Isotope Notes
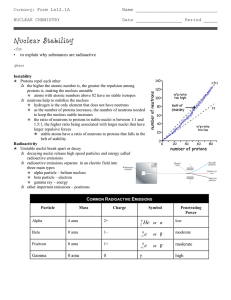
... b. In order for a nucleus to be _____________________, there must be enough neutrons present between the protons to block the repulsive forces between the protons. c. If an isotope of an element is _________________________, it is radioactive and will undergo nuclear decay. ...
... b. In order for a nucleus to be _____________________, there must be enough neutrons present between the protons to block the repulsive forces between the protons. c. If an isotope of an element is _________________________, it is radioactive and will undergo nuclear decay. ...
Nuclear Fission
... • The amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample of radioactive element to decay – Amount of time it takes for half of atom to decay • Vary from few seconds to billions of years ...
... • The amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample of radioactive element to decay – Amount of time it takes for half of atom to decay • Vary from few seconds to billions of years ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • N/P ratio of stable nuclei • Stable small atoms (atomic # less than 20) are near 1/1 ratio • Stable large atoms are near 1.5/1 ratio. • Predict the stability of the following: carbon-12 mercury-200 hydrogen-3 uranium-238 ...
... • N/P ratio of stable nuclei • Stable small atoms (atomic # less than 20) are near 1/1 ratio • Stable large atoms are near 1.5/1 ratio. • Predict the stability of the following: carbon-12 mercury-200 hydrogen-3 uranium-238 ...
Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
... more stable daughter nuclides plus large amounts of energy and two to three fast neutrons depending on the reaction. ...
... more stable daughter nuclides plus large amounts of energy and two to three fast neutrons depending on the reaction. ...
Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted
... A. Alpha Decay * Emission of alpha particle -- a : • Nucleus releases a particle that is 2 protons & 2 neutrons = Helium nucleus. (4 amu, 2+ charge) ...
... A. Alpha Decay * Emission of alpha particle -- a : • Nucleus releases a particle that is 2 protons & 2 neutrons = Helium nucleus. (4 amu, 2+ charge) ...
Radioactivity - Mrs. Sjuts` Science Site
... nuclei the number of half-‐lives since the rock was formed can be calculated ! U-‐235 " 0.7 billion years ...
... nuclei the number of half-‐lives since the rock was formed can be calculated ! U-‐235 " 0.7 billion years ...
Multiple Choice Questions
... 17. The amount of energy released from a nuclear reaction is much greater than a chemical reaction because (1) mass is converted into energy (2) energy is converted into mass (3) ionic bonds are broken (4) covalent bonds are broken 18. Which reaction releases the greatest amount of energy per mole o ...
... 17. The amount of energy released from a nuclear reaction is much greater than a chemical reaction because (1) mass is converted into energy (2) energy is converted into mass (3) ionic bonds are broken (4) covalent bonds are broken 18. Which reaction releases the greatest amount of energy per mole o ...
SMP Quiz Session 1
... You have two atoms, one has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons and the other has 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6 electrons. Which of the following best describes the difference between them? The ...
... You have two atoms, one has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons and the other has 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6 electrons. Which of the following best describes the difference between them? The ...
Nuclear Fission and Fusion
... the heart of long dead stars. Along with nearly every other element that we have on earth. ...
... the heart of long dead stars. Along with nearly every other element that we have on earth. ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 3. Nuclear Decay: Identify the properties of alpha particle, beta particle and gamma rays. Give the symbol, nature of the radiation, penetrating power, and ionizing power. Identify the decay products for each of the types of radiations. Predict the products formed when a Uranium nucleus undergoes al ...
... 3. Nuclear Decay: Identify the properties of alpha particle, beta particle and gamma rays. Give the symbol, nature of the radiation, penetrating power, and ionizing power. Identify the decay products for each of the types of radiations. Predict the products formed when a Uranium nucleus undergoes al ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 3. Nuclear Decay: Identify the properties of alpha particle, beta particle and gamma rays. Give the symbol, nature of the radiation, penetrating power, and ionizing power. Identify the decay products for each of the types of radiations. Predict the products formed when a Uranium nucleus undergoes al ...
... 3. Nuclear Decay: Identify the properties of alpha particle, beta particle and gamma rays. Give the symbol, nature of the radiation, penetrating power, and ionizing power. Identify the decay products for each of the types of radiations. Predict the products formed when a Uranium nucleus undergoes al ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Xavier High School
... one element to an atom of another element • Alpha particle – emitted helium nucleus • Beta particle – energetic electron from decomposed neutron ...
... one element to an atom of another element • Alpha particle – emitted helium nucleus • Beta particle – energetic electron from decomposed neutron ...
TERM 2 Unit 3 YR 9 SCI It is elementary
... according to currently accepted understandings. They will identify patterns in atomic structure that allow prediction of the products of chemical reactions and are reflected by the periodic table. They recognise that new substances are formed during a chemical reaction, and are able to list and desc ...
... according to currently accepted understandings. They will identify patterns in atomic structure that allow prediction of the products of chemical reactions and are reflected by the periodic table. They recognise that new substances are formed during a chemical reaction, and are able to list and desc ...
Fission and Fusion of Atomic Nuclei
... – Nucleus captures a neutron and splits into fragments and produces three neutrons – Products start a new reaction • Critical mass – The minimum mass required to support a self-sustaining chain reaction ...
... – Nucleus captures a neutron and splits into fragments and produces three neutrons – Products start a new reaction • Critical mass – The minimum mass required to support a self-sustaining chain reaction ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... In β− decay, the weak interaction converts a neutron into a proton while emitting an electron *the math must equal on both sides ...
... In β− decay, the weak interaction converts a neutron into a proton while emitting an electron *the math must equal on both sides ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma rays are produced when nuclear particles undergo transitions in energy levels; beta and gamma rays are usually emitted together 3. Gamma emission usually follows other types of decay that leave the nucleus i ...
... emitted from a nucleus as it changes from an excited state to a ground energy state 2. Gamma rays are produced when nuclear particles undergo transitions in energy levels; beta and gamma rays are usually emitted together 3. Gamma emission usually follows other types of decay that leave the nucleus i ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... Transmutation in Beta Radiation • During beta decay, the atom now has one more proton so it becomes the element with an atomic number one greater than that of the original element. • Since the neutron decays into a proton, the total number of protons and neutrons does not change during beta transmu ...
... Transmutation in Beta Radiation • During beta decay, the atom now has one more proton so it becomes the element with an atomic number one greater than that of the original element. • Since the neutron decays into a proton, the total number of protons and neutrons does not change during beta transmu ...
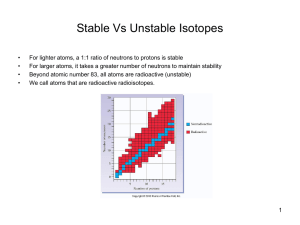
Stable Vs Unstable Isotopes
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
... For lighter atoms, a 1:1 ratio of neutrons to protons is stable For larger atoms, it takes a greater number of neutrons to maintain stability Beyond atomic number 83, all atoms are radioactive (unstable) We call atoms that are radioactive radioisotopes. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... • Nuclear reactions NOT Affected by: – Changes in temperature, pressure or the presence of catalyst – Unaffected by compounds in which the unstable isotopes are composed – Can not be slowed down, speed up or turned ...
... • Nuclear reactions NOT Affected by: – Changes in temperature, pressure or the presence of catalyst – Unaffected by compounds in which the unstable isotopes are composed – Can not be slowed down, speed up or turned ...
25.3 section summary
... that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons. In nuclear fusion, nuclei combine to make nuclei of greater mass. The sun’s energy is produced when hydrogen nuclei fuse to make helium nuclei. Fusion releases even more energy than fission. Fusion only occurs at very high temperature- in the excess ...
... that decreases the number of slow-moving neutrons. In nuclear fusion, nuclei combine to make nuclei of greater mass. The sun’s energy is produced when hydrogen nuclei fuse to make helium nuclei. Fusion releases even more energy than fission. Fusion only occurs at very high temperature- in the excess ...
Radioisotopes
... – One element can change into another element via radioactive decay or transmutation ...
... – One element can change into another element via radioactive decay or transmutation ...
Chapter 16 – Nuclear Energy
... radioactive, although a much larger volume of these are generated. • Mine wastes scattered around uranium mine, contaminated protective clothing from workers, also produced by hospitals and laboraties. ...
... radioactive, although a much larger volume of these are generated. • Mine wastes scattered around uranium mine, contaminated protective clothing from workers, also produced by hospitals and laboraties. ...