* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-1
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Radiation protection wikipedia , lookup
Effects of nuclear explosions wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Chien-Shiung Wu wikipedia , lookup
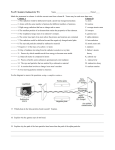
Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-1 (standards 1.e, 11a-11e) 1. Compared to the charge and mass of a proton, an electron has (1.e) A. the same charge and a smaller mass C. the same charge and the same mass B. an opposite charge and a smaller mass D. an opposite charge and the same mass 2. Which symbols represent atoms that are isotopes (11.c)? A. C-14 and N-14 C. O-16 and O-18 B. I-131 and I-131 D. Rn-222 and Ra-222 3. Which radioactive emanations have a charge of -1 (11.d)? A. neutrons C. gamma rays C. alpha particles D. beta particles 4. In a fusion reaction, reacting nuclei must collide. Collisions between two nuclei are difficult to achieve because the nuclei are (11.b) A. both negatively charged and repel each other C. both positively charged and repel each other B. oppositely charged and attract each other D. oppositely charged and repel each other 5. Most atomic nuclei are stable, even though they contain positively charged protons that repel each other. Which force stabilizes the nucleus of an atom (11.a)? A. the electrostatic force C. the gravitational force B. the strong nuclear force D. the electromagnetic force 6. Mr. Watson performs an experiment on a radioactive source. He passes alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) radiation through three different media of varying thicknesses, as shown in the diagram below (11.e). Which statement about the penetration power of these types of radiation is true? A. The beta and gamma radiation can penetrate lead. B. The beta and gamma radiation will not penetrate lead. C. The alpha and beta radiation will not penetrate paper. D. The alpha and gamma radiation can penetrate aluminum. Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-2 (standards 1.e, 11a-11e) 1. When alpha particles are used to bombard gold foil, most of the alpha particles pass through undeflected. This result indicates that most of the volume of a gold atom consists of ____ (1.e). A. deuterons C. neutrons B. protons D. unoccupied space 2. What kind of radiation will travel through an electric field on a pathway that remains unaffected by the field (11.d)? A. a proton C. a gamma ray B. an electron D. an alpha particle 3. Which nuclide is a radioisotope used in the study of organic reaction mechanisms (11.c)? A. carbon-12 C. carbon-14 B. uranium-235 D. uranium-238 4. In the equation E = mc 2 , ‶c″ stands for (11.b) A. carbon. B. the speed of light. C. the total energy. D. the size of the particle. 5. Which action is primarily the result of the strong nuclear force (11.a)? A. the release of photons by an excited electron C. attraction between particles of the same charge B. a change in a magnetic field caused by a moving charge D. attraction to the center of mass of a nearby large object 6. What characteristics of gamma rays enable them to penetrate matter up to several meters thick (11.e)? A. no electrical charge and no rest mass B. no electrical charge and large rest mass C. positive electrical charge and no rest mass D. positive electrical charge and large rest mass Exit Slip: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-3 (standards 1.e, 11a-11e) 1. A proton has approximately the same mass as (1.e) A. a neutron B. a beta particle C. an alpha particle D. an electron 2. The equation E = mc² describes (11.b) A. the number of half lives of an element. B. the alpha emission of an element. C. the speed of radioactive decay in a nuclear reaction. D. the amount of energy released in a nuclear reaction. 3. Which force is responsible for the reactions that release most of the energy coming from the Sun (11.a)? A. gravitational force C. electrostatic force B. weak nuclear force D. strong nuclear force 4. Which statement best describes the difference in penetration between alpha, beta, and gamma radiation? A. Alpha and beta radiation can be stopped by thick layers of lead or concrete, while gamma radiation can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper (11.e). B. Alpha and beta radiation can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper, while gamma radiation can be stopped by thick layers of lead or concrete. C. Alpha and beta radiation can be stopped by thick layers of lead or concrete, while gamma radiation can be stopped by wood that is a few centimeters thick. D. Alpha and beta radiation can be stopped by wood that is a few centimeters thick, while gamma radiation can be stopped by thick layers of lead or concrete. 5. The table below contains information about three isotopes (11.c). Which statement BEST describes the isotopes in the chart? A. All of the isotopes are naturally occurring. B. All of the isotopes are created only in particle accelerators. C. Atom 1 is a naturally occurring isotope, but Atom 3 is created only in particle accelerators. D. Atom 3 is a naturally occurring isotope, but Atom 1 is only created in particle accelerators. 6. During radioactive decay, a cesium atom with 55 protons and a total of 137 particles in its nucleus transforms into a barium atom with 56 protons and the same number of total particles in its nucleus. Which kind of radiation is emitted by this decay (11.d)? A. x-ray C. gamma ray B. beta particle D. alpha particle Exit Slip: (Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry-4 (standards 1.e, 11a-11e) 1. A neutron has approximately the same mass as a (1.e) A. an alpha particle C. a beta particle B. an electron D. a proton 2. Some reactions conserve neither mass nor energy. If the equation is used to equate mass and energy, then it can be seen that the combined value of mass plus energy is conserved in these reactions. Which of these is the BEST example of such a reaction (11.b)? A. conversion of prehistoric plants to fossil fuels B. sudden explosive reactions with gaseous products C. splitting of a uranium nucleus into barium and krypton nuclei D. return of ground state of electrons that have been excited to a higher energy level 3. Nuclei with too many or too few neutrons are (11.a) A. never found. C. unstable. B. unnatural. D. stable. 4. Arrange the forms of radiation from longest to shortest penetration range (11.e). A. alpha, beta, gamma C. alpha, gamma, beta B. gamma, alpha, beta D. gamma, beta, alpha 5. Iodine 131 is a radioactive isotope. Which property makes an isotope radioactive (11.c)? A. an unstable nucleus C. a high mass number B. having more neutrons than protons D. having more electrons than protons 6. Two radioactive elements, X and Y, undergo nuclear decay, forming new elements. The element X emits an alpha particle, forming , and the element Y emits a beta particle, forming radioactive elements X and Y? A. X = ,Y= B. X = ,Y= C. X = ,Y= D. X = ,Y= . What are the