* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Meiosis - Solon City Schools
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
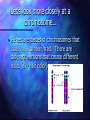
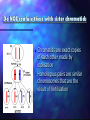
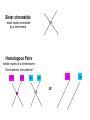
Intro to Meiosis • Chromatin • Unwound, stringy • In interphase • Chromatids • ½ of a replicated chromosome • In Prophase, Metaphase • Chromosome • After the sisters split in Anaphase, they are separate chromosomes (until they unwind into chromatin again) Let’s look more closely at a chromosome… • Genes are pieces of chromosomes that code for a protein/trait. There are different versions that create different traits (ex- hair color) Homologues • You have 23 pairs of chromosomes. In each pair you received one from your mom and one from your dad. Each pair is similar, but not exactly alike…we call them •HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS Note that the chromosomes have the gene in the same place, but different versions of it. (one may be for brown hair, one for blonde) Homologous Chromosomes • They are similar in size, shape, and the genetic traits that they carry Do NOT confuse these with sister chromatids • Chromatids are exact copies of each other made by replication • Homologous pairs are similar chromosomes that are the result of fertilization Sister chromatids -exact copies connected by a centromere Homologous Pairs similar copies of a chromosome One maternal, one paternal 1m 1m 1p 1m 1p or 1p Boy Karyotype- displays homologous pairs Replicated chromosomes after “S” phase of interphase Haploid vs. Diploid • DIPLOID CELLS: have two versions of each chromosome (one from mom AND one from dad) • • • • • Has the homologous pairs Somatic cells (body cells) Made by mitosis or fertilization “2n” In this picture, what is “n”? • n=2 Diploid vs. Haploid • Haploid cells: Have only ONE copy of each chromosome. • NO HOMOLOGOUS PAIRS present • Gametes (sex cells: egg and sperm) • Made by MEIOSIS • “1n” Mitosis- divides somatic cells to get tissues and organs built; makes individual grow into an adult