Chapter 9 Nuclear Radiation 9.1 Natural Radioactivity Radioactive
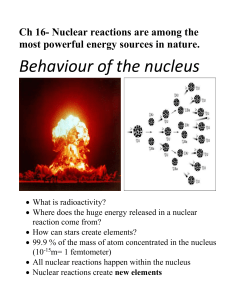
... • an unstable nucleus of 236U undergoes fission (splits). • smaller nuclei are produced, such as Kr-91 and Ba-142. • neutrons are released to bombard more 235U. 1n ...
... • an unstable nucleus of 236U undergoes fission (splits). • smaller nuclei are produced, such as Kr-91 and Ba-142. • neutrons are released to bombard more 235U. 1n ...
Ch9
... Which of the following radioisotopes are most likely to be used in nuclear medicine? Radioisotopes with short half-lives are used in nuclear medicine. ...
... Which of the following radioisotopes are most likely to be used in nuclear medicine? Radioisotopes with short half-lives are used in nuclear medicine. ...
Nuclear Notation
... y Because the nucleus experiences the intense conflict between the two strongest forces in nature, it should not be surprising that there are many nuclear isotopes which are unstable and emit some kind of radiation. y The most common types of radiation are called α, β, and γ radiation, b ...
... y Because the nucleus experiences the intense conflict between the two strongest forces in nature, it should not be surprising that there are many nuclear isotopes which are unstable and emit some kind of radiation. y The most common types of radiation are called α, β, and γ radiation, b ...
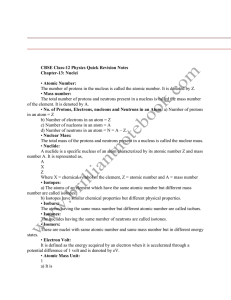
Atomic Concepts and Nuclear Chemistry Regents Review Page 1 A
... – A U-235 atom has 92 protons and 143 neutrons, and a U-238 atom has 92 protons and 146 neutrons. – A U-235 atom and a U-238 atom have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. ...
... – A U-235 atom has 92 protons and 143 neutrons, and a U-238 atom has 92 protons and 146 neutrons. – A U-235 atom and a U-238 atom have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... electrons of atoms are forced into the nucleus. The protons join with the electrons to form neutrons. Each atom is 100,000 times smaller for the same mass and so incredibly dense. This creates a large ‘gravity well’. ...
... electrons of atoms are forced into the nucleus. The protons join with the electrons to form neutrons. Each atom is 100,000 times smaller for the same mass and so incredibly dense. This creates a large ‘gravity well’. ...
Adobe Acrobat file () - Wayne State University Physics and
... fragments be equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. Thus, from KE = p2/2m, the lighter alpha particle has more kinetic energy that the more massive daughter nucleus. ...
... fragments be equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. Thus, from KE = p2/2m, the lighter alpha particle has more kinetic energy that the more massive daughter nucleus. ...
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Elemental Chemistry
... A bit of history is required before we start into the chemistry stuff. During the good old days (i.e., 100's of years ago), "chemists" were essentially magicians. They had learned some basic data about the planet around them, including basic elements. At the time, most people thought that their univ ...
... A bit of history is required before we start into the chemistry stuff. During the good old days (i.e., 100's of years ago), "chemists" were essentially magicians. They had learned some basic data about the planet around them, including basic elements. At the time, most people thought that their univ ...
12_physics_notes_ch13_nuclei
... One Rutherford is the decay rate of 106 disintegrations per second. • Natural Radioactivity: It is the phenomenon of the spontaneous emission of-α , β and γ radiations from the nuclei of naturally occurring isotopes. • Artificial or Induced Radioactivity: It is the phenomenon of inducing radioactivi ...
... One Rutherford is the decay rate of 106 disintegrations per second. • Natural Radioactivity: It is the phenomenon of the spontaneous emission of-α , β and γ radiations from the nuclei of naturally occurring isotopes. • Artificial or Induced Radioactivity: It is the phenomenon of inducing radioactivi ...
do physics online from quanta to quarks radioactivity
... All radioactive emissions are extremely dangerous to living organisms. When alpha, beta or gamma radioactive emissions hit living cells they cause ionize atoms. They can kill cells directly or cause genetic damage to the DNA molecules. High radiation doses will cause burn effects as well as kill the ...
... All radioactive emissions are extremely dangerous to living organisms. When alpha, beta or gamma radioactive emissions hit living cells they cause ionize atoms. They can kill cells directly or cause genetic damage to the DNA molecules. High radiation doses will cause burn effects as well as kill the ...
Nuclear reactions: fission and fusion
... The stray neutrons released by a spontaneous fission can prematurely initiate a chain reaction. This means that the assembly time to reach a critical mass has to be less than the rate of spontaneous fission. Scientists have to consider the spontaneous fission rate of each material when designing nuc ...
... The stray neutrons released by a spontaneous fission can prematurely initiate a chain reaction. This means that the assembly time to reach a critical mass has to be less than the rate of spontaneous fission. Scientists have to consider the spontaneous fission rate of each material when designing nuc ...
CHAPTER 4: ABUNDANCE AND RADIOACTIVITY OF UNSTABLE
... against cosmic particles. Cosmic radiation produces radioactive nuclei in the atmosphere primarily through two different types of reactions: (i) high-energy reactions by the secondary particles such as protons, neutrons and He nuclei bombarding atmospheric nuclei (N, O, Ar); these reactions are the ...
... against cosmic particles. Cosmic radiation produces radioactive nuclei in the atmosphere primarily through two different types of reactions: (i) high-energy reactions by the secondary particles such as protons, neutrons and He nuclei bombarding atmospheric nuclei (N, O, Ar); these reactions are the ...
Ernest Rutherford Essay Research Paper Rutherford was
... main components of radiation and named them alpha, beta, and gammy rays. Alpha particles are actually the nuclei of helium atoms. Each alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons, with a charge of 2+ and a mass of 4 atomic mass units. On the average, their speed is about 1/10 the speed ...
... main components of radiation and named them alpha, beta, and gammy rays. Alpha particles are actually the nuclei of helium atoms. Each alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons, with a charge of 2+ and a mass of 4 atomic mass units. On the average, their speed is about 1/10 the speed ...
120 min This paper - University of Southampton
... • larger natural abundances of elements with Z magic A2 Solution (partly new, partly seen in the notes and problem sheets) For a nuclide P with atomic number, Z P and atomic mass number AP , write down the relation between nuclear mass, the proton mass, the neutron mass, and the binding energy, BEP ...
... • larger natural abundances of elements with Z magic A2 Solution (partly new, partly seen in the notes and problem sheets) For a nuclide P with atomic number, Z P and atomic mass number AP , write down the relation between nuclear mass, the proton mass, the neutron mass, and the binding energy, BEP ...
3 main types of particle
... (the beta particle which is ejected) and a proton (which stays in the nucleus) During beta decay the mass number stays the same but the proton number goes up by 1. Remember the electron comes from the nucleus! ...
... (the beta particle which is ejected) and a proton (which stays in the nucleus) During beta decay the mass number stays the same but the proton number goes up by 1. Remember the electron comes from the nucleus! ...
SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES
... Isotopes are written using standard atomic notation. ...
... Isotopes are written using standard atomic notation. ...
Nuclear - Orangefield ISD
... ◦ Electrons are MUCH smaller ◦ B/c the masses are so small (must use scientific notation, which is cumbersome), chemists developed a standard for measurement Carbon-12 atom Exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of carbon-12 atom ...
... ◦ Electrons are MUCH smaller ◦ B/c the masses are so small (must use scientific notation, which is cumbersome), chemists developed a standard for measurement Carbon-12 atom Exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of carbon-12 atom ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger.__________________________ 14. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____________ ...
... 13. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, an undergraduate student who worked with Geiger.__________________________ 14. Worked in Rutherford’s lab on the gold foil experiment, a graduate student who suggested that Rutherford should let Marsden get some lab experience. ____________ ...
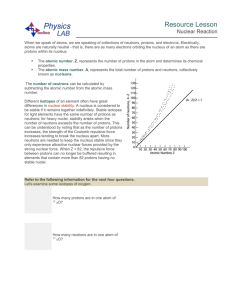
Resource Lesson Nuclear Reaction When we speak of atoms, we
... behavior of the reactants or the products. Customarily, atomic masses are stated in atomic mass units, or amu, when given during nuclear reactions. Energies are also often given in electronvolts, eV, instead of Joules. However, virtually all the formulas require standard SI units of kg and J instead ...
... behavior of the reactants or the products. Customarily, atomic masses are stated in atomic mass units, or amu, when given during nuclear reactions. Energies are also often given in electronvolts, eV, instead of Joules. However, virtually all the formulas require standard SI units of kg and J instead ...
Environmental Science Chapter 17 Test Student Copy
... ____ 12. During the process of nuclear fission, a. a neutron splits a uranium-235 atom, forming new elements and releasing several neutrons, plus energy. b. a neutron splits a daughter nucleus, thus creating uranium-234. c. radioactivity causes the neutron of a uranium-235 atom to split in two. d. a ...
... ____ 12. During the process of nuclear fission, a. a neutron splits a uranium-235 atom, forming new elements and releasing several neutrons, plus energy. b. a neutron splits a daughter nucleus, thus creating uranium-234. c. radioactivity causes the neutron of a uranium-235 atom to split in two. d. a ...
Radioactive decay of nucleus
... 7. In an experiment, a researcher studied the decay of Po-210, which decays by the alpha emission and releases a stable Pb-206 atom. The half-life of Po-210 is 138.4 days. The mass of the Po-210 sample at the start of the experiment was 34.0g. (a)Write an equation for the alpha-decay of Po-210 (b)Wh ...
... 7. In an experiment, a researcher studied the decay of Po-210, which decays by the alpha emission and releases a stable Pb-206 atom. The half-life of Po-210 is 138.4 days. The mass of the Po-210 sample at the start of the experiment was 34.0g. (a)Write an equation for the alpha-decay of Po-210 (b)Wh ...
Modern Physics TEST
... The binding energy per nucleon remains constant as atomic number increases. b. The binding energy per nucleon remains constant as atomic number decreases. c. The binding energy per nucleon increases as atomic number increases. d. The binding energy per nucleon decreases as atomic number increases. _ ...
... The binding energy per nucleon remains constant as atomic number increases. b. The binding energy per nucleon remains constant as atomic number decreases. c. The binding energy per nucleon increases as atomic number increases. d. The binding energy per nucleon decreases as atomic number increases. _ ...
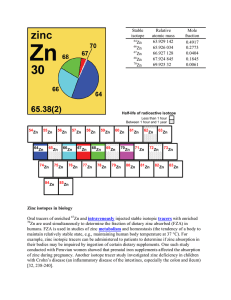
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...
Chapter 26
... the decay of radium ◦ It is present in uranium mines and in certain types of rocks, bricks, etc that may be used in home building ◦ May also come from the ground itself ...
... the decay of radium ◦ It is present in uranium mines and in certain types of rocks, bricks, etc that may be used in home building ◦ May also come from the ground itself ...