* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ernest Rutherford Essay Research Paper Rutherford was
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
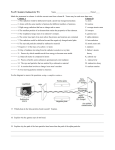
Ernest Rutherford Essay, Research Paper Rutherford was born on August 30, 1871, in Nelson, New Zealand. He was educated at the University of New Zealand and the University of Cambridge. He was a professor of physics at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec from 1989 to 1907. He was also professor at the University of Manchester in England. After 1919 he was professor of experimental physics and director of the Cavendish Lab at the University of Cambridge moreover held a professorship, after 1920, at the Royal Institution of Great Britain in London. Rutherford stated that an atom consists largely of empty space, with an electrically positive nucleus in the center and electrically negative electrons orbiting the nucleus. He identified the 3 main components of radiation and named them alpha, beta, and gammy rays. Alpha particles are actually the nuclei of helium atoms. Each alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons, with a charge of 2+ and a mass of 4 atomic mass units. On the average, their speed is about 1/10 the speed of the light. Usually they travel only a few centimeters through air. They can be stopped by a single sheet of paper. Alpha particles electrically charge molecules in the air through which they travel. Beta particles consist of streams of electrons traveling at very high speeds, often approaching the speed of light. They have a mass of 0.000 55 atomic mass unit and a charge of 1-. They have a greater power to penetrate than alpha particles but less electrical charge ability. Beta particles can be stopped by a thin sheet of aluminum. Gamma rays are type of electromagnetic radiation. They are similar to X rays but have greater penetrating power than X rays, alpha or beta particles. It takes several centimeters of lead and an even greater thickness of iron to block gamma rays. Gamma rays, like alpha and beta particles, can ionize atoms they strike. His study of radiation led to his formulation of the theory of atomic structure, which was the first to describe the atom as adense nucleus about which electrons circulate in orbits. He conducted his most important experiment in nuclear physics when he bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and obtained atoms on oxygen isotope and protons. This transmutation of nitrogen into the oxygen was the first artificially induced nuclear reaction. It inspired he intensive research of later scientists on other nuclear transformations and on the nature and properties on radiation. In his experiment, Rutherford used the setup shown in the next page. As shown in the drawing, Rutheford used a very thin sheet of gold as a target. On one side of the foil was a lead box containing a radioactive particle. A small hole in the box permitted a narrow stream of alpha particles to shoot out. These particles were directed at right angles to the surface of the foil. Surrounding the foil was a screen coated with zinc sulfide. Each time an alpha particles hit this coating, a flash of light, it was possible to see whether the alpha particles that passed through the foil had been deflected. Rutherford and the British physicist Fedrick Soddy developed the explanation of radioactivity that scientists accept today. The rutherford, a unit of radioactivity was named in his honor. Royal Society in 1903 and served as president of that institution from 1925 through 1930. His successful experiment led him to be fellow of Royal Society. He awarded Nobel Prize in chemistry. He died in London on October 19, 1937, and was buried in Westminster Abbey. He also published many books. He wrote the book Radioactivity in 904 : Radiation from Radioactive Substances in 1930, which he wrote with British physicists Sir James Chadwick and Chales Drummond Ellis, and which has become standard text; and The Newer Alchemy in 1937. His experiment brought new ideas of radiation by identifying three main radioactive particles. A lot of scientist in today studies radioactivity according Rutherford?s theory.