Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
Nuclear Chem Notes - Warren County Schools
... neutrons will not escape due to energy that is higher than optimum for inducing further fission. A chain reaction should maintain a constant rate. Critical mass – The smallest amount of fissionable material necessary to support a continuing chain reaction. ...
... neutrons will not escape due to energy that is higher than optimum for inducing further fission. A chain reaction should maintain a constant rate. Critical mass – The smallest amount of fissionable material necessary to support a continuing chain reaction. ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
The Atom.jet.2013 - Petal School District
... Basic Rules (continued): The Pauli Exclusion Principle: ◦ No more than 2 electrons may occupy any ...
... Basic Rules (continued): The Pauli Exclusion Principle: ◦ No more than 2 electrons may occupy any ...
Notes: Nuclear Chemistry
... a. During a nuclear fission reaction, enormous amounts of energy are produced. b. Nuclear fission occurs as a chain reaction (critical mass needed) and must be controlled. c. If a fission reaction is left uncontrolled, then it results in a nuclear explosion. d. There are only two naturally occurring ...
... a. During a nuclear fission reaction, enormous amounts of energy are produced. b. Nuclear fission occurs as a chain reaction (critical mass needed) and must be controlled. c. If a fission reaction is left uncontrolled, then it results in a nuclear explosion. d. There are only two naturally occurring ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
CHAPTER 13: Nuclear Interactions and Applications
... released into the atmosphere or groundwater is of great concern to the general public. Thermal pollution both in the atmosphere and in lakes and rivers used for cooling may be a significant ecological problem. A more serious problem is the safe disposal of the radioactive wastes produced in the fiss ...
... released into the atmosphere or groundwater is of great concern to the general public. Thermal pollution both in the atmosphere and in lakes and rivers used for cooling may be a significant ecological problem. A more serious problem is the safe disposal of the radioactive wastes produced in the fiss ...
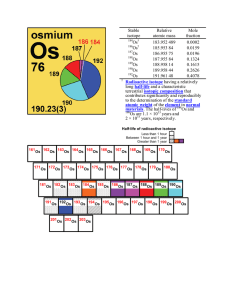
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an ato ...
... radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an ato ...
nuclear fusion
... (sheet of paper). • There is often gamma radiation emitted along with alpha and/or beta particles. • The disintegration of a radioactive nucleus is called radioactive decay. ...
... (sheet of paper). • There is often gamma radiation emitted along with alpha and/or beta particles. • The disintegration of a radioactive nucleus is called radioactive decay. ...
Nuclear Radiation and Decay File
... However, gamma rays cause more damage to biological molecules as they pass through ...
... However, gamma rays cause more damage to biological molecules as they pass through ...
Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
... ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for ______________ of the __________________ lost during _________________________ decays. Since g ...
... ray is high-energy and contains no _____________ and is represented by the symbol __________. Gamma rays usually accompany ___________________ and ___________________ radiation. Gamma rays also account for ______________ of the __________________ lost during _________________________ decays. Since g ...
Ch.7 Summary Notes
... Radiocarbon dating is the process of determining the age of an object by measuring the amount of carbon-14 remaining in that object. Carbon’s isotopes include carbon-12 and carbon14. When an organism is alive, the ratio of carbon- 14 atoms to carbon-12 atoms in the organism remains nearly constant. ...
... Radiocarbon dating is the process of determining the age of an object by measuring the amount of carbon-14 remaining in that object. Carbon’s isotopes include carbon-12 and carbon14. When an organism is alive, the ratio of carbon- 14 atoms to carbon-12 atoms in the organism remains nearly constant. ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Mrs. Carlyle`s Classroom
... Half-lives can be short as a fraction of a second or as long as several million years. Artificial radioisotopes have very short half-lives. Good for nuclear medicine. It is possible to use this method to date rocks as old as our solar system. ...
... Half-lives can be short as a fraction of a second or as long as several million years. Artificial radioisotopes have very short half-lives. Good for nuclear medicine. It is possible to use this method to date rocks as old as our solar system. ...
Unit 2: The Atom
... Gamma decay never happens alone! (it usually accompanies alpha or beta decay) It represents a photon of energy or light Gamma decay alone involves no transformation or change of an atom’s nucleus ...
... Gamma decay never happens alone! (it usually accompanies alpha or beta decay) It represents a photon of energy or light Gamma decay alone involves no transformation or change of an atom’s nucleus ...
A – Z - washburnsciencelies
... This occurs when two smaller nuclei combine together to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out ...
... This occurs when two smaller nuclei combine together to form a single larger nuclei. This produces far more energy than a fission reaction, and also does not have a dangerous by-product. However we currently don’t have the means to use it as a reliable energy source, as we barely get more energy out ...
1.6--NOTES--Detecting Radiation Nuclear Rxtns
... • bubble chamber = similar to the cloud chamber, only filled with superheated liquid instead. Ions cause small bubbles to form in the liquid as it boils, leaving trails of bubbles behind. •Geiger counter = a device the size of a microphone filled with gas and connected to a meter. Ions stripped fro ...
... • bubble chamber = similar to the cloud chamber, only filled with superheated liquid instead. Ions cause small bubbles to form in the liquid as it boils, leaving trails of bubbles behind. •Geiger counter = a device the size of a microphone filled with gas and connected to a meter. Ions stripped fro ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... Organic & Biochemical Chemistry-(2) 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements ...
... Organic & Biochemical Chemistry-(2) 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
... Example 2: Cobalt – 60, with a half-life of 5 years, is used in cancer radiation treatments. If a hospital purchases a supply of 30.0 g, how much would be left after 15 years? ______________ ...
radioactive decay
... Skin can stop alpha radiation Beta radiation – usually only penetrates 1-2cm beneath the skin Alpha, beta and gamma are “ionizing radiation” – they have enough energy to break bonds in molecules which ionizes them, which makes them unstable, and very reactive inside the organism Find out more at Ion ...
... Skin can stop alpha radiation Beta radiation – usually only penetrates 1-2cm beneath the skin Alpha, beta and gamma are “ionizing radiation” – they have enough energy to break bonds in molecules which ionizes them, which makes them unstable, and very reactive inside the organism Find out more at Ion ...
Radioactive Reactions
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
... Radioactive Reactions • When an atom emits part of its NUCLEUS (protons or neutrons) this is called radiation • This happens because the nucleus is unstable. • When an atom emits protons its identity changes • This can happen naturally (sun) or through man made isotopes in a lab ...
Name Period ______ Due Date Review Stations Key Station 1
... Stopped by paper, wood, cloth, etc. ...
... Stopped by paper, wood, cloth, etc. ...
Chapter 32 Nuclear Physics
... The nucleus of an atom is incredibly small. The diameter of the nucleus is about 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of the atom. Although small, the nucleus contains more than 99.9% of the mass of an atom, because each of its constitutes (protons and neutrons) is about 1800 times more massive t ...
... The nucleus of an atom is incredibly small. The diameter of the nucleus is about 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of the atom. Although small, the nucleus contains more than 99.9% of the mass of an atom, because each of its constitutes (protons and neutrons) is about 1800 times more massive t ...