Unit 6 - Cell Cycle fact sheet.pub
... Cleavage furrow - in Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I animal cell where cell pinches during cytokenesis. Cell Plate - in plant cells where the cell wall starts to form to form during Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Cytokenesis cytokenesis. ...
... Cleavage furrow - in Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I animal cell where cell pinches during cytokenesis. Cell Plate - in plant cells where the cell wall starts to form to form during Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Cytokenesis cytokenesis. ...
Meiosis Reading - Mr-Paullers-wiki
... Genetic diversity plays an important role in the survival and adaptability of a species. When a population's habitat changes (climate, food availability, new pathogens that cause disease, new competition for ...
... Genetic diversity plays an important role in the survival and adaptability of a species. When a population's habitat changes (climate, food availability, new pathogens that cause disease, new competition for ...
Meiosis - Grant County Schools
... arranged in the same order Because there are different possible alleles for the same gene, the two chromosomes in the homologous pairs are not always identical to each other. ...
... arranged in the same order Because there are different possible alleles for the same gene, the two chromosomes in the homologous pairs are not always identical to each other. ...
Reproduction Unit Test Review
... 21. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for humans? _______ The haploid number? ______ 22. How can you tell the difference between a male and a female by looking at a karyotype? 23. Meiosis produces ____ cells each with ______ number of chromosomes as the original. 24. During Meiosis I, ______ ...
... 21. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for humans? _______ The haploid number? ______ 22. How can you tell the difference between a male and a female by looking at a karyotype? 23. Meiosis produces ____ cells each with ______ number of chromosomes as the original. 24. During Meiosis I, ______ ...
Reproduction
... chromosomes line up in metaphase. This is when genetic recombination can occur… so not all offspring from the same pair will be identical! Very important for variation within a population and for the rise of new species. -Results in 2 hapliod cells – Meiosis II –DNA in NOT replicated in the two hapl ...
... chromosomes line up in metaphase. This is when genetic recombination can occur… so not all offspring from the same pair will be identical! Very important for variation within a population and for the rise of new species. -Results in 2 hapliod cells – Meiosis II –DNA in NOT replicated in the two hapl ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • The recombination frequency between two genes on one chromosome is mathematically related to the distance between them • The further apart 2 genes are the higher the probability of a crossing over event ...
... • The recombination frequency between two genes on one chromosome is mathematically related to the distance between them • The further apart 2 genes are the higher the probability of a crossing over event ...
Full Lecture 2 pdf - Institute for Behavioral Genetics
... - genes coded by their DNA are known as sex-linked humans XX = female XY = male ...
... - genes coded by their DNA are known as sex-linked humans XX = female XY = male ...
Sexual Preproduction and Meiosis
... – This is when genetic recombination can occur… so not all offspring from the same pair will be identical! Very important for variation within a population and for the rise of new species. – Results in 2 haploid cells ...
... – This is when genetic recombination can occur… so not all offspring from the same pair will be identical! Very important for variation within a population and for the rise of new species. – Results in 2 haploid cells ...
Biology 9 - Unit 4b Meiosis Practice Name: 1. (a) Draw a
... Outline the differences, in a table, between the behaviour of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis. ...
... Outline the differences, in a table, between the behaviour of the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis. ...
Chapter 3/Lesson 1 Part 2 Notes
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
Biology Study Guide/Test Review CH 11
... Gametes have _______________ allele for each gene. Define CROSSING OVER and be sure you understand the diagram of crossing over! Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of __________________ genetically _____________ cells. Gametes are produced by the process of ___________________. An orga ...
... Gametes have _______________ allele for each gene. Define CROSSING OVER and be sure you understand the diagram of crossing over! Unlike mitosis, meiosis results in the formation of __________________ genetically _____________ cells. Gametes are produced by the process of ___________________. An orga ...
Mitosis *. Part II
... prometaphase. Proteins attach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores. Microtubules attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. ...
... prometaphase. Proteins attach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores. Microtubules attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. ...
Meisosis ppt
... • Cells that have ½ the normal number of chromosomes are called “Haploid” • Meiosis results in 4 Haploid cells that are genetically different from each other (and remember the parent cell was diploid) ...
... • Cells that have ½ the normal number of chromosomes are called “Haploid” • Meiosis results in 4 Haploid cells that are genetically different from each other (and remember the parent cell was diploid) ...
100 Interphase Mitosis Meiosis Essential Cell structures
... The phase of mitosis that is characterized by the arrangement of all chromosomes along the center of the cell is called… ...
... The phase of mitosis that is characterized by the arrangement of all chromosomes along the center of the cell is called… ...
Review - Peoria Public Schools
... metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. 9. Crossing over, exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, may occur during prophase I resulting in genetic variation. 10. Meiosis actually involves two reduct ...
... metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. 9. Crossing over, exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, may occur during prophase I resulting in genetic variation. 10. Meiosis actually involves two reduct ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
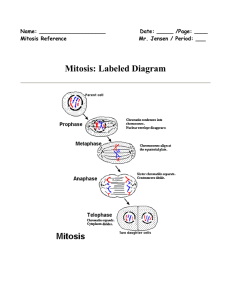
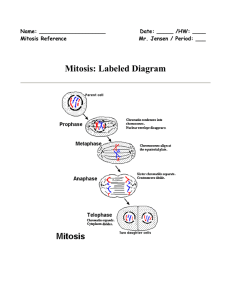
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
Cell Reproduction Study Guide
... 6. Describe the events in the following parts of Interphase: a. G1 ...
... 6. Describe the events in the following parts of Interphase: a. G1 ...
DNA Repilication and Transmission
... Cancer occurs when the genes involved in producing proteins involved in transduction become corrupted. ...
... Cancer occurs when the genes involved in producing proteins involved in transduction become corrupted. ...
Meiosis Notes - Brookwood High School
... Prophase I – during this phase, chromosomes in tetrads may exchange portions of their chromatids in process = crossing over (gives new gene combinations ...
... Prophase I – during this phase, chromosomes in tetrads may exchange portions of their chromatids in process = crossing over (gives new gene combinations ...
Cell Cycle Study Guide
... 1. Be able to identify and describe the five stages of the cell cycle if given pictures (these are not in any order). ...
... 1. Be able to identify and describe the five stages of the cell cycle if given pictures (these are not in any order). ...
Name Date
... Crossing over contributes to genetic variation when it exchanges chromosomal regions between a. sister chromatids of a chromosome c. non-sister chromatids of homologues b. chromatids of non-homologues d. autosomes and sex chromosomes ...
... Crossing over contributes to genetic variation when it exchanges chromosomal regions between a. sister chromatids of a chromosome c. non-sister chromatids of homologues b. chromatids of non-homologues d. autosomes and sex chromosomes ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.