Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
... atomic mass number (A) - the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic mass unit - the unit of mass equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus; the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number is called the mass number. atomic number (Z) - the number of protons in the nu ...
... atomic mass number (A) - the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic mass unit - the unit of mass equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 nucleus; the atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number is called the mass number. atomic number (Z) - the number of protons in the nu ...
Nuclear Equations
... A balanced chemical reaction equation re ects the fact that during a chemical reaction, bonds break and form, and atoms are rearranged, but the total numbers of atoms of each element are conserved and do not change. A balanced nuclear reaction equation indicates that there is a rearrangement during ...
... A balanced chemical reaction equation re ects the fact that during a chemical reaction, bonds break and form, and atoms are rearranged, but the total numbers of atoms of each element are conserved and do not change. A balanced nuclear reaction equation indicates that there is a rearrangement during ...
atoms - Somerset Academy Silver Palms Middle/High
... The particles and energy produced during radioactive decay are forms of nuclear radiation. An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons and is positively charged. It is the same as a helium nucleus. Alpha radiation can cause an injury much like a bad burn. After alpha radiation the ato ...
... The particles and energy produced during radioactive decay are forms of nuclear radiation. An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons and is positively charged. It is the same as a helium nucleus. Alpha radiation can cause an injury much like a bad burn. After alpha radiation the ato ...
Radioactivity Reading Assignment Name: Chemistry Date: Hour
... into a more stable atom. This radioactive decay is completely spontaneous. When an unstable nucleus decays, there are three ways that it can do so. It may give out an alpha particle (we use the symbol á), a beta particle (symbol â), or a gamma ray (symbol ã). Many radioactive substances emit á parti ...
... into a more stable atom. This radioactive decay is completely spontaneous. When an unstable nucleus decays, there are three ways that it can do so. It may give out an alpha particle (we use the symbol á), a beta particle (symbol â), or a gamma ray (symbol ã). Many radioactive substances emit á parti ...
Document
... 1.35% is by beta emission, and 0.49% is by positron emission. (a) Why should we expect 40K to be radioactive? (b) Write the nuclear equations for the three modes by which 40K decays. (c) How many 40K+ ions are present in 1.00 g of KCl? (d) How long does it take for 1.00% of the 40K in a sample to un ...
... 1.35% is by beta emission, and 0.49% is by positron emission. (a) Why should we expect 40K to be radioactive? (b) Write the nuclear equations for the three modes by which 40K decays. (c) How many 40K+ ions are present in 1.00 g of KCl? (d) How long does it take for 1.00% of the 40K in a sample to un ...
Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-1
... A. both negatively charged and repel each other C. both positively charged and repel each other B. oppositely charged and attract each other D. oppositely charged and repel each other 5. Most atomic nuclei are stable, even though they contain positively charged protons that repel each other. Which f ...
... A. both negatively charged and repel each other C. both positively charged and repel each other B. oppositely charged and attract each other D. oppositely charged and repel each other 5. Most atomic nuclei are stable, even though they contain positively charged protons that repel each other. Which f ...
chapters 1-4
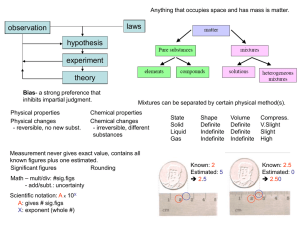
... names of elements, how many element of each kind, atomic ratio. Does not specify arrangement of atoms. ...
... names of elements, how many element of each kind, atomic ratio. Does not specify arrangement of atoms. ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Matter
... properties •There are more than 118 known elements; 92 are natural elements •A natural element is one that is found in nature ...
... properties •There are more than 118 known elements; 92 are natural elements •A natural element is one that is found in nature ...
PS7aChemistryReviewRevised
... Alcohol boils. Paint dries. A photosynthesizing plant produces sugar. ...
... Alcohol boils. Paint dries. A photosynthesizing plant produces sugar. ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... nucleus of each atom. He was unsuccessful because the neutron had not been discovered yet. ...
... nucleus of each atom. He was unsuccessful because the neutron had not been discovered yet. ...
the atomic theory
... 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
... 3. Ernest Rutherford 4. James Chadwick 5. Neils Bohr 6. nucleus 7. proton 8. neutron 9. electron 10. shell 11. atomic number 12. atomic mass 13. Bohr Model 14. subatomic particle 15. isotope 16. empty bus seat rule B/ THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM: - John Dalton ...
Chapter 32 Applied Nucleonics
... The discovery of nuclear fission in 1938 by Hahn and Strassman suggested the possibility of tapping the energy of the nucleus. Recall that it is a conversion of some of the nuclear binding energy into kinetic energy that characterizes both fission and fusion. The basis of this conversion can be seen ...
... The discovery of nuclear fission in 1938 by Hahn and Strassman suggested the possibility of tapping the energy of the nucleus. Recall that it is a conversion of some of the nuclear binding energy into kinetic energy that characterizes both fission and fusion. The basis of this conversion can be seen ...
SCI 3101 Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. 1) The sky is blue because air
... 14) If an atom has 43 electrons, 56 neutrons, and 43 protons, what is its approximate atomic mass? What is the name of this element? A) Atomic mass 142 amu; Einsteinium (Es) B) Atomic mass, 99 amu; Radon (Ra) C) Atomic mass, 137 amu; Barium (Ba) D) Atomic mass, 99 amu; Technetium (Tc) 15) Why are t ...
... 14) If an atom has 43 electrons, 56 neutrons, and 43 protons, what is its approximate atomic mass? What is the name of this element? A) Atomic mass 142 amu; Einsteinium (Es) B) Atomic mass, 99 amu; Radon (Ra) C) Atomic mass, 137 amu; Barium (Ba) D) Atomic mass, 99 amu; Technetium (Tc) 15) Why are t ...
Quanta to Quarks part 2 - Connecting-Sharing-and
... two lighter nuclei, each of which is more stable than the original nucleus. The first artificially induced nuclear fission reaction was achieved by Enrico Fermi in 1934, although at the time he did not realise that fission had occurred. Fermi bombarded uranium with neutrons and produced radioactive ...
... two lighter nuclei, each of which is more stable than the original nucleus. The first artificially induced nuclear fission reaction was achieved by Enrico Fermi in 1934, although at the time he did not realise that fission had occurred. Fermi bombarded uranium with neutrons and produced radioactive ...
Lecture 1 - Asimow.com
... – Photodisintegration rearrangement: when thermal radiation reaches gamma-ray energies it drives rapid nuclear rearrangement creating everything up to 56Fe, but nothing heavier – Neutron irradiation: most nuclei heavier than 56Fe are generated by neutron capture, which follows two paths depending on ...
... – Photodisintegration rearrangement: when thermal radiation reaches gamma-ray energies it drives rapid nuclear rearrangement creating everything up to 56Fe, but nothing heavier – Neutron irradiation: most nuclei heavier than 56Fe are generated by neutron capture, which follows two paths depending on ...
Lecture 30/3 Nuclear processes Ulf Torkelsson 1 Nuclear reactions
... Fe, in which they are the most strongly bound, and in heavier nuclei the binding energy per nucleon decreases with the size of the nucleus. Therefore there are two ways of deriving energy from atomic nuclei, by fusing light nuclei, and by fissioning heavy nuclei. The nuclei that are involved in a fu ...
... Fe, in which they are the most strongly bound, and in heavier nuclei the binding energy per nucleon decreases with the size of the nucleus. Therefore there are two ways of deriving energy from atomic nuclei, by fusing light nuclei, and by fissioning heavy nuclei. The nuclei that are involved in a fu ...
Physics 535 lectures notes: 1 * Sep 4th 2007
... up to keV. Quantum mechanics, rejected this idea since an electron bound in 1 fm area would have an energy on order 100MeV. Also there would have to be some new strong interaction to explain why the electron would be bound in a new very small orbital and no evidence for such an interaction has been ...
... up to keV. Quantum mechanics, rejected this idea since an electron bound in 1 fm area would have an energy on order 100MeV. Also there would have to be some new strong interaction to explain why the electron would be bound in a new very small orbital and no evidence for such an interaction has been ...
chapter2 2012 (no naming) 2014
... • Bombardment of gold foil with α particles (helium atoms minus their electrons) • Expected to see the particles pass through the foil • Found that some of the alpha particles were deflected by the foil • Led to the discovery of a region of heavy mass at the center of the atom = nucleus ...
... • Bombardment of gold foil with α particles (helium atoms minus their electrons) • Expected to see the particles pass through the foil • Found that some of the alpha particles were deflected by the foil • Led to the discovery of a region of heavy mass at the center of the atom = nucleus ...
Nuclear
... Positron emission, also A nucleus emits a positron and a neutrino Beta-Positive decay Electron capture A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state Electron capture with A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one po ...
... Positron emission, also A nucleus emits a positron and a neutrino Beta-Positive decay Electron capture A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state Electron capture with A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one po ...
Chapter 10-11 Unit: Vapor Pressure and Solutions
... Positron emission, also A nucleus emits a positron and a neutrino Beta-Positive decay Electron capture A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state Electron capture with A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one po ...
... Positron emission, also A nucleus emits a positron and a neutrino Beta-Positive decay Electron capture A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state Electron capture with A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one po ...
Critical Thinking Questions 2
... Model 1: Radioactive Decay A nuclide is a particular nuclear species with a specified number of protons and neutrons. The 6 most important ways in which radioactive nuclides decay are: (a) α decay: the nucleus loses an α particle ( !!He!! ) (b) β decay: a neutron in the nucleus is converted into a p ...
... Model 1: Radioactive Decay A nuclide is a particular nuclear species with a specified number of protons and neutrons. The 6 most important ways in which radioactive nuclides decay are: (a) α decay: the nucleus loses an α particle ( !!He!! ) (b) β decay: a neutron in the nucleus is converted into a p ...
Document
... fragments be equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. Thus, from KE = p2/2m, the lighter alpha particle has more kinetic energy that the more massive daughter nucleus. ...
... fragments be equal in magnitude and oppositely directed. Thus, from KE = p2/2m, the lighter alpha particle has more kinetic energy that the more massive daughter nucleus. ...