involve using a chemical explosive of some sort to force a uranium or plutonium core to implode to critical mass (the state where the atoms of the radioactive material are so t ...
Chapter 29
... • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive for ...
... • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulomb repulsive for ...
File
... Isotopes are atoms of an element with identical chemical properties but with different a. numbers of protons. b. masses. c. numbers of electrons. d. atomic numbers. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of an element with identical chemical properties but with different a. numbers of protons. b. masses. c. numbers of electrons. d. atomic numbers. ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
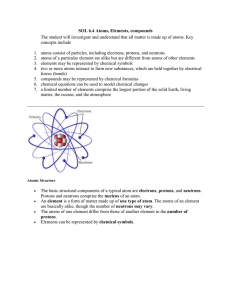
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Chemistry (B) HW Chapter 25
... ____ 44. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Water is used to moderate (slow down) neutrons in a nuclear reactor. b. Carbon control rods are used to absorb neutrons in a nuclear fission reaction. c. A very high temperature is required to initiate a nuclear fission reaction. d. The energ ...
... ____ 44. Which of the following statements is correct? a. Water is used to moderate (slow down) neutrons in a nuclear reactor. b. Carbon control rods are used to absorb neutrons in a nuclear fission reaction. c. A very high temperature is required to initiate a nuclear fission reaction. d. The energ ...
Topic 7 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... Nuclei with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Nucleon: A particle found in the nucleus (i.e. a proton or neutron). Nucleon number (A) The number of protons plus neutrons in a nucleus Proton number (Z): The number of protons in a nucleus. Neutron number (N): The number of ...
... Nuclei with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Nucleon: A particle found in the nucleus (i.e. a proton or neutron). Nucleon number (A) The number of protons plus neutrons in a nucleus Proton number (Z): The number of protons in a nucleus. Neutron number (N): The number of ...
Chapter 30: Nuclear Physics What will we learn in this chapter?
... Slow neutrons are more efficient in triggering reactions. Hence the radioactive material is submerged in a moderator (H20) which slows the neutrons via collisions. To ensure the right amount of neutrons are in the reactor, control rods can be inserted/removed. Cadmium works best since it absorbs neu ...
... Slow neutrons are more efficient in triggering reactions. Hence the radioactive material is submerged in a moderator (H20) which slows the neutrons via collisions. To ensure the right amount of neutrons are in the reactor, control rods can be inserted/removed. Cadmium works best since it absorbs neu ...
Nuclear Chemistry Radioactivity
... from an excited nucleus of a gamma photon, corresponding to radiation with a wavelength of about 10-12 m. – In many cases, radioactive decay produces a product nuclide in a metastable excited state. – The excited state is unstable and emits a gamma photon and goes to a lower energy state. ...
... from an excited nucleus of a gamma photon, corresponding to radiation with a wavelength of about 10-12 m. – In many cases, radioactive decay produces a product nuclide in a metastable excited state. – The excited state is unstable and emits a gamma photon and goes to a lower energy state. ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Element - Pure substance that can’t be broken into other types of matter • Each element has its own symbol and specific number of protons ...
... • Element - Pure substance that can’t be broken into other types of matter • Each element has its own symbol and specific number of protons ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
Energy Basics
... Decay continues, often producing a series of different radioisotopes, until a stable, nonradioactive isotope is formed. The half-life estimates how long a sample of radioactive isotope must be stored in a safe container before it decays to a safe level and can be released into the environment. ...
... Decay continues, often producing a series of different radioisotopes, until a stable, nonradioactive isotope is formed. The half-life estimates how long a sample of radioactive isotope must be stored in a safe container before it decays to a safe level and can be released into the environment. ...
Nuclear Hazards - SNS Courseware
... cosmic rays, visible,microwave radiation. • Among these X rays which produce out 95% of radiation exposure. • Nuclear energy(power plants) is used to produce electricity .But fuel used in power plants is radioactive,which is very dangerous & waste matrls are hazardous. ...
... cosmic rays, visible,microwave radiation. • Among these X rays which produce out 95% of radiation exposure. • Nuclear energy(power plants) is used to produce electricity .But fuel used in power plants is radioactive,which is very dangerous & waste matrls are hazardous. ...
Chemistry: The Nature of Matter
... Elements ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Periodic Table of Elements Over 100 elements known, but only about 2 dozen commonly found in living systems ...
... Elements ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Periodic Table of Elements Over 100 elements known, but only about 2 dozen commonly found in living systems ...
Nuclear_Chem_016
... nuclides would be left after 360 days? 2) A medical institution requests 1 g of bismuth-214, which has a half life of 20 min. How many grams of bismuth-214 must be prepared if the shipping time is 2 h? 3) Use reference table to write the nuclear equation for the decay of iodine 131. What particle is ...
... nuclides would be left after 360 days? 2) A medical institution requests 1 g of bismuth-214, which has a half life of 20 min. How many grams of bismuth-214 must be prepared if the shipping time is 2 h? 3) Use reference table to write the nuclear equation for the decay of iodine 131. What particle is ...
GRAMMAR: verb tenses
... radioactive decay, and the pieces they throw off during the decay as radiation. Radioactive nuclei may decay very rapidly (millionths of a second after they are formed) or may hang around for quite a while before decaying. For example, U-238 is radioactive, but it takes roughly 4 billion years for a ...
... radioactive decay, and the pieces they throw off during the decay as radiation. Radioactive nuclei may decay very rapidly (millionths of a second after they are formed) or may hang around for quite a while before decaying. For example, U-238 is radioactive, but it takes roughly 4 billion years for a ...
Chapter 28
... Poland) and higher there are NO naturally occurring stable isotopes. Elements with a HIGH atomic number that are unstable usually have too many neutrons. They decay by α decay, primarily until they reach 206Pb, which is a stable isotope of lead. ...
... Poland) and higher there are NO naturally occurring stable isotopes. Elements with a HIGH atomic number that are unstable usually have too many neutrons. They decay by α decay, primarily until they reach 206Pb, which is a stable isotope of lead. ...
33 Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity Answers and Solutions for
... 25. When an element emits an alpha particle, atomic number decreases by 2. For emission of a beta particle, atomic number increases by 1. For gamma emission, no change in atomic number. 26. Uranium ultimately transmutes to lead. 27. Ernest Rutherford in 1919 was the first to intentionally transmute ...
... 25. When an element emits an alpha particle, atomic number decreases by 2. For emission of a beta particle, atomic number increases by 1. For gamma emission, no change in atomic number. 26. Uranium ultimately transmutes to lead. 27. Ernest Rutherford in 1919 was the first to intentionally transmute ...
2013 Q9 - Loreto Balbriggan
... Name one device used to detect ionising radiations. (3) Compare alpha, beta, and gamma emissions using the following headings: (a) penetrating ability, (b) deflection in a magnetic field. (9) The photograph shows one of the nuclear reactors at Chernobyl, where there was a fire in April 1986 that rel ...
... Name one device used to detect ionising radiations. (3) Compare alpha, beta, and gamma emissions using the following headings: (a) penetrating ability, (b) deflection in a magnetic field. (9) The photograph shows one of the nuclear reactors at Chernobyl, where there was a fire in April 1986 that rel ...
- Physics
... each other. If the uranium-235 is in the shape of a sphere about 13 pounds of uranium form a critical mass where a runaway chain reaction (bomb) can occur. I would restate the last paragraph on page 20-4. In the process of fission some mass becomes kinetic energy of the fission fragments. It is true ...
... each other. If the uranium-235 is in the shape of a sphere about 13 pounds of uranium form a critical mass where a runaway chain reaction (bomb) can occur. I would restate the last paragraph on page 20-4. In the process of fission some mass becomes kinetic energy of the fission fragments. It is true ...
ppt
... 3)Gamma rays (γ) ● High energy electromagnetic radiation – more energetic than x-rays ● No rest mass or charge ● More dangerous than other radiation – may take several feet of concrete/lead to stop ● Breaks chemical bonds, damages DNA ● Gamma radiation accompanies other radioactive emissions. ...
... 3)Gamma rays (γ) ● High energy electromagnetic radiation – more energetic than x-rays ● No rest mass or charge ● More dangerous than other radiation – may take several feet of concrete/lead to stop ● Breaks chemical bonds, damages DNA ● Gamma radiation accompanies other radioactive emissions. ...
Chapter 37
... • Radioactivity was discovered by Antoine Henri Becquerel in 1896. – The work involved uranium salts which lead to the conclusion that the minerals gave off some sort of radiation. – This radiation was later shown to be separable by electric (and magnetic) fields into three types; alpha (a), beta (b ...
... • Radioactivity was discovered by Antoine Henri Becquerel in 1896. – The work involved uranium salts which lead to the conclusion that the minerals gave off some sort of radiation. – This radiation was later shown to be separable by electric (and magnetic) fields into three types; alpha (a), beta (b ...
nuclear physics ppt
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
Nuclear Reactions - Kelso High School
... 66. Here is a list of atomic numbers: a) 6 b) 25 c) 47 d) 80 e) 86 f) 92. Use a periodic table to identify the corresponding elements. 67. For each of the isotopes below state: a) the number of protons b) the number of neutrons. ...
... 66. Here is a list of atomic numbers: a) 6 b) 25 c) 47 d) 80 e) 86 f) 92. Use a periodic table to identify the corresponding elements. 67. For each of the isotopes below state: a) the number of protons b) the number of neutrons. ...
Power point
... high-Z elements that undergo fission have much larger neutron-proton ratios than the stable nuclides in fission product region primary product decays by series of successive processes to its stable isobar • Yields can be determined Independent yield: specific for a nuclide Cumulative yield: ...
... high-Z elements that undergo fission have much larger neutron-proton ratios than the stable nuclides in fission product region primary product decays by series of successive processes to its stable isobar • Yields can be determined Independent yield: specific for a nuclide Cumulative yield: ...