Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
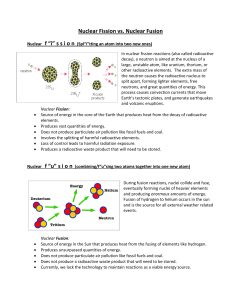
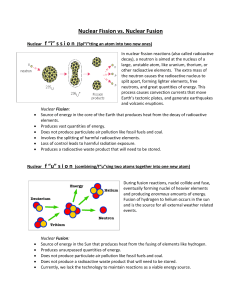
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
... parts, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. Most commonly this is done by "firing" a neutron at the nucleus of an atom. The energy of the neutron "bullet" causes the target element to split into two (or more) elements that are lighter than the parent atom. • During the fission of U235, ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... 1. A very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei of intermediate mass 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy a. Small amounts of missing mass are converted to HUGE amounts of energy (E = mc2) ...
... 1. A very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei of intermediate mass 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy a. Small amounts of missing mass are converted to HUGE amounts of energy (E = mc2) ...
Half-Life - Chemistry 1 at NSBHS
... Transmutation Reactions • The conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element is called transmutation. Transmutation can occur by radioactive decay. Transmutation can also occur when particles bombard the nucleus of an atom. ...
... Transmutation Reactions • The conversion of an atom of one element to an atom of another element is called transmutation. Transmutation can occur by radioactive decay. Transmutation can also occur when particles bombard the nucleus of an atom. ...
Review of Nuclear Chemistry
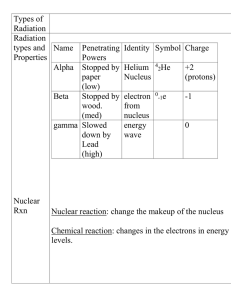
... You should know how penetrating and the relative speeds of the particles in Table 1. An alpha particle is the largest radiation particle; while a gamma particle is the fastest. A gamma particle is the most dangerous form of radiation outside the body, while an alpha particle is the most dangerous in ...
... You should know how penetrating and the relative speeds of the particles in Table 1. An alpha particle is the largest radiation particle; while a gamma particle is the fastest. A gamma particle is the most dangerous form of radiation outside the body, while an alpha particle is the most dangerous in ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
... In 1902, Frederick Soddy proposed the theory that "radioactivity is the result of a natural change of an isotope of one element into an isotope of a different element." Nuclear reactions involve changes in particles in an atom's nucleus and thus cause a change in the atom itself. All elements heavie ...
File
... deeper into material they hit. •Pass through paper and skin •Aluminum foil will stop a beta particle •Can damage human cells if released inside the body ...
... deeper into material they hit. •Pass through paper and skin •Aluminum foil will stop a beta particle •Can damage human cells if released inside the body ...
NUCLEAR CHANGES
... What happens when an element undergoes radioactive decay? • During radioactive decay an unstable nuclei of an isotope emits particles and releases energy, to become a stable isotope. ...
... What happens when an element undergoes radioactive decay? • During radioactive decay an unstable nuclei of an isotope emits particles and releases energy, to become a stable isotope. ...
nuclear powperpoint
... Nuclear Reactors cont. Nuclear Waste *Fuel rods from nuclear power plants are one source of nuclear waste. *Fuel rods contain some Uranium-235 or Plutonium-239 *takes a long time (more than a decade) for any remaining radioactive fuel to decay *the fuel rods must be stored in water cooling tanks or ...
... Nuclear Reactors cont. Nuclear Waste *Fuel rods from nuclear power plants are one source of nuclear waste. *Fuel rods contain some Uranium-235 or Plutonium-239 *takes a long time (more than a decade) for any remaining radioactive fuel to decay *the fuel rods must be stored in water cooling tanks or ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Ector County ISD.
... Traditional chemical reactions occur as a result of the interaction between valence electrons around an atom's nucleus . In 1896, Henri Becquerel expanded the field of chemistry to include nuclear changes when he discovered that uranium emitted radiation. Soon after Becquerel's discovery, Marie Sklo ...
... Traditional chemical reactions occur as a result of the interaction between valence electrons around an atom's nucleus . In 1896, Henri Becquerel expanded the field of chemistry to include nuclear changes when he discovered that uranium emitted radiation. Soon after Becquerel's discovery, Marie Sklo ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... The decay reaction and T½ of a substance are specific to the isotope of the element undergoing radioactive decay. For example, Bi210 can undergo decay to Tl206 with a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of ...
... The decay reaction and T½ of a substance are specific to the isotope of the element undergoing radioactive decay. For example, Bi210 can undergo decay to Tl206 with a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of ...
Types of Radiation
... The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions, but lower than the energy released by nuclear fusion. ...
... The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions, but lower than the energy released by nuclear fusion. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... – If you have a sample of 50 grams. How much of the sample will be remaining after 1 half life? • After 2 half lives? ...
... – If you have a sample of 50 grams. How much of the sample will be remaining after 1 half life? • After 2 half lives? ...
Stoichiometry Introduction
... Fusion Reactions • 2 small nuclei release energy when they are fused together to form a single, larger nucleus • The process releases energy ...
... Fusion Reactions • 2 small nuclei release energy when they are fused together to form a single, larger nucleus • The process releases energy ...
Radioactivity - Mrs. Sjuts` Science Site
... Protons and neutrons are held together less tightly in large nuclei. Why? Small nuclei have few protons, so the repulsive force on a proton due to other protons is small In a large nuclei, the attractive strong force is exerted only by the nearest neighbors. All the protons exert repulsive forces ma ...
... Protons and neutrons are held together less tightly in large nuclei. Why? Small nuclei have few protons, so the repulsive force on a proton due to other protons is small In a large nuclei, the attractive strong force is exerted only by the nearest neighbors. All the protons exert repulsive forces ma ...
Radioactive Decay Series
... Nuclear Chain Reaction A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. A critical mass is the minimum amount of nuclides that provide the number of neutrons needed to maintain a chain reaction ...
... Nuclear Chain Reaction A chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction. A critical mass is the minimum amount of nuclides that provide the number of neutrons needed to maintain a chain reaction ...
Chapter 19 Radioactive Material An Isotope is an element with a
... uranium atoms split. The hot water turns into steam which then spins a turbine that is hooked u to a generator. To prevent the uranium from creating to much heat that might melt the walls ...
... uranium atoms split. The hot water turns into steam which then spins a turbine that is hooked u to a generator. To prevent the uranium from creating to much heat that might melt the walls ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... protons!) Natural transmutation = the change of naturally radioactive elements by emission of a radioactive particle Isotopes of elements with atomic numbers less than 20 whose neutron: proton ratio is NOT 1:1 are likely to undergo spontaneous nuclear “decay” (i.e. loss of a radioactive particle) ...
... protons!) Natural transmutation = the change of naturally radioactive elements by emission of a radioactive particle Isotopes of elements with atomic numbers less than 20 whose neutron: proton ratio is NOT 1:1 are likely to undergo spontaneous nuclear “decay” (i.e. loss of a radioactive particle) ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... AE = Substance amount A0 = Initial substance amount t = time elapsed t1/2 = half-life ...
... AE = Substance amount A0 = Initial substance amount t = time elapsed t1/2 = half-life ...
SIMPLE NUCLEAR REACTIONS
... A neutron is fired at a large nucleus (usually uranium-235). It is absorbed briefly which makes the unstable isotope of uranium-236. This then splits into two or more smaller nuclei releasing neutrons and energy in the process. The products are radioactive. Ex. uranium-235 + neutron [uranium-236] ...
... A neutron is fired at a large nucleus (usually uranium-235). It is absorbed briefly which makes the unstable isotope of uranium-236. This then splits into two or more smaller nuclei releasing neutrons and energy in the process. The products are radioactive. Ex. uranium-235 + neutron [uranium-236] ...
Chapter 25
... isotopic symbols and apply the law of matter conservation. Let’s write the symbols for these particles. ...
... isotopic symbols and apply the law of matter conservation. Let’s write the symbols for these particles. ...
Nuclear Fission vs. Nuclear Fusion
... unable to perform these reactions on Earth. ________________ 11. The one with a “u” in it._________________ 12. The one with two “i’s” in it. ___________________ 13. The one that sounds like “fuse” ______________ 14. The one that almost rhymes with “split.” ______________ 15. Creates enough energy f ...
... unable to perform these reactions on Earth. ________________ 11. The one with a “u” in it._________________ 12. The one with two “i’s” in it. ___________________ 13. The one that sounds like “fuse” ______________ 14. The one that almost rhymes with “split.” ______________ 15. Creates enough energy f ...
Nuclear Fission vs Fusion
... unable to perform these reactions on Earth. ________________ 11. The one with a “u” in it._________________ 12. The one with two “i’s” in it. ___________________ 13. The one that sounds like “fuse” ______________ 14. The one that almost rhymes with “split.” ______________ 15. C ...
... unable to perform these reactions on Earth. ________________ 11. The one with a “u” in it._________________ 12. The one with two “i’s” in it. ___________________ 13. The one that sounds like “fuse” ______________ 14. The one that almost rhymes with “split.” ______________ 15. C ...
Chapter 25.2 Nuclear Transformations
... The neutron-to-proton ratio determines the type of decay that occurs If a nucleus has too many neutrons, a neutron can change into a proton and a high energy electron (beta particle) is shot out of the nucleus. ...
... The neutron-to-proton ratio determines the type of decay that occurs If a nucleus has too many neutrons, a neutron can change into a proton and a high energy electron (beta particle) is shot out of the nucleus. ...
Nuclear Energy
... Nuclear Fusion is the combining of 2 atomic nuclei to produce a single larger nucleus. Advantages: 1. It produces more energy per atom than nuclear fission. 2. It is readily available. 3. It is safer 4. Less polluting than nuclear fission. ...
... Nuclear Fusion is the combining of 2 atomic nuclei to produce a single larger nucleus. Advantages: 1. It produces more energy per atom than nuclear fission. 2. It is readily available. 3. It is safer 4. Less polluting than nuclear fission. ...
Nuclear Reactions
... Nuclear reactions The stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. Each radioactive isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay (half-life). A change in the nucleu ...
... Nuclear reactions The stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. Each radioactive isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay (half-life). A change in the nucleu ...