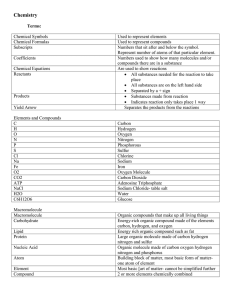
1st Term Review
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
Chemistry DCA Review Sheet
... 1. What are subatomic particles, what are their charges, and where are they found? ...
... 1. What are subatomic particles, what are their charges, and where are they found? ...
Chemical Elements and atoms - Cuda Anatomy
... • atoms of almost all elements exhibit two or more structural variations called isotopes 1. isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons, but vary in the number of neutrons they contain - thus, 2. has the same atomic number (same chemical properties) of the element, but has a different ato ...
... • atoms of almost all elements exhibit two or more structural variations called isotopes 1. isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons, but vary in the number of neutrons they contain - thus, 2. has the same atomic number (same chemical properties) of the element, but has a different ato ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... 1. Elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from one another. 3. Atoms of one element can mix or chemically combine with atoms of other elements, creating compounds with simple ...
... 1. Elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from one another. 3. Atoms of one element can mix or chemically combine with atoms of other elements, creating compounds with simple ...
Matter
... Elements with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical properties. Group 1 has 1 valence electron, group 2 has 2, 13 has 3, 14 / 4, 15 / 5, 16 / 6, 17 / 7, 18 / 8. ...
... Elements with the same number of valence electrons have similar chemical properties. Group 1 has 1 valence electron, group 2 has 2, 13 has 3, 14 / 4, 15 / 5, 16 / 6, 17 / 7, 18 / 8. ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... d. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds e. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. 3. Describe how Thomson’s CRT experiment led to the discovery of the electron. Describe a CRT and T ...
... d. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds e. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. 3. Describe how Thomson’s CRT experiment led to the discovery of the electron. Describe a CRT and T ...
Learning Guide – Poisons (I)
... HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat Can you think of anything else that releases light or heat? ...
... HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat Can you think of anything else that releases light or heat? ...
7.2 - Moodle
... • So in a large nucleus all the protons repel each other, but each nucleon attracts only its nearest neighbours. • More neutrons are needed to hold the nucleus together (although adding too many neutrons can also cause instability). • There is an upper limit to the size of a stable nucleus, because ...
... • So in a large nucleus all the protons repel each other, but each nucleon attracts only its nearest neighbours. • More neutrons are needed to hold the nucleus together (although adding too many neutrons can also cause instability). • There is an upper limit to the size of a stable nucleus, because ...
Balancing a Nuclear Equation
... to break into smaller atoms, thereby increasing their stability. • Using a neutron to split a nucleus into fragments is called nuclear fission. ...
... to break into smaller atoms, thereby increasing their stability. • Using a neutron to split a nucleus into fragments is called nuclear fission. ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... fission of one U-235 nucleus is 215 million electron-Volts (about 3.4×10-11 joules). By comparison, the average energy involved in chemical process, e.g., metabolism in your body, is about 10 electron-Volts fro each molecule involved. ...
... fission of one U-235 nucleus is 215 million electron-Volts (about 3.4×10-11 joules). By comparison, the average energy involved in chemical process, e.g., metabolism in your body, is about 10 electron-Volts fro each molecule involved. ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... oxygen atoms and you still have hydrogen and oxygen atoms after the chemical reaction has occurred…they have simply bonded together to make a water molecule. Nuclear reactions like those that occur in a nuclear power plant or in a star are very different from chemical reactions. They are called nucl ...
... oxygen atoms and you still have hydrogen and oxygen atoms after the chemical reaction has occurred…they have simply bonded together to make a water molecule. Nuclear reactions like those that occur in a nuclear power plant or in a star are very different from chemical reactions. They are called nucl ...
ENERGY IN THE NUCLEUS OF THE ATOM
... Somewhere around 10,000 times more energy is released from a single nuclear reaction compared to a single chemical reaction (like the combustion of TNT). ...
... Somewhere around 10,000 times more energy is released from a single nuclear reaction compared to a single chemical reaction (like the combustion of TNT). ...
have shown no evidence
... and neutrons • Not usually equal numbers • Plotting neutron number (A) against proton number (Z) for all known nuclei, shows area of stability • For very light elements N ≈ Z gives stable elements • 1:1 up to 4020Ca • Ratio gradually rises (A>Z) until by element 83 (Bi, the last one with a stable is ...
... and neutrons • Not usually equal numbers • Plotting neutron number (A) against proton number (Z) for all known nuclei, shows area of stability • For very light elements N ≈ Z gives stable elements • 1:1 up to 4020Ca • Ratio gradually rises (A>Z) until by element 83 (Bi, the last one with a stable is ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
投影片 - 中正大學化生系
... 3. The arrangement of the elements in groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of th ...
... 3. The arrangement of the elements in groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of th ...
Topic 7.1-Discrete energy and radioactivity
... distributed throughout the atom, with their charge balanced by the presence of a uniform sea of positive charge (the plum pudding ...
... distributed throughout the atom, with their charge balanced by the presence of a uniform sea of positive charge (the plum pudding ...
Atomic number
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
... decay and thereby lose energy. Why would nucleii tend to fall apart?? (Think about what protons do to each other) These unstable elements are called RADIOACTIVE. All elements with more than 83 protons are RADIOACTIVE. ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
power point notes
... Discovered that atoms contain negatively charged particles called “corpuscles” later called electrons ...
... Discovered that atoms contain negatively charged particles called “corpuscles” later called electrons ...