Radioactive Decay
... Example: Assuming a half-life of _________, how many years will be needed for the decay of ________ of a given amount of radium-226? Amount remaining = 1/16 = 0.0625 = (½)4 = ____________ Years needed for decay of 15/16 = (1599 years) (__) = ___________ ...
... Example: Assuming a half-life of _________, how many years will be needed for the decay of ________ of a given amount of radium-226? Amount remaining = 1/16 = 0.0625 = (½)4 = ____________ Years needed for decay of 15/16 = (1599 years) (__) = ___________ ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... Describe matter using properties, including physical and chemical, intensive and extensive. Distinguish among elements, compounds, and mixtures. Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Differentiate among the physical states of matter. Classify changes in matter as exothermic ...
... Describe matter using properties, including physical and chemical, intensive and extensive. Distinguish among elements, compounds, and mixtures. Distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Differentiate among the physical states of matter. Classify changes in matter as exothermic ...
first lecture - الدكتورة / زينب بنت زكي الفل
... Nuclei with the same Z, but different A are called isotopes. A particular element with a given Z may have isotopes of different mass numbers. Their nuclei contain the same number of protons and different number of neutrons. Isotopes were first discovered amongst naturally radioactive elements J.J. T ...
... Nuclei with the same Z, but different A are called isotopes. A particular element with a given Z may have isotopes of different mass numbers. Their nuclei contain the same number of protons and different number of neutrons. Isotopes were first discovered amongst naturally radioactive elements J.J. T ...
nuclear radiation, continued
... 〉How does radiation affect the nucleus of an unstable isotope? 〉Anytime that an unstable nucleus emits alpha or beta particles, the number of protons or neutrons. Nuclear-decay equations are similar to those used for chemical reactions. ...
... 〉How does radiation affect the nucleus of an unstable isotope? 〉Anytime that an unstable nucleus emits alpha or beta particles, the number of protons or neutrons. Nuclear-decay equations are similar to those used for chemical reactions. ...
Modern Physics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Isotopes of a given element correspond to nuclei with different numbers of neutrons. This results in a variety of different properties for the nuclei, including the obvious one of mass. The chemical behavior, however, is governed by the lectrons. All isotopes of a given element have the same number ...
... Isotopes of a given element correspond to nuclei with different numbers of neutrons. This results in a variety of different properties for the nuclei, including the obvious one of mass. The chemical behavior, however, is governed by the lectrons. All isotopes of a given element have the same number ...
Earth`s Chemistry
... protons in the atom. An uncharged atom has the same amount of protons & electrons so there’s no charge. It’s said to be neutral Example --- Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 so it has 8 protons & 8 ...
... protons in the atom. An uncharged atom has the same amount of protons & electrons so there’s no charge. It’s said to be neutral Example --- Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 so it has 8 protons & 8 ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
... Atomic mass unit. Equal to the mass of a proton or neutron. 14.) What is a radioactive isotope? An unstable atom which decay (break down) and give off radioactive energy. 15.) What makes an atom unstable? An imbalance in the ratio of protons to neutrons. The farther this ratio gets from 1:1, the mor ...
Nuclear Decay
... Problems With Gamma Rays • Carry a lot of energy • Most penetrating of the three types of radiation – Pass through several cm of lead ...
... Problems With Gamma Rays • Carry a lot of energy • Most penetrating of the three types of radiation – Pass through several cm of lead ...
mass numbers
... Radioisotopes that are naturally occurring tend to have long half-lives. used in nuclear medicine have short half-lives. ...
... Radioisotopes that are naturally occurring tend to have long half-lives. used in nuclear medicine have short half-lives. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... “existing” nuclei. Unstable nuclei are short-lived, decaying usually by beta emission, but they are stable against particle emission. Where are the limits of the driplines? How do the properties of these nuclei differ from those of ordinary nuclei? ...
... “existing” nuclei. Unstable nuclei are short-lived, decaying usually by beta emission, but they are stable against particle emission. Where are the limits of the driplines? How do the properties of these nuclei differ from those of ordinary nuclei? ...
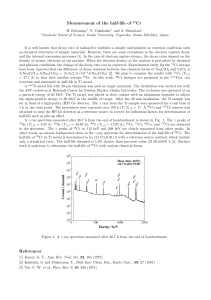
Measurement of the half-life of
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
... It is well known that decay rate of radioactive nuclides is usually independent on external conditions such as chemical structures of sample materials. However, there are some exceptions in the electron capture decay and the internal conversion processes [1]. In the case of electron capture decays, ...
Article 2: Key Concepts and Vocabulary
... in many different forms, and the quantity of energy does not change as it is transformed from one form to another. In a magnetic fusion reactor, there are many forms of energy. Electric currents flowing through coils of conducting wires create magnetic energy in the form of magnetic fields that conf ...
... in many different forms, and the quantity of energy does not change as it is transformed from one form to another. In a magnetic fusion reactor, there are many forms of energy. Electric currents flowing through coils of conducting wires create magnetic energy in the form of magnetic fields that conf ...
Nuclear Chemistry - HCC Learning Web
... slowly because it is absorbed by the nucleus, • The heavy 235U nucleus can split into many different daughter nuclei, e.g. 1 n + 238 U 142 Ba + 91 Kr + 31 n ...
... slowly because it is absorbed by the nucleus, • The heavy 235U nucleus can split into many different daughter nuclei, e.g. 1 n + 238 U 142 Ba + 91 Kr + 31 n ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ element with an imbalance in the number of neutrons and protons ___ uncharged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ physica ...
... ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ element with an imbalance in the number of neutrons and protons ___ uncharged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ physica ...
cps ch 10 notes
... sunlight to emit rays; uranium salts emitted rays that had never been discovered before ...
... sunlight to emit rays; uranium salts emitted rays that had never been discovered before ...
Nuclear Notes
... Consists of photons, are not particles of matter Unaffected by electric or magnetic fields Example: ...
... Consists of photons, are not particles of matter Unaffected by electric or magnetic fields Example: ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the air conduct electricity. 4. Ernest Rutherford did an experiment using pieces of aluminum foil. The first few sheets absorbed the _________ radiation. The later sheets stopped the ________ ...
... 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the air conduct electricity. 4. Ernest Rutherford did an experiment using pieces of aluminum foil. The first few sheets absorbed the _________ radiation. The later sheets stopped the ________ ...
Year 11 PHYSICS revision notes
... been expanding, pushing galaxies further apart (redshift). In the future, the universe could: Expand forever – OPEN universe Slow down & stop expanding – FLAT universe Stop expanding & collapse again (Big Crunch) – CLOSED universe It all depends on how much matter there is to pull everything t ...
... been expanding, pushing galaxies further apart (redshift). In the future, the universe could: Expand forever – OPEN universe Slow down & stop expanding – FLAT universe Stop expanding & collapse again (Big Crunch) – CLOSED universe It all depends on how much matter there is to pull everything t ...
Unit 3 - Princeton High School
... ___________ proposed, in his law of ____________ _____________, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of _____________ ______________ , proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of another element in ...
... ___________ proposed, in his law of ____________ _____________, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of _____________ ______________ , proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of another element in ...
Nuclear Reactions
... If there is enough uranium (critical mass) a chain reaction occurs. Huge amounts of energy are released very quickly. ...
... If there is enough uranium (critical mass) a chain reaction occurs. Huge amounts of energy are released very quickly. ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
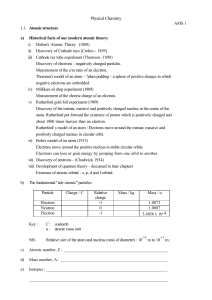
穨 Ams1a
... In a nuclear reaction, there is a rearrangement of ________ and _________ in the nucleus of the atom. New elements are formed. ...
... In a nuclear reaction, there is a rearrangement of ________ and _________ in the nucleus of the atom. New elements are formed. ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 31. What are the three types of radioactive decay you learned about? Write the symbol for each (include all relevant numbers). ...
... 31. What are the three types of radioactive decay you learned about? Write the symbol for each (include all relevant numbers). ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...