CH2ch19_1
... i) Reactor core: enriched uranium (3% U-235) sustains the reaction ii) Control rods absorb neutrons to regulate the reaction ...
... i) Reactor core: enriched uranium (3% U-235) sustains the reaction ii) Control rods absorb neutrons to regulate the reaction ...
atoms - Groupfusion.net
... Isotopes = atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. = same atomic number ; different mass number Almost all elements have isotopes. Some have many and some have only a few. The isotopes of an element always occur in the same percentage. Isotopes of ...
... Isotopes = atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. = same atomic number ; different mass number Almost all elements have isotopes. Some have many and some have only a few. The isotopes of an element always occur in the same percentage. Isotopes of ...
File - Dr. Wall`s Science
... • Put experiment in desk drawer, where there was no light • Image still showed up on paper, due to energy from minerals • This energy is nuclear radiation ...
... • Put experiment in desk drawer, where there was no light • Image still showed up on paper, due to energy from minerals • This energy is nuclear radiation ...
Foldable - Georgetown ISD
... Gamma (γ) Rays (*deadliest form of radiation) – no particle (only radiation/energy) Shielding: thick layers of lead or concrete Fission: *splitting an atom into smaller atoms (also releases energy), *a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable, intermediate-size nuclei Uses: nuclear power plants (* ...
... Gamma (γ) Rays (*deadliest form of radiation) – no particle (only radiation/energy) Shielding: thick layers of lead or concrete Fission: *splitting an atom into smaller atoms (also releases energy), *a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable, intermediate-size nuclei Uses: nuclear power plants (* ...
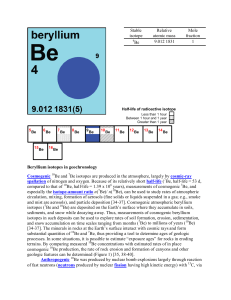
Beryllium isotopes in geochronology Cosmogenic Be and Be
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
... Cosmogenic 10Be and 7Be isotopes are produced in the atmosphere, largely by cosmic-ray spallation of nitrogen and oxygen. Because of its relatively short half-life (7 Be, half-life = 53 d, compared to that of 10Be, half-life = 1.39 x 106 years), measurements of cosmogenic 7Be, and especially the iso ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • Atom releases a beta particle with zero mass & negative charge • Atomic number increases (becomes new element!) ...
... • Atom releases a beta particle with zero mass & negative charge • Atomic number increases (becomes new element!) ...
Physical Science: Nuclear Chemistry Study Guide
... 28. What is the time required for half a sample of radioactive nuclei to decay called? 29. After three half-lives, what fraction of the original radioactive element remains? 30. To determine the age of fairly recent remains (in the tens of thousands of years as opposed to millions of years), scienti ...
... 28. What is the time required for half a sample of radioactive nuclei to decay called? 29. After three half-lives, what fraction of the original radioactive element remains? 30. To determine the age of fairly recent remains (in the tens of thousands of years as opposed to millions of years), scienti ...
• Bond: come together • Charge: there is either a positive or negative
... Charge: there is either a positive or negative charge ...
... Charge: there is either a positive or negative charge ...
nuclear chemistry notes 1
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
... Elements 93-110 are man-made radioactive elements. Since these man-made atoms are so big, they can be created by combining two smaller atoms together. The protons and neutrons combine into one large nucleus. ...
File
... Promising instant curative and beautifying effects, Tho-Radia gained wide popularity in France during the early 1930's as a range of beauty products and perfumes. The face cream was especially popular and contained of 0.5g thorium chloride and 0.25mg radium bromide per 100g. It was even advertised a ...
... Promising instant curative and beautifying effects, Tho-Radia gained wide popularity in France during the early 1930's as a range of beauty products and perfumes. The face cream was especially popular and contained of 0.5g thorium chloride and 0.25mg radium bromide per 100g. It was even advertised a ...
Chemistry Test: Transmutation Multiple Choice 1. Identify the new
... Identify the new element when an alpha particle is emitted from Pu-244. a. Cm-240 b. Am-244 c. U-240 d. Np-244 Which of the following lists ranks nuclear radiation from most massive to least massive? a. alpha, beta, and gamma c. gamma, alpha, and beta b. beta, gamma, and alpha d. gamma, beta, and al ...
... Identify the new element when an alpha particle is emitted from Pu-244. a. Cm-240 b. Am-244 c. U-240 d. Np-244 Which of the following lists ranks nuclear radiation from most massive to least massive? a. alpha, beta, and gamma c. gamma, alpha, and beta b. beta, gamma, and alpha d. gamma, beta, and al ...
Nuclear Fission & Fusion
... •Stable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is ________ than repulsion force •Unstable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is less ________ than repulsion force ...
... •Stable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is ________ than repulsion force •Unstable Nuclei = strong nuclear force is less ________ than repulsion force ...
13.4 The nucleus 3 - Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
... together two nuclei to create a new nucleus. The new nucleus will be an isotope of a new, heavier element. Nuclear fusion produces even more energy than nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion is the process that fuels the stars, including the sun (see Module 11.2). A series of nuclear fusion reactions resu ...
... together two nuclei to create a new nucleus. The new nucleus will be an isotope of a new, heavier element. Nuclear fusion produces even more energy than nuclear fission. Nuclear fusion is the process that fuels the stars, including the sun (see Module 11.2). A series of nuclear fusion reactions resu ...
Nuclear Power Plant Notes
... photons (electromagnetic wave) • Gamma radiation is able to travel many meters in air and many centimeters in human tissue. It readily penetrates most materials and is sometimes called "penetrating radiation." ...
... photons (electromagnetic wave) • Gamma radiation is able to travel many meters in air and many centimeters in human tissue. It readily penetrates most materials and is sometimes called "penetrating radiation." ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY PACKET - Student
... A change in the nucleus of an atom that converts it from one element to another is called transmutation. This can occur naturally or can be induced by the bombardment of the nucleus by high-energy particles. (5.3a) Spontaneous decay can involve the release of alpha particles, beta particles, positro ...
... A change in the nucleus of an atom that converts it from one element to another is called transmutation. This can occur naturally or can be induced by the bombardment of the nucleus by high-energy particles. (5.3a) Spontaneous decay can involve the release of alpha particles, beta particles, positro ...
10 facts about NUCLEAR FISSION
... huge amount of energy, because mass has been converted into energy! ...
... huge amount of energy, because mass has been converted into energy! ...
The discovery of the natural radioactive decay of uranium in 1896 by
... different atomic weights owing to variations in the number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element with differing atomic weights are called isotopes. Radioactive decay is a spontaneous process in which an isotope (the parent) loses particles from its nucleus to form an isotope of a new element (the d ...
... different atomic weights owing to variations in the number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element with differing atomic weights are called isotopes. Radioactive decay is a spontaneous process in which an isotope (the parent) loses particles from its nucleus to form an isotope of a new element (the d ...
Nuclear Chemistry Test Topics
... Transmutation occurs when one element is changed to another by changing the number of protons (atomic number). Artificial transmutation occurs in particle accelerators. Becquerel discovered that uranium gives off radiation by exposing photographic plates to uranium salts. Marie and Pierre Curie disc ...
... Transmutation occurs when one element is changed to another by changing the number of protons (atomic number). Artificial transmutation occurs in particle accelerators. Becquerel discovered that uranium gives off radiation by exposing photographic plates to uranium salts. Marie and Pierre Curie disc ...
Nuclear Notes Introduction
... nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucleus. 5. band of stability- a stable nuclei cluster shown as a neutron to proton ratio a. most stable nuclei ar ...
... nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucleus. 5. band of stability- a stable nuclei cluster shown as a neutron to proton ratio a. most stable nuclei ar ...
Nuclear - chemmybear.com
... (b) Alpha particles have a greater mass than beta par(b) Identify the type of decay expected for carbon-14 ticles. Thus, their speed (penetrating potential) is and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are ...
... (b) Alpha particles have a greater mass than beta par(b) Identify the type of decay expected for carbon-14 ticles. Thus, their speed (penetrating potential) is and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are ...
Chapter 1 Learning Objective Summary
... 6. Learn to balance common nuclear reactions, know the common radioactive particles involved, and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that ...
... 6. Learn to balance common nuclear reactions, know the common radioactive particles involved, and understand fission and fusion Chemical reactions involve the gain, loss, or sharing of the outer electrons, whereas nuclear reactions involve changes to the composition of the nucleus. This means that ...