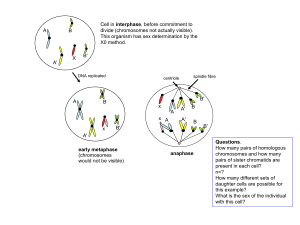
The Stages of Meiosis
... diversity by randomly dividing a cell’s genes in two. It results in two haploid cells. ...
... diversity by randomly dividing a cell’s genes in two. It results in two haploid cells. ...
Unit 5 review
... 2. The longest phase of the cell cycle is _____________________. 3. In G1, they cell __________________. 4. The DNA is copied during ___________________. 5. The last stage of interphase is _______. 6. The goal of mitosis is to get cells that are genetically ______________. The chromosome number goes ...
... 2. The longest phase of the cell cycle is _____________________. 3. In G1, they cell __________________. 4. The DNA is copied during ___________________. 5. The last stage of interphase is _______. 6. The goal of mitosis is to get cells that are genetically ______________. The chromosome number goes ...
Cell Division Review Quiz
... e. True / False: Homologous chromosomes line up side by side during metaphase. (Careful, this one’s tricky…) f. True / False: Sister chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 3. Meiosis a. Meiosis produces ____ (number) cells that are: identical / unique (circle one) b. The cells produced the end ...
... e. True / False: Homologous chromosomes line up side by side during metaphase. (Careful, this one’s tricky…) f. True / False: Sister chromatids are pulled apart during anaphase. 3. Meiosis a. Meiosis produces ____ (number) cells that are: identical / unique (circle one) b. The cells produced the end ...
homologous pairs
... 2. Egg and sperm combine to make a _______________ 3. Egg and sperm are both known as _______________ 4. A cell that only has half of a set of chromosomes is said to be _______________. 5. Genes are located on ___________________ ...
... 2. Egg and sperm combine to make a _______________ 3. Egg and sperm are both known as _______________ 4. A cell that only has half of a set of chromosomes is said to be _______________. 5. Genes are located on ___________________ ...
Chapter 8
... Directions: Write questions and answer on a separate sheet of paper. Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs. a) histone, nonhistone b) chromatid, centromere c) sex chromosome, autosome d) diploid cell, haploid cell ...
... Directions: Write questions and answer on a separate sheet of paper. Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs. a) histone, nonhistone b) chromatid, centromere c) sex chromosome, autosome d) diploid cell, haploid cell ...
II. Process of Meiosis (6.2) A. Cells go through in meiosis 1. Meiosis
... 2. _______________________ - two __________________ - one from mother, one from father. a. very similar to each other- _______________________ ___________ b. Each half of duplicated chromosome is called a __________________. (together called sister chromatids) 1). _______________________ ___________ ...
... 2. _______________________ - two __________________ - one from mother, one from father. a. very similar to each other- _______________________ ___________ b. Each half of duplicated chromosome is called a __________________. (together called sister chromatids) 1). _______________________ ___________ ...
Chapter 10
... crosses between different genotypes. Gametes – produced by each parent and shown along the sides of the punnett square Heredity – passing on of traits from parents to offspring Law of independent assortment – inheritance of alleles do not affect different traits as long as the genes for the tr ...
... crosses between different genotypes. Gametes – produced by each parent and shown along the sides of the punnett square Heredity – passing on of traits from parents to offspring Law of independent assortment – inheritance of alleles do not affect different traits as long as the genes for the tr ...
Name
... 8. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. 9. If an organism’s haploid number is 6, its diploid number is 3. ...
... 8. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. 9. If an organism’s haploid number is 6, its diploid number is 3. ...
Meiosis Homework Questions
... ● The differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. ● The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. ● The importance of homologous chromosomes in meiosis. ● How the chromosome number is reduced from diploid to haploid through the stages of meiosis. ● Three important ...
... ● The differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. ● The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. ● The importance of homologous chromosomes in meiosis. ● How the chromosome number is reduced from diploid to haploid through the stages of meiosis. ● Three important ...
Class Presentation Questions for CH 11
... 7. The Diploid (2N) number for the fruit fly=_________; The Haploid (N) number for the fruit fly= _________________. 8. Meiosis usually involves two distinct divisions called ____________________ & ___________________-. 9. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol_________. ...
... 7. The Diploid (2N) number for the fruit fly=_________; The Haploid (N) number for the fruit fly= _________________. 8. Meiosis usually involves two distinct divisions called ____________________ & ___________________-. 9. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the symbol_________. ...
The process of meiosis - Deans Community High School
... gamete as a result of crossing over at chiasmata resulting in new combinations of alleles for genes on the same chromosome. This can give 4 genetically different chromatids each of which ends up in a different gamete. Also, during the first meiotic division, the homologous pairs of chromosomes line ...
... gamete as a result of crossing over at chiasmata resulting in new combinations of alleles for genes on the same chromosome. This can give 4 genetically different chromatids each of which ends up in a different gamete. Also, during the first meiotic division, the homologous pairs of chromosomes line ...
Notes
... a. Cell contains ½ of somatic (body) cell chromosomes b. 23 chromosomes c. Haploid = n =23 Phases of Meiosis – meiosis takes place in…. A. 2 stages called Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 B. Meiosis 1 – diploid = 46 and copies to 23 C. Meiosis 2 - 23 and copies to Haploid 23 D. Crossing over occurs during me ...
... a. Cell contains ½ of somatic (body) cell chromosomes b. 23 chromosomes c. Haploid = n =23 Phases of Meiosis – meiosis takes place in…. A. 2 stages called Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 B. Meiosis 1 – diploid = 46 and copies to 23 C. Meiosis 2 - 23 and copies to Haploid 23 D. Crossing over occurs during me ...
Meiosis II
... egg) • Gametes have half the number of chromosomes • Occurs in the gonads (testes or ovaries) – Male: spermatogenesis – Female: oogenesis ...
... egg) • Gametes have half the number of chromosomes • Occurs in the gonads (testes or ovaries) – Male: spermatogenesis – Female: oogenesis ...
Add Meiosis Vocabulary to notes
... that contain double the amount of chromosomes than haploid cells Usually called the “normal” number of chromosomes Two copies of each gene ...
... that contain double the amount of chromosomes than haploid cells Usually called the “normal” number of chromosomes Two copies of each gene ...
Inheritence of Genes - New Century Academy
... 1. Precise replication of DNA 2. Meiosis to maintain a chromosomal number specific to a species ...
... 1. Precise replication of DNA 2. Meiosis to maintain a chromosomal number specific to a species ...
Reading Guide for Chapter 10
... 4. What is the human female gamete? ______________ Is it haploid or diploid? ______________ 5. What is the human male gamete? ________________ Is it haploid or diploid? _______________ 6. Why does meiosis have to occur? _______________________________________________________ 7. Why is it called sexu ...
... 4. What is the human female gamete? ______________ Is it haploid or diploid? ______________ 5. What is the human male gamete? ________________ Is it haploid or diploid? _______________ 6. Why does meiosis have to occur? _______________________________________________________ 7. Why is it called sexu ...
Genetic Diversity and Differentiation
... Crossing Over • Parts of homologous chromatids cross over in Prophase I – Pieces (genes) break off & switch places ...
... Crossing Over • Parts of homologous chromatids cross over in Prophase I – Pieces (genes) break off & switch places ...
GAMETE FORMATION IN ANIMALS
... 1. A diploid cell called a spermatogonium reproduces by mitosis. 2. At puberty each spermatogonium undergoes meiosis to form 4 haploid cells. 3. Following Meiosis II, each cell develops into a mature sperm. Head nucleus and molecules required by cell Midsection holds many mitochondria (Energy so ...
... 1. A diploid cell called a spermatogonium reproduces by mitosis. 2. At puberty each spermatogonium undergoes meiosis to form 4 haploid cells. 3. Following Meiosis II, each cell develops into a mature sperm. Head nucleus and molecules required by cell Midsection holds many mitochondria (Energy so ...
a. What kind of cell – diploid or haploid – are the body
... c. How many chromosomes do the sex cells of the insect contain? 20 Are these cells haploid or diploid? Haploid d. Through what process are the sex cells produced? Meiosis e. How many chromosomes are in the zygote that was formed when the insect reproduced? 40 Is the zygote haploid or diploid? Diploi ...
... c. How many chromosomes do the sex cells of the insect contain? 20 Are these cells haploid or diploid? Haploid d. Through what process are the sex cells produced? Meiosis e. How many chromosomes are in the zygote that was formed when the insect reproduced? 40 Is the zygote haploid or diploid? Diploi ...
Biology - edl.io
... 7. What are the six stages of cell division in order? (Mitosis includes four of the six stages) ...
... 7. What are the six stages of cell division in order? (Mitosis includes four of the six stages) ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.























