Nuclear Physics and Bombs
... To sustain the chain reaction, it is necessary to have many fissionable atoms around to catch neutrons. The smallest amount of fissile material is called critical mass. The critical mass depends on the density of the material and how easy for 235U to capture a neutron. Inside a nuclear power plant, ...
... To sustain the chain reaction, it is necessary to have many fissionable atoms around to catch neutrons. The smallest amount of fissile material is called critical mass. The critical mass depends on the density of the material and how easy for 235U to capture a neutron. Inside a nuclear power plant, ...
chapter2 2012 (no naming)
... Atomic Theory 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms 2. All atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties 3. In an ordinary chemical reaction, atoms rearrange their bonds but atoms are not created or destroyed 4. Compounds are formed when two or more atoms of differe ...
... Atomic Theory 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms 2. All atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties 3. In an ordinary chemical reaction, atoms rearrange their bonds but atoms are not created or destroyed 4. Compounds are formed when two or more atoms of differe ...
Atomic number
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
... How many protons does Calcium have? What element has 17 protons and 18 neutrons? What is its atomic number? What is its atomic mass? ...
Natural Radioactivity
... determines how many (negatively-charged) electrons will encircle it, thus determining its position in the periodic table of elements. The number of protons in a nucleus is also called the atomic number. Neutrons have no effect on the chemical properties of an element. They only change the mass of a ...
... determines how many (negatively-charged) electrons will encircle it, thus determining its position in the periodic table of elements. The number of protons in a nucleus is also called the atomic number. Neutrons have no effect on the chemical properties of an element. They only change the mass of a ...
Understanding Nuclear Power
... The commercial power reactors operating in the United States are termed light water reactors. They use ordinary water as the coolant and moderator. The coolant is what cools the reactor and transports the heat generated in the fuel. Neutrons born from fission are prompt neutrons and to successfully ...
... The commercial power reactors operating in the United States are termed light water reactors. They use ordinary water as the coolant and moderator. The coolant is what cools the reactor and transports the heat generated in the fuel. Neutrons born from fission are prompt neutrons and to successfully ...
FIREWORKS EMC summary notes
... Most elements are solid at room temperature, e.g. carbon and copper. The two elements that are liquid at room temperature are bromine and mercury. Some elements are gases at room temperature, e.g. oxygen and hydrogen.* Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals. There are many more metals t ...
... Most elements are solid at room temperature, e.g. carbon and copper. The two elements that are liquid at room temperature are bromine and mercury. Some elements are gases at room temperature, e.g. oxygen and hydrogen.* Elements can be classified as metals and non-metals. There are many more metals t ...
WRL1007.tmp
... The positive ions created in the GM tube migrate to the cylinder walls and are neutralized. Until most of these ions are neutralized, the electric field is lower than during the initial ionization events. If another ionizing particle enters the GM tube, the number of (secondary) electrons reaching t ...
... The positive ions created in the GM tube migrate to the cylinder walls and are neutralized. Until most of these ions are neutralized, the electric field is lower than during the initial ionization events. If another ionizing particle enters the GM tube, the number of (secondary) electrons reaching t ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... Xe(l ), Kr(l), Ar(l), Ne(l ) Kr(l), Xe(l), Ar(l), Ne(l) Ar(l), Kr(l), Ne(l), Xe(l) Ne(l), Ar(l), Kr(l), Xe(l ) ...
... Xe(l ), Kr(l), Ar(l), Ne(l ) Kr(l), Xe(l), Ar(l), Ne(l) Ar(l), Kr(l), Ne(l), Xe(l) Ne(l), Ar(l), Kr(l), Xe(l ) ...
A = 27
... Radiation of +2 charge is an alpha particle, and table “N” lists natural decay. Find the alpha emitter on table n from the choices. The answer is Fr-220 d), the only alpha emitter – Cs-137, Fe-53 and Au-198 are beta #29) Co-60 undergoes beta decay, this type of radiation is a) natural transmutation ...
... Radiation of +2 charge is an alpha particle, and table “N” lists natural decay. Find the alpha emitter on table n from the choices. The answer is Fr-220 d), the only alpha emitter – Cs-137, Fe-53 and Au-198 are beta #29) Co-60 undergoes beta decay, this type of radiation is a) natural transmutation ...
6.6
... a third particle in the products of a beta decay in 1933. This third very light particle would carry the remainder of the available energy. Fermi coined the word neutrino, the Italian word for “little ...
... a third particle in the products of a beta decay in 1933. This third very light particle would carry the remainder of the available energy. Fermi coined the word neutrino, the Italian word for “little ...
The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus
... hold the nucleus together only act over a very short distance. When a uranium nucleus absorbs a neutron it knocks the nucleus out of shape. If the nucleus deforms enough, the electrostatic repulsion between the protons in each half becomes greater than the strong force. It then splits in two. The nu ...
... hold the nucleus together only act over a very short distance. When a uranium nucleus absorbs a neutron it knocks the nucleus out of shape. If the nucleus deforms enough, the electrostatic repulsion between the protons in each half becomes greater than the strong force. It then splits in two. The nu ...
nuclear physics - review
... hold the nucleus together only act over a very short distance. When a uranium nucleus absorbs a neutron it knocks the nucleus out of shape. If the nucleus deforms enough, the electrostatic repulsion between the protons in each half becomes greater than the strong force. It then splits in two. The nu ...
... hold the nucleus together only act over a very short distance. When a uranium nucleus absorbs a neutron it knocks the nucleus out of shape. If the nucleus deforms enough, the electrostatic repulsion between the protons in each half becomes greater than the strong force. It then splits in two. The nu ...
Chemistry Terms
... periodic table of elements. periodic table of elements A gridlike listing of the known elements that is arranged such that elements within vertical row have similar properties. proton One of the two types of particles that make up an atomic nucleus. It has an electric charge of +1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs ...
... periodic table of elements. periodic table of elements A gridlike listing of the known elements that is arranged such that elements within vertical row have similar properties. proton One of the two types of particles that make up an atomic nucleus. It has an electric charge of +1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs ...
Core Idea PS1 Matter and Its Interactions How can one explain the
... periods (orders elements horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus) families (place those with similar chemical properties in columns) valence (reflect patterns of outer electron states) ...
... periods (orders elements horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus) families (place those with similar chemical properties in columns) valence (reflect patterns of outer electron states) ...
Nuclear Power, Uranium Mining and Public Health
... attack could also lead to a major release of radiation. ...
... attack could also lead to a major release of radiation. ...
8.5C Vocabulary
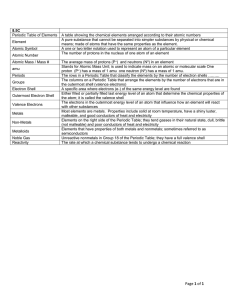
... A table showing the chemical elements arranged according to their atomic numbers A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means; made of atoms that have the same properties as the element. A one or two letter notation used to represent an atom of a pa ...
... A table showing the chemical elements arranged according to their atomic numbers A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means; made of atoms that have the same properties as the element. A one or two letter notation used to represent an atom of a pa ...
File
... A substance that can be broken down A homogenous mixture in aqueous suspension Unit of measurement for measuring mass of elements The name of columns on the periodic table The name of rows on the periodic table The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negat ...
... A substance that can be broken down A homogenous mixture in aqueous suspension Unit of measurement for measuring mass of elements The name of columns on the periodic table The name of rows on the periodic table The electronic charge of an atom All elements in order A unit of energy Positive or negat ...
Glencoe Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom for the Wiki
... in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element can be expressed in small whole numbers. ...
... in the same ratio by mass. Law of Multiple Proportions Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element can be expressed in small whole numbers. ...
File
... 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two or more elements combine chemically you get a mixture. 4. __________________: The properties of elements do not change when mixtures are f ...
... 1. __________________: Atoms are smallest form of matter. 2. __________________: Electrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. 3. __________________: When two or more elements combine chemically you get a mixture. 4. __________________: The properties of elements do not change when mixtures are f ...
solutions - Physics@Brock
... controllable. Which alternative occurs depends on how closely packed the fissionable nuclei are, and also on whether there are substances around that might absorb some of the neutrons or slow some of them down. Neutron absorbers may be able to absorb a sufficient number of neutrons to prevent explos ...
... controllable. Which alternative occurs depends on how closely packed the fissionable nuclei are, and also on whether there are substances around that might absorb some of the neutrons or slow some of them down. Neutron absorbers may be able to absorb a sufficient number of neutrons to prevent explos ...
Chemical reactions revision
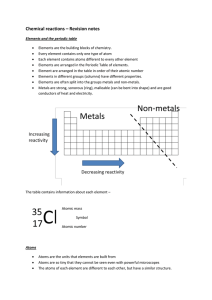
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
Word - The Physics Teacher.ie
... The photograph shows one of the nuclear reactors at Chernobyl, where there was a fire in April 1986 that released large quantities of radioactive contaminants. Among the contaminants were iodine–131 and caesium–137, which are two of the unstable isotopes formed by the fission of uranium–235. (iv) Ex ...
... The photograph shows one of the nuclear reactors at Chernobyl, where there was a fire in April 1986 that released large quantities of radioactive contaminants. Among the contaminants were iodine–131 and caesium–137, which are two of the unstable isotopes formed by the fission of uranium–235. (iv) Ex ...
on Nuclear Physics - Good Earth School
... Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity) is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiations ...
... Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity) is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiations ...