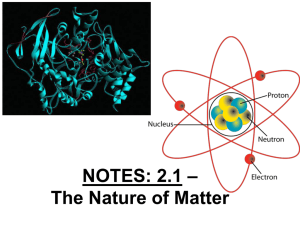
Notes
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
... -the number of protons in an atom of an element •all atoms of an element have the same atomic # •written as a subscript next to the element’s symbol •in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons (balanced charges). ...
chp. 7
... more neutrons that are produced per reaction the great the chances of creating a chain reaction ...
... more neutrons that are produced per reaction the great the chances of creating a chain reaction ...
Radioactive Decay
... of an atom. Transmutation: a change in the identity of a nucleus as a result of a change in the number of its protons. Nuclear Particles Type Symbol Charge ...
... of an atom. Transmutation: a change in the identity of a nucleus as a result of a change in the number of its protons. Nuclear Particles Type Symbol Charge ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 47. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. 48. The chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are ionic. 49. Large molecules (pol ...
... 47. Atoms combine to form molecules by sharing electrons to form covalent or metallic bonds or by exchanging electrons to form ionic bonds. 48. The chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are ionic. 49. Large molecules (pol ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... What is the charge on the whole atom of helium? neutral How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
... What is the charge on the whole atom of helium? neutral How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
Rhenium isotopes in geochronology Stable isotope Relative atomic
... radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an ato ...
... radioactive decay – the process by which unstable (or radioactive) isotopes lose energy by emitting alpha particles (helium nuclei), beta particles (positive or negative electrons), gamma radiation, neutrons or protons to reach a final stable energy state. radioisotope (radioactive isotope) – an ato ...
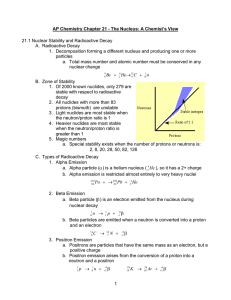
1 AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist`s View 21.1
... AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 21.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
... AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 21.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
Chapter 18 Notes
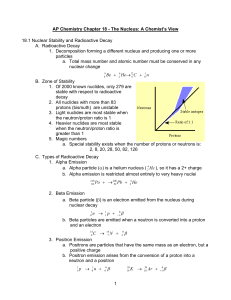
... AP Chemistry Chapter 18 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 18.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
... AP Chemistry Chapter 18 - The Nucleus: A Chemist’s View 18.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay A. Radioactive Decay 1. Decomposition forming a different nucleus and producing one or more particles a. Total mass number and atomic number must be conserved in any nuclear change ...
Chapter 2, section 4 Formation of Elements
... of the man-made isotopes are unstable. Unstable isotopes can become stable by releasing different types of particles. This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes/. ...
... of the man-made isotopes are unstable. Unstable isotopes can become stable by releasing different types of particles. This process is called radioactive decay and the elements which undergo this process are called radioisotopes/. ...
Nuclear Chemistry I: Radioactivity Reading: Moore chapter 20
... •The greater the binding energy per nucleon, the greater is the stability of the nucleus •The maximum stability is achieved in the iron nucleus: 2656Fe. •All elements heavier than iron may split, or fusion, to give more stable nuclei with atomic numbers nearer to iron, releasing energy. •Lighter nuc ...
... •The greater the binding energy per nucleon, the greater is the stability of the nucleus •The maximum stability is achieved in the iron nucleus: 2656Fe. •All elements heavier than iron may split, or fusion, to give more stable nuclei with atomic numbers nearer to iron, releasing energy. •Lighter nuc ...
TIMELINE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... 1913 Soddy and Richards discover the property of “atomic weight” and coin term “isotope” to describe atoms of the same element that have different mass. In addition, they discover that some elements have radioactive “isotopes”, atoms of an element with different masses. They recognized that the term ...
... 1913 Soddy and Richards discover the property of “atomic weight” and coin term “isotope” to describe atoms of the same element that have different mass. In addition, they discover that some elements have radioactive “isotopes”, atoms of an element with different masses. They recognized that the term ...
Week 1: Nuclear timeline (pdf, 233 KB)
... The reader must understand that this is not a total outline of the development of physics but what I deem is the line of discoveries that leads directly to the development of atomic energy. As an example I offer thermodynamics. For this, I could develop a separate trail with some similar names such ...
... The reader must understand that this is not a total outline of the development of physics but what I deem is the line of discoveries that leads directly to the development of atomic energy. As an example I offer thermodynamics. For this, I could develop a separate trail with some similar names such ...
nuclear radiation
... Rutherford was the first to identify and name two different types of radiation given off when an atom of one element underwent transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that ...
... Rutherford was the first to identify and name two different types of radiation given off when an atom of one element underwent transmutation and became an atom of another element. The two types of radiation he found were: •The alpha particle (a) •The beta particle (b) A third type of radiation that ...
Nuclear Chemistry 1997 D
... the “mass defect” where mass is converted into energy as shown in Einstein’s equation ...
... the “mass defect” where mass is converted into energy as shown in Einstein’s equation ...
Document
... – Radioactive decay = when nuclei break apart + release ___________ from the nucleus as __________________. Radioactive decay continues until a _________ element forms. An element may have only certain isotopes that are radioactive called ____________________ Uranium goes through many decay step ...
... – Radioactive decay = when nuclei break apart + release ___________ from the nucleus as __________________. Radioactive decay continues until a _________ element forms. An element may have only certain isotopes that are radioactive called ____________________ Uranium goes through many decay step ...
1. Nucleons Protons and neutrons 2. Nuclide A atom in
... type of radioactive decay called electron capture, an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom. • Gamma rays- high energy emr waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from ...
... type of radioactive decay called electron capture, an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus of its own atom. • Gamma rays- high energy emr waves emitted from a nucleus as it changes from ...
Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry
... Nuclear Power involves the conversion of mass to energy. Each time the atom spits, mass is converted into energy. Chain reaction- after each nucleus splits, 3 neutrons are released that will collide with 3 more nuclei and so on. The splitting grows exponentially. Atomic bombs are uncontrolled nuclea ...
... Nuclear Power involves the conversion of mass to energy. Each time the atom spits, mass is converted into energy. Chain reaction- after each nucleus splits, 3 neutrons are released that will collide with 3 more nuclei and so on. The splitting grows exponentially. Atomic bombs are uncontrolled nuclea ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
Chapter 7 Worksheet
... C Fission reactions involve a heavy unstable nucleus splitting apart to form 2 smaller nuclei, while fusion reactions involve combining two lightweight nuclei to form a heavier nucleus C Fission reactions often produce daughter products that are also radioactive, while fission reactions often do not ...
... C Fission reactions involve a heavy unstable nucleus splitting apart to form 2 smaller nuclei, while fusion reactions involve combining two lightweight nuclei to form a heavier nucleus C Fission reactions often produce daughter products that are also radioactive, while fission reactions often do not ...
UNIT 2 CLASSIFICATION
... … place IN which a fission NUCLEAR reaction TAKES place. It contains …in THE form of rods to produce the appropriate result. The reactor consists OF a fuel, a moderator and A cooling system. An instrument …neutron WHICH strikes the nucleus of an atom of U-235. The nucleus … which collide WITH other ...
... … place IN which a fission NUCLEAR reaction TAKES place. It contains …in THE form of rods to produce the appropriate result. The reactor consists OF a fuel, a moderator and A cooling system. An instrument …neutron WHICH strikes the nucleus of an atom of U-235. The nucleus … which collide WITH other ...
1 Intro to Nuclear Chemistry
... • Strontium-90 is found in nuclear fall-out. How long will it take for a mole of it (90.0g) to decay to a safe level of 0.150 g? ...
... • Strontium-90 is found in nuclear fall-out. How long will it take for a mole of it (90.0g) to decay to a safe level of 0.150 g? ...
Lithium 6.941 - mrkearsley.com
... Fusion is a nuclear reaction where two light atomic nuclei fuse or combine to form a single heavier nucleus. ...
... Fusion is a nuclear reaction where two light atomic nuclei fuse or combine to form a single heavier nucleus. ...
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... When applied to nuclear reactions, a process in which the splitting of atoms by neutrons releases more neutrons that, in turn, causes more atoms to split. ...
... When applied to nuclear reactions, a process in which the splitting of atoms by neutrons releases more neutrons that, in turn, causes more atoms to split. ...
Atom and Nucleus. Radioactivity. Nuclear Energy.
... A.Becquerel found that uranium (U) exposed photographic film. In other words, uranium emitted penetrating radiation. Marie and Pierre Curie soon discovered 2 more radioactive elements, which were called polonium and radium. Radioactivity is associated with the nucleus and is not affected by chemical ...
... A.Becquerel found that uranium (U) exposed photographic film. In other words, uranium emitted penetrating radiation. Marie and Pierre Curie soon discovered 2 more radioactive elements, which were called polonium and radium. Radioactivity is associated with the nucleus and is not affected by chemical ...
Nuclear Fission and Fusion Notes
... splits into two or more smaller fragments, releasing neutrons and energy. (The production of lighter nuclei from heavy nuclei) ...
... splits into two or more smaller fragments, releasing neutrons and energy. (The production of lighter nuclei from heavy nuclei) ...