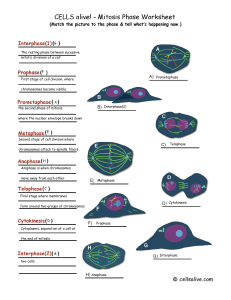
01 - wcusd15
... 9. Identifying Relationships Put the following in order of smallest to largest: chromosome, gene, and cell. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 10. Applying Concepts A pea plant has purple flowers. What allel ...
... 9. Identifying Relationships Put the following in order of smallest to largest: chromosome, gene, and cell. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 10. Applying Concepts A pea plant has purple flowers. What allel ...
Review Guide Cell Division CP
... a. Diploid – two sets of chromosomes (2n) –one set from each parent i. In somatic (body) cells b. Haploid – one set of chromosomes (n) i. In sex cells, gametes – egg and sperm B) Meiosis – for making gametes a. two cell divisions, reduces chromosome number by half b. Interphase - DNA replicates c. M ...
... a. Diploid – two sets of chromosomes (2n) –one set from each parent i. In somatic (body) cells b. Haploid – one set of chromosomes (n) i. In sex cells, gametes – egg and sperm B) Meiosis – for making gametes a. two cell divisions, reduces chromosome number by half b. Interphase - DNA replicates c. M ...
Cell Division Worksheet
... 2. Two gametes fuse to form a single diploid cell called a(n) ____________. 3. The process of gametes fusing to form a new cell is called _____________. Meiosis 1. What is synapsis? 2. Describe crossing over. 3. In what stage of meiosis does crossing over occur? ...
... 2. Two gametes fuse to form a single diploid cell called a(n) ____________. 3. The process of gametes fusing to form a new cell is called _____________. Meiosis 1. What is synapsis? 2. Describe crossing over. 3. In what stage of meiosis does crossing over occur? ...
Concept Check 9 - Plain Local Schools
... 2. Describe two ways in which asexual and sexual reproduction differ. 3. How is cell division involved in growth? Concept Check 9.2 1. Describe how the appearance of chromosomes changes as a cell is about to divide. 2. Interphase used to be described as a resting phase. Why is this description inacc ...
... 2. Describe two ways in which asexual and sexual reproduction differ. 3. How is cell division involved in growth? Concept Check 9.2 1. Describe how the appearance of chromosomes changes as a cell is about to divide. 2. Interphase used to be described as a resting phase. Why is this description inacc ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_6820\.aptcache
... inherit one from each parent, carry the same genes although the genes may code for different alleles, separate in meiosis I ...
... inherit one from each parent, carry the same genes although the genes may code for different alleles, separate in meiosis I ...
Study Guide Questions Genetics for blog
... Meiosis results in how many daughter cells? Are the daughter cells in meiosis genetically alike? Explain. What is crossing over and when does it occur? Identify the stages in meiosis when the cells are 2N. (diploid) Identify the stages in meiosis when the cells are 1N. (haploid) At which stage are t ...
... Meiosis results in how many daughter cells? Are the daughter cells in meiosis genetically alike? Explain. What is crossing over and when does it occur? Identify the stages in meiosis when the cells are 2N. (diploid) Identify the stages in meiosis when the cells are 1N. (haploid) At which stage are t ...
Biol 211 (2) Chapter 13 KEY
... division of meiosis, in which synapsis and crossing over occur and homologous chromosomes are separated from each other, producing daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell ...
... division of meiosis, in which synapsis and crossing over occur and homologous chromosomes are separated from each other, producing daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell ...
Intro to Meiosis - Solon City Schools
... Each pair is similar, but not exactly alike…we call them ...
... Each pair is similar, but not exactly alike…we call them ...
Unit 4 – Cellular Reproduction Meiosis Notes Name: Number
... In meiosis, each of the four cells contains _______ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. In mitosis, each new cell contains the _______ number of chromosomes as the original cell. In mitosis, the homologous pairs do not come together to form ___________. In meiosis, the homologous pairs ...
... In meiosis, each of the four cells contains _______ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. In mitosis, each new cell contains the _______ number of chromosomes as the original cell. In mitosis, the homologous pairs do not come together to form ___________. In meiosis, the homologous pairs ...
11.4 Meiosis 323-329 Chromosome Number
... 7. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. 8. If an organism’s haploid number is 6, its diploid number is 3. ...
... 7. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. 8. If an organism’s haploid number is 6, its diploid number is 3. ...
HL#1 Meiosis - hutchhighIBbiology
... of two chromatids. • Because of crossing-over the two chromatids are not identical • At the end of anaphase I the chromosomes reach the poles. ...
... of two chromatids. • Because of crossing-over the two chromatids are not identical • At the end of anaphase I the chromosomes reach the poles. ...
GENES AND CHROMOSOMES
... A. alleles carried on homologs (sketch these) 1. homologs segregate during meiosis 2. gametes carry one allele or the other, but not both B. when two pairs of alternate alleles carried on two pairs of homologs 1. homologs separate during meiosis I 2. chromatids separate during meiosis II 3. alleles ...
... A. alleles carried on homologs (sketch these) 1. homologs segregate during meiosis 2. gametes carry one allele or the other, but not both B. when two pairs of alternate alleles carried on two pairs of homologs 1. homologs separate during meiosis I 2. chromatids separate during meiosis II 3. alleles ...
For example eye color (One gene from each parent).
... Cell division resulting in the number of chromosomes in a cell being divided in half, through the separation of homologous chromosomes. Diploid cells divide to produce haploid cells. ...
... Cell division resulting in the number of chromosomes in a cell being divided in half, through the separation of homologous chromosomes. Diploid cells divide to produce haploid cells. ...
CHAPTER 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES The Basis of
... 6. Explain why fertilization and meiosis must alternate in all sexual life cycles. 7. List the phases of meiosis I and meiosis II and describe the events characteristic of each phase. 8. Recognize the phases of meiosis from diagrams or micrographs. Be able to draw them. 9. Describe the process of sy ...
... 6. Explain why fertilization and meiosis must alternate in all sexual life cycles. 7. List the phases of meiosis I and meiosis II and describe the events characteristic of each phase. 8. Recognize the phases of meiosis from diagrams or micrographs. Be able to draw them. 9. Describe the process of sy ...
The “M” phase of the cell cycle. Is it Mitosis or Meiosis?
... cones, and body parts related to sexual reproduction. ...
... cones, and body parts related to sexual reproduction. ...
Meiosis
... Diploid – 2 sets of chromosomes (2N) Haploid – 1 set of chromosomes (N) Homologous – chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex parent Tetrad – 4 chromatids in a homologous pair Synapsis – the pairing of 2 homologous chromosomes (during prophase I) Gametes – sex cell ...
... Diploid – 2 sets of chromosomes (2N) Haploid – 1 set of chromosomes (N) Homologous – chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosome from the opposite sex parent Tetrad – 4 chromatids in a homologous pair Synapsis – the pairing of 2 homologous chromosomes (during prophase I) Gametes – sex cell ...
11-13-12 Meiosis FILL IN THE BLANK NOTES
... that are involved in _________________________________________________________________. ___________________- two cylindrical cellular structures that form at the poles of a cell during meiosis. ...
... that are involved in _________________________________________________________________. ___________________- two cylindrical cellular structures that form at the poles of a cell during meiosis. ...
Cell cycle reading guide
... ______________________ The sperm and egg are collectively called this. ______________________ The cells that are not gametes are called this. ______________________ This is one point on a chromosome indicating the location of a gene. ______________________ A cell that has only one copy of each chrom ...
... ______________________ The sperm and egg are collectively called this. ______________________ The cells that are not gametes are called this. ______________________ This is one point on a chromosome indicating the location of a gene. ______________________ A cell that has only one copy of each chrom ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.