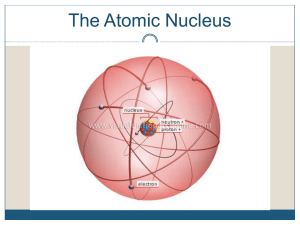
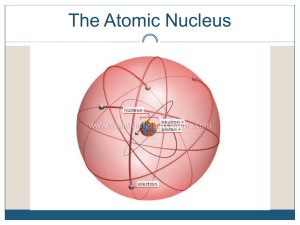
Nuclear Stability
... • All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable with respect to radio active decay. • Light nuclides are stable when neutron/proton = 1. For heavier elements the neutron /proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. • Nuclides with even numbers of protons and neutr ...
... • All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable with respect to radio active decay. • Light nuclides are stable when neutron/proton = 1. For heavier elements the neutron /proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. • Nuclides with even numbers of protons and neutr ...
Nuclear For Forensics
... Bombardment of the radioactive nuclide with a neutron starts the process. ...
... Bombardment of the radioactive nuclide with a neutron starts the process. ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... Some elements have isotopes, with different #s of neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
Objectives for Nuclear Chemistry
... mass. The calculated mass is derived from adding the masses of protons and neutrons that are present. The actual mass is less than this. The difference is due to the fact that the formation of a nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy. Objective 11 The energy released in the formation of an a ...
... mass. The calculated mass is derived from adding the masses of protons and neutrons that are present. The actual mass is less than this. The difference is due to the fact that the formation of a nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy. Objective 11 The energy released in the formation of an a ...
Radioactivity - Miami Beach Senior High School
... • A sample of radioactive C-14 has decayed to 12.5 % of its original amount. If the halflife of C-14 is 5730 years, how old is the sample? ...
... • A sample of radioactive C-14 has decayed to 12.5 % of its original amount. If the halflife of C-14 is 5730 years, how old is the sample? ...
The New Alchemy
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
printable version
... b. Beta emission occurs in isotopes that have too many neutrons ( more neutrons than protons in small atoms) like Cobalt – 60 ( 27 protons and 33 neutrons) c. Isotopes that have too few neutrons (like nitrogen-13) would attain stability by electron capture or positron emission ...
... b. Beta emission occurs in isotopes that have too many neutrons ( more neutrons than protons in small atoms) like Cobalt – 60 ( 27 protons and 33 neutrons) c. Isotopes that have too few neutrons (like nitrogen-13) would attain stability by electron capture or positron emission ...
File - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... Have atomic numbers above 92 undergo transmutation Do not occur in nature Have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators Are radioactive ...
... Have atomic numbers above 92 undergo transmutation Do not occur in nature Have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators Are radioactive ...
radioactive decay - Aurora City Schools
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
Nuclear Reactions Review
... Which of the following is a disadvantage of nuclear energy as a power source? a.Nuclear energy produces less energy than the burning of coal. b.Nuclear energy produces air pollution. c.Nuclear waste must be safely stored. d.The fuel source is very limited. ...
... Which of the following is a disadvantage of nuclear energy as a power source? a.Nuclear energy produces less energy than the burning of coal. b.Nuclear energy produces air pollution. c.Nuclear waste must be safely stored. d.The fuel source is very limited. ...
Nuclear Reactions Review powerpt
... Which of the following is a disadvantage of nuclear energy as a power source? a.Nuclear energy produces less energy than the burning of coal. b.Nuclear energy produces air pollution. c.Nuclear waste must be safely stored. d.The fuel source is very limited. ...
... Which of the following is a disadvantage of nuclear energy as a power source? a.Nuclear energy produces less energy than the burning of coal. b.Nuclear energy produces air pollution. c.Nuclear waste must be safely stored. d.The fuel source is very limited. ...
2005 Nuclear FRQs - AP Chemistry Olympics
... and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are observed during the radioactive too large and they emit beta particles (converting decay of carbon-11. Why is it unnecessary to inneutrons into protons) to low ...
... and write the balanced nuclear reaction for that less. decay process. (c) The neutron/proton ratio in Sr-90 and Cs-137 is (c) Gamma rays are observed during the radioactive too large and they emit beta particles (converting decay of carbon-11. Why is it unnecessary to inneutrons into protons) to low ...
Chapter 9: Nuclear Changes
... - ____________- the process by which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - _____ ________- process radioactive materials undergo - radioactive materials have an unstable nucleus - become stable by undergoing nuclear decay - results in a ...
... - ____________- the process by which an unstable nucleus emits one or more particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation - _____ ________- process radioactive materials undergo - radioactive materials have an unstable nucleus - become stable by undergoing nuclear decay - results in a ...
Nuclear Reactions
... • differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus • This gives them a different atomic mass. • The nucleus of an isotope with a certain atomic number and mass is called a nuclide. • Radiation energy is given off from unstable (large) nuclides. – Radioactive decay ...
... • differ in their number of neutrons in the nucleus • This gives them a different atomic mass. • The nucleus of an isotope with a certain atomic number and mass is called a nuclide. • Radiation energy is given off from unstable (large) nuclides. – Radioactive decay ...
radioactivity-ppt
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
Radioactivity
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
... Alpha particles may be completely stopped by a sheet of paper, beta particles by aluminum shielding. Gamma rays, however, can only be reduced by much more ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... breeder reactor (9.4) a nuclear reactor that produces its own fuel in the process of providing electrical energy. chain reaction (9.4) in a fission reactor, involves neutron production causing subsequent reactions accompanied by the production of more neutrons in a continuing process. curie (9.7) th ...
... breeder reactor (9.4) a nuclear reactor that produces its own fuel in the process of providing electrical energy. chain reaction (9.4) in a fission reactor, involves neutron production causing subsequent reactions accompanied by the production of more neutrons in a continuing process. curie (9.7) th ...
isotope - Aurora City Schools
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
... • An element with a different number of neutrons • Because has same number of protons, still that element and has all chem/phys properties • Write isotopes using atomic # & mass # ...
Types of Radiation
... good n/p ratio (high stability, low energy state). Form a new kind of atom. Each isotope or nuclide decays in a certain manner to get a better n/p ratio. The decay mode is named for the particle emitted. See Table N. ...
... good n/p ratio (high stability, low energy state). Form a new kind of atom. Each isotope or nuclide decays in a certain manner to get a better n/p ratio. The decay mode is named for the particle emitted. See Table N. ...
Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic
... 3. Potassium-42 has a half life of 12 hours. At present, a given ore sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclea ...
... 3. Potassium-42 has a half life of 12 hours. At present, a given ore sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclea ...
Summative Assessment Review!
... larger atom is called fusion • Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium ...
... larger atom is called fusion • Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium ...
I. Ch. 21.1 Nuclear Radiation
... What happens in a nuclear chain reaction? a) When the nuclei of certain isotopes are bombarded with neutrons, they undergo _________________, the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments. b) In a chain reaction, some of the neutrons produced react with other fissionable atoms, producing more ne ...
... What happens in a nuclear chain reaction? a) When the nuclei of certain isotopes are bombarded with neutrons, they undergo _________________, the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments. b) In a chain reaction, some of the neutrons produced react with other fissionable atoms, producing more ne ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • Helium nuclei – Contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons – Net charge of +2 – Has a mass of 4 amu ...
... • Helium nuclei – Contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons – Net charge of +2 – Has a mass of 4 amu ...
Nuclear Fission sim
... • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with quickly produces more neutrons which cause more and more atoms to fission, ...
... • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with quickly produces more neutrons which cause more and more atoms to fission, ...
Nuclear Energy
... • A chain reaction is an ongoing series of fission reactions. Billions of reactions occur each second in a chain reaction. ...
... • A chain reaction is an ongoing series of fission reactions. Billions of reactions occur each second in a chain reaction. ...