notes ch 39 1st half Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... • Visible light is given off when electrons jump from one orbit to another of lower energy, and gamma rays are emitted when nucleons do a similar sort of thing inside the nucleus. • Gamma rays require lead or other heavy shielding to stop them. ...
... • Visible light is given off when electrons jump from one orbit to another of lower energy, and gamma rays are emitted when nucleons do a similar sort of thing inside the nucleus. • Gamma rays require lead or other heavy shielding to stop them. ...
Introduction to Radiation and Radioactivity
... Atomic number = Z the number of protons in the atom. Determines which element it is. Atomic mass (or Mass number) = A the total number of protons and neutrons. A = Z + N (# of neutrons) ...
... Atomic number = Z the number of protons in the atom. Determines which element it is. Atomic mass (or Mass number) = A the total number of protons and neutrons. A = Z + N (# of neutrons) ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... Fusion (release more E) H-bomb ...
... Fusion (release more E) H-bomb ...
Chapter 4 - Elements and the Periodic Table I. Introduction to atoms
... a. Soft, malleable, shiny b. High conductivity c. Mixed with common metals to make alloy 7. Actinides a. Only 4 occur naturally on Earth b. Others created artificially in laboratories c. Very unstable 8. Synthetic elements a. Have atomic numbers higher than 92 b. Made in particle accelerators ...
... a. Soft, malleable, shiny b. High conductivity c. Mixed with common metals to make alloy 7. Actinides a. Only 4 occur naturally on Earth b. Others created artificially in laboratories c. Very unstable 8. Synthetic elements a. Have atomic numbers higher than 92 b. Made in particle accelerators ...
Phys214 Final Exam
... 12. Consider two different samples of radioactive isotopes, one naturally occurring and the other artificially produced. If the samples have the same number of nuclei, then A. the one with the shorter half-life is likely more dangerous. B. the one with the smaller atomic mass is likely more dangerou ...
... 12. Consider two different samples of radioactive isotopes, one naturally occurring and the other artificially produced. If the samples have the same number of nuclei, then A. the one with the shorter half-life is likely more dangerous. B. the one with the smaller atomic mass is likely more dangerou ...
solutions - Physicsland
... 22. The Earth’s natural energy that heats the water in the hot spring is the energy of radioactive decay, which keeps the Earth’s interior molten. Radioactivity heats the water, but doesn’t make the water itself radioactive. The warmth of hot springs is one of the “nicer effects” of radioactive deca ...
... 22. The Earth’s natural energy that heats the water in the hot spring is the energy of radioactive decay, which keeps the Earth’s interior molten. Radioactivity heats the water, but doesn’t make the water itself radioactive. The warmth of hot springs is one of the “nicer effects” of radioactive deca ...
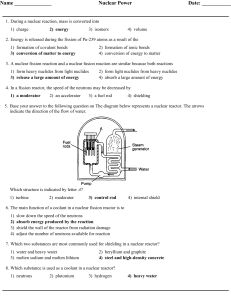
Nuclear Power Date
... Which phrase best describes this type of reaction and the overall energy change that occurs? 1) nuclear, and energy is released 3) chemical, and energy is released ...
... Which phrase best describes this type of reaction and the overall energy change that occurs? 1) nuclear, and energy is released 3) chemical, and energy is released ...
nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... A. def. – a symbolic representation of a nuclear reaction B. Only nuclei are represented – not necessary to indicate electron charges for any ions involved. ...
... A. def. – a symbolic representation of a nuclear reaction B. Only nuclei are represented – not necessary to indicate electron charges for any ions involved. ...
Radioactivity
... • The number of protons is the atomic number. • The number of protons and neutrons together is the mass of the atom. • Nuclide, is the nucleus of an atom having a specific atomic number and atomic mass # ...
... • The number of protons is the atomic number. • The number of protons and neutrons together is the mass of the atom. • Nuclide, is the nucleus of an atom having a specific atomic number and atomic mass # ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Mass number does not change Add 1 to atomic number Identify new element from atomic number Add beta particle ...
... Mass number does not change Add 1 to atomic number Identify new element from atomic number Add beta particle ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... sources of food and nutrition, fossil fuels). Describe at least three chemical reactions of particular importance to humans (e.g., burning of fossil fuels, photosynthesis, rusting of metals). Use a chemical equation to illustrate how the atoms in molecules are arranged before and after a reactio ...
... sources of food and nutrition, fossil fuels). Describe at least three chemical reactions of particular importance to humans (e.g., burning of fossil fuels, photosynthesis, rusting of metals). Use a chemical equation to illustrate how the atoms in molecules are arranged before and after a reactio ...
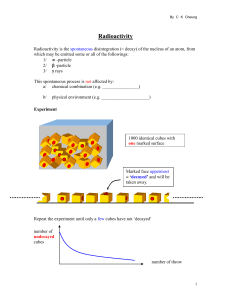
Radioactivity
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration (= decay) of the nucleus of an atom, from which may be emitted some or all of the followings: 1/ -particle 2/ -particle 3/ rays This spontaneous process is not affected by: a/ chemical combination (e.g. ________________) b/ ...
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration (= decay) of the nucleus of an atom, from which may be emitted some or all of the followings: 1/ -particle 2/ -particle 3/ rays This spontaneous process is not affected by: a/ chemical combination (e.g. ________________) b/ ...
1412-PracticeExam4
... Which of these species are structural isomers of C6H14? A. I and II B. I and III C. II and III D. II and IV E. III and IV Which of these species is an aromatic compound? A. C2H2 B. C6H12 C. C6H4Br2 D. C5H10 E. C2H4Br2 The name for the compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2OH is A. ...
... Which of these species are structural isomers of C6H14? A. I and II B. I and III C. II and III D. II and IV E. III and IV Which of these species is an aromatic compound? A. C2H2 B. C6H12 C. C6H4Br2 D. C5H10 E. C2H4Br2 The name for the compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2OH is A. ...
AP Chem
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
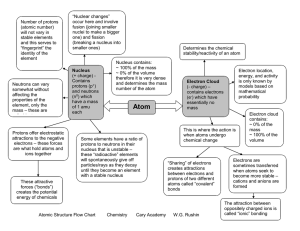
Atomic Structure Flow Chart Chemistry Cary Academy W.G. Rushin
... are what hold atoms and ions together ...
... are what hold atoms and ions together ...
Ch. 21.1 Nuclear Radiation
... – These changes are always accompanied by the emission of large amounts of energy. – Unlike chemical reactions, nuclear reactions are not affected by changes in temperature, pressure, or the presence of catalysts. – Nuclear reactions of given radioisotope cannot be slowed down, speeded up, or stopp ...
... – These changes are always accompanied by the emission of large amounts of energy. – Unlike chemical reactions, nuclear reactions are not affected by changes in temperature, pressure, or the presence of catalysts. – Nuclear reactions of given radioisotope cannot be slowed down, speeded up, or stopp ...
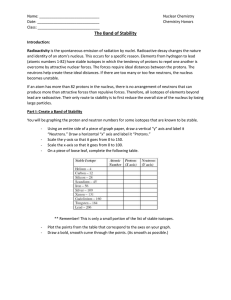
The Band of Stability
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation by nuclei. Radioactive decay changes the nature and identity of an atom’s nucleus. This occurs for a specific reason. Elements from hydrogen to lead (atomic numbers 1-82) have stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another ...
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation by nuclei. Radioactive decay changes the nature and identity of an atom’s nucleus. This occurs for a specific reason. Elements from hydrogen to lead (atomic numbers 1-82) have stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another ...
Fission vs Fusion Worksheet
... There are two main types of nuclear weapons: atomic bombs, which are powered by fission reactions similar to those in nuclear reactors [power plants], and hydrogen bombs, which derive their explosive power from fusion reactions. An atomic bomb slams together two pieces of fissionable material, usual ...
... There are two main types of nuclear weapons: atomic bombs, which are powered by fission reactions similar to those in nuclear reactors [power plants], and hydrogen bombs, which derive their explosive power from fusion reactions. An atomic bomb slams together two pieces of fissionable material, usual ...
Nuclear Fusion
... Reactions begin with unstable isotopes called radioisotopes that undergo change to become stable ...
... Reactions begin with unstable isotopes called radioisotopes that undergo change to become stable ...
CHM 123-Chapter 2.7
... What type of radiation occurs when carbon-11 decays to boron -11? How has the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus changed? ...
... What type of radiation occurs when carbon-11 decays to boron -11? How has the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus changed? ...
Chapter1
... How were the elements created? Were they created at the same time as the universe (in the Big ...
... How were the elements created? Were they created at the same time as the universe (in the Big ...
Types of Radiation
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc ...
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc ...
Unit 2 – The Atom
... • The splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments is called nuclear fission. • Heavy atoms (mass number>60) tend to break into smaller atoms, thereby increasing their stability. ...
... • The splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments is called nuclear fission. • Heavy atoms (mass number>60) tend to break into smaller atoms, thereby increasing their stability. ...
Chapter 21 - Richsingiser.com
... where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. • When a nuclear change occurs a measurable difference in the mass of the products and reactants is observed. ...
... where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. • When a nuclear change occurs a measurable difference in the mass of the products and reactants is observed. ...