Radioactivity
... It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into two nuclei. This is nuclear fission (it is not the same as spontaneous radioactivity). One such splitting is: e. g ...
... It was found (in 1939) that if uranium was bombarded with neutrons (these have no charge and are not repelled by the nuclei), that a uranium nucleus could be split into two nuclei. This is nuclear fission (it is not the same as spontaneous radioactivity). One such splitting is: e. g ...
Adobe Acrobat file ()
... 1919 Rutherford and coworkers first observed nuclear reactions in which naturally occurring alpha particles bombarded nitrogen nuclei to produce oxygen 1932 Cockcroft and Walton first used artificially accelerated protons to produce nuclear reactions 1932 Chadwick discovered the neutron 1933 the Cur ...
... 1919 Rutherford and coworkers first observed nuclear reactions in which naturally occurring alpha particles bombarded nitrogen nuclei to produce oxygen 1932 Cockcroft and Walton first used artificially accelerated protons to produce nuclear reactions 1932 Chadwick discovered the neutron 1933 the Cur ...
2 α
... and create a nuclear reaction that produces neutrons. The neutrons bombard everything in the reactor, including the stable isotope, and the it absorbs the neutrons into its nucleus. Radioactive Iridium-192 is produced in a small-scale nuclear reactor by bombarding naturally occurring Iridium-191 wit ...
... and create a nuclear reaction that produces neutrons. The neutrons bombard everything in the reactor, including the stable isotope, and the it absorbs the neutrons into its nucleus. Radioactive Iridium-192 is produced in a small-scale nuclear reactor by bombarding naturally occurring Iridium-191 wit ...
1 slide per page() - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... The sun is a large fusion reactor The sun balances gravity with fusion energy ...
... The sun is a large fusion reactor The sun balances gravity with fusion energy ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint presentation
... decrease the emission of radiation, especially gamma rays, from nuclear reactors. Control rods – neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting free neutrons. Moderator – used to slow down the fast neutrons produced by fission Uranium-235 is usually the fuel Coolant is simply wate ...
... decrease the emission of radiation, especially gamma rays, from nuclear reactors. Control rods – neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting free neutrons. Moderator – used to slow down the fast neutrons produced by fission Uranium-235 is usually the fuel Coolant is simply wate ...
Chapter 4 Section 1
... chemical symbol for iron. 14. Stars consist of matter in the form of plasma, a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atomic nuclei. 15. Elements are created when the extreme high pressure inside the stars forces atomic nuclei to collide. 16. The process is called nuclear fusion. 17. Nuclear fusion, ...
... chemical symbol for iron. 14. Stars consist of matter in the form of plasma, a gas-like mixture of free electrons and atomic nuclei. 15. Elements are created when the extreme high pressure inside the stars forces atomic nuclei to collide. 16. The process is called nuclear fusion. 17. Nuclear fusion, ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain reaction (bomb) or controlled (energy plants) ...
... usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain reaction (bomb) or controlled (energy plants) ...
Radioactivity
... • γ rays do not directly ionise other atoms, although they may cause atoms to emit other particles which will then cause ionisation. – We don't find pure gamma sources - γ rays are emitted alongside alpha or beta particles. – Strictly speaking, gamma emission isn't 'radioactive decay' because it doe ...
... • γ rays do not directly ionise other atoms, although they may cause atoms to emit other particles which will then cause ionisation. – We don't find pure gamma sources - γ rays are emitted alongside alpha or beta particles. – Strictly speaking, gamma emission isn't 'radioactive decay' because it doe ...
File
... naturally in the environment – Examples – radioisotopes in air, water, rocks, plants and ...
... naturally in the environment – Examples – radioisotopes in air, water, rocks, plants and ...
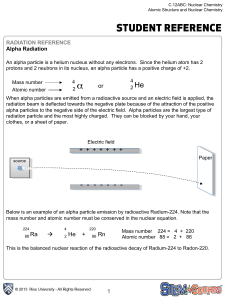
Chapter 25 – Types of Radiation 1. Alpha Radiation Alpha decay
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
... Positron decay is the mirror image of beta decay and can be described as: a. Something inside the nucleus breaks down causing a proton to become a neutron. b. It emits a positron which goes zooming off. c. The atomic number goes down by one and the mass number remains unchanged. Here is a typical po ...
Click here for printer-friendly sample test questions
... A. are responsible for the formation of most elements. B. are commonly used in nuclear power plants. C. are used in Russian-style nuclear reactors. D. occur when electrons combine with neutrons. 3. Nuclear fission reactions A. are responsible for the formation of most elements. B. are commonly used ...
... A. are responsible for the formation of most elements. B. are commonly used in nuclear power plants. C. are used in Russian-style nuclear reactors. D. occur when electrons combine with neutrons. 3. Nuclear fission reactions A. are responsible for the formation of most elements. B. are commonly used ...
31.1 Nuclear Structure
... where P is the parent nucleus, D is the daughter nucleus and The process whereby one element becomes another is called transmutation. This reaction occurs when the mass of the parent nucleus is greater than the mass of the daughter nucleus plus the mass of an alpha particle. This is the case for som ...
... where P is the parent nucleus, D is the daughter nucleus and The process whereby one element becomes another is called transmutation. This reaction occurs when the mass of the parent nucleus is greater than the mass of the daughter nucleus plus the mass of an alpha particle. This is the case for som ...
AP Chem
... 14-24.Answer the multiple choice questions attached and free response question 25. Read about Japanese nuclear power plant accident. Write facts about the accident and current effects. ( ½ page) ...
... 14-24.Answer the multiple choice questions attached and free response question 25. Read about Japanese nuclear power plant accident. Write facts about the accident and current effects. ( ½ page) ...
7.2 - Haiku
... • Then Marie and Pierre Curie discovered more radioactive elements including polonium and radium. • Scientists soon realised that there were three different types of radiation. • These were called alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) rays • from the first three letters of the Greek alphabet. ...
... • Then Marie and Pierre Curie discovered more radioactive elements including polonium and radium. • Scientists soon realised that there were three different types of radiation. • These were called alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) rays • from the first three letters of the Greek alphabet. ...
Physics 102, Class 25 The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
... – If + charges are emitted, the atomic number goes down by the number of + charges – If – charges are emitted, the atomic number goes up by the number of – charges – If neutrons are emitted, the atomic mass goes down by the number of neutrons – If gamma rays are emitted, atomic number and atomic mas ...
Isotopes of an atom have the same number of protons, but a different
... ● This means that they have no mass and no charge. ● In Gamma decay: atomic number unchanged, atomic mass unchanged. ● Gamma rays have a high penetrating power - it takes a thick sheet of metal such as lead to reduce them. ● Gamma rays do not directly ionize other atoms, although they may cause atom ...
... ● This means that they have no mass and no charge. ● In Gamma decay: atomic number unchanged, atomic mass unchanged. ● Gamma rays have a high penetrating power - it takes a thick sheet of metal such as lead to reduce them. ● Gamma rays do not directly ionize other atoms, although they may cause atom ...
Untitled
... Every radioisotope decays at a specific rate that can be expressed as a half-life. A half-life is the time required for one-half of a sample of a radioisotope to decay. After one half-life, half the atoms in a radioactive sample have decayed, while the other half remain unchanged. After two ha ...
... Every radioisotope decays at a specific rate that can be expressed as a half-life. A half-life is the time required for one-half of a sample of a radioisotope to decay. After one half-life, half the atoms in a radioactive sample have decayed, while the other half remain unchanged. After two ha ...
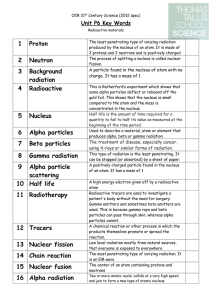
3 Background radiation
... atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. A chemical reaction or other process in which the ...
... atom Radioactive tracers are used to investigate a patient's body without the need for surgery. Gamma emitters and sometimes beta emitters are used. This is because gamma rays and beta particles can pass through skin, whereas alpha particles cannot. A chemical reaction or other process in which the ...
Radioactivity Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Radiation and radioactivity are a part of our everyday lives. Radioactivity results from instability within atomic nuclei, which causes them to decay, or split apart. This is happening all the time, all around us. Flying on an airplane will actually give you a similar dose of radiation to getting a ...
... Radiation and radioactivity are a part of our everyday lives. Radioactivity results from instability within atomic nuclei, which causes them to decay, or split apart. This is happening all the time, all around us. Flying on an airplane will actually give you a similar dose of radiation to getting a ...
Chapter 16 Notes - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... F. Producing radioactive isotopes. 1. Commonly, technetium-99m is used as a gamma emitter because it has a short half-life. 2. Radioisotopes can be made by a process named transmutation, where a stable nucleus is bombarded by a high-speed particle, such as alpha particles, protons, neutrons and oth ...
... F. Producing radioactive isotopes. 1. Commonly, technetium-99m is used as a gamma emitter because it has a short half-life. 2. Radioisotopes can be made by a process named transmutation, where a stable nucleus is bombarded by a high-speed particle, such as alpha particles, protons, neutrons and oth ...
The Stars, the Elements and You
... we accelerate and smash them together (tiny amounts, safe and controlled), and as a byproduct of nuclear reactions including the kinds that occur in nuclear power plants (amounts large enough to accumulate over time and be used or stored where they won’t do harm, potentially dangerous but usually co ...
... we accelerate and smash them together (tiny amounts, safe and controlled), and as a byproduct of nuclear reactions including the kinds that occur in nuclear power plants (amounts large enough to accumulate over time and be used or stored where they won’t do harm, potentially dangerous but usually co ...
Radioactivity
... However they have different physical properties because their mass is different. Some isotopes exist naturally. Isotopes can also be made artificially. ...
... However they have different physical properties because their mass is different. Some isotopes exist naturally. Isotopes can also be made artificially. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... decrease the emission of radiation, especially gamma rays, from nuclear reactors. Control rods – neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting free neutrons. Moderator – used to slow down the fast neutrons produced by fission Uranium-235 is usually the fuel Coolant is simply wate ...
... decrease the emission of radiation, especially gamma rays, from nuclear reactors. Control rods – neutron-absorbing rods that help control the reaction by limiting free neutrons. Moderator – used to slow down the fast neutrons produced by fission Uranium-235 is usually the fuel Coolant is simply wate ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... A neutron has no charge and a relative mass of one. TOPIC TWO: COMPOUNDS & BONDING (PAGE 2) Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and ...
... A neutron has no charge and a relative mass of one. TOPIC TWO: COMPOUNDS & BONDING (PAGE 2) Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and ...