Notes: Meiosis
... E.Q.: What is the purpose of Meiosis? What are the sources of variation in a population? Definition: A type of cell division that only certain cells in the gonads of multicellular organism undergo to produce gametes (sex cells) In the process of Meiosis, PMAT happens twice - 1st = reduce the amo ...
... E.Q.: What is the purpose of Meiosis? What are the sources of variation in a population? Definition: A type of cell division that only certain cells in the gonads of multicellular organism undergo to produce gametes (sex cells) In the process of Meiosis, PMAT happens twice - 1st = reduce the amo ...
Meiosis Guided Reading Unit 6.3 (Chapter 11.4)
... Describe two similarities between mitosis and meiosis. c) _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ d) _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Mitosis can be a form of __ ...
... Describe two similarities between mitosis and meiosis. c) _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ d) _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Mitosis can be a form of __ ...
Ch 8 HW - TeacherWeb
... 2. Vocabulary- on a separate sheet of paper number terms and write definitions. When there is 2 words (vs.) be sure to distinguish differences between them. Indent on the line below and write an example or sentence or draw a picture. 1. binary fission 2. chromosomes 3. asexual reproduction 4. sexual ...
... 2. Vocabulary- on a separate sheet of paper number terms and write definitions. When there is 2 words (vs.) be sure to distinguish differences between them. Indent on the line below and write an example or sentence or draw a picture. 1. binary fission 2. chromosomes 3. asexual reproduction 4. sexual ...
3/10/15- Phases of Meiosis WS
... The fibers pull the homologous chromosomes toward opposite ends of the cell Nuclear membranes form, the cell separates into two cells ...
... The fibers pull the homologous chromosomes toward opposite ends of the cell Nuclear membranes form, the cell separates into two cells ...
Study Guide for Mitosis and Meiosis Name:
... How is the growth of cancer cells different from that of non-cancerous cells? ...
... How is the growth of cancer cells different from that of non-cancerous cells? ...
Meiosis
... • G1 – cell growth • S – replication of chromosoms • G2 – growth and preparation for cell division ...
... • G1 – cell growth • S – replication of chromosoms • G2 – growth and preparation for cell division ...
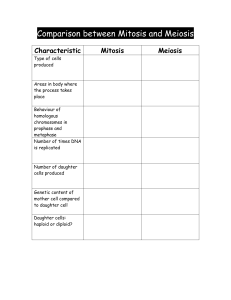
Biology 12: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
... Biology 12: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Name : __________________________ Instructions: Compare the two processes of mitosis and meiosis by completing the table below. Read each characteristic and make short jot notes discussing any important differences, similarities or events occurring in each p ...
... Biology 12: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Name : __________________________ Instructions: Compare the two processes of mitosis and meiosis by completing the table below. Read each characteristic and make short jot notes discussing any important differences, similarities or events occurring in each p ...
MEIOSIS
... G and S phases help enlarge the cell and replicate the genetic material Prepares the cell for nuclear division ...
... G and S phases help enlarge the cell and replicate the genetic material Prepares the cell for nuclear division ...
Practice Quiz Answers
... 2. In what phase of meiosis are sister chromatids separated? Anaphase II Mitosis? Anaphase 3. Other DNA-containing organelles besides the nucleus (such as mitochondria) replicate their DNA through what process? Binary fission 4. What is metastasis? When cells detach from neighboring cells and spread ...
... 2. In what phase of meiosis are sister chromatids separated? Anaphase II Mitosis? Anaphase 3. Other DNA-containing organelles besides the nucleus (such as mitochondria) replicate their DNA through what process? Binary fission 4. What is metastasis? When cells detach from neighboring cells and spread ...
Ch 9 The Cellular Basis of Life
... asexual reproduction (clones of one parent) Meiosis: sexual reproduction (two parents) Video clip (3 minute overview of mitosis/cancer) ...
... asexual reproduction (clones of one parent) Meiosis: sexual reproduction (two parents) Video clip (3 minute overview of mitosis/cancer) ...
LAB 10-A - BrainMass
... 2- Which cell division process (meiosis I, Meiosis II, mitosis, or some combination) corresponds to the following statements? a. b. c. d. ...
... 2- Which cell division process (meiosis I, Meiosis II, mitosis, or some combination) corresponds to the following statements? a. b. c. d. ...
3 Genetics - Kerboodle
... amniotic fluid using a needle and syringe. Chorionic villus sampling technique for diagnosing genetic defects while a foetus is in the uterus. A small sample of the placenta is removed and analysed. Crossing over exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during meiosis I. Diploid a ...
... amniotic fluid using a needle and syringe. Chorionic villus sampling technique for diagnosing genetic defects while a foetus is in the uterus. A small sample of the placenta is removed and analysed. Crossing over exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during meiosis I. Diploid a ...
11-4 Meiosis - The Biology Corner
... 1. Genes are located on _________________________________ in the cell nucleus. 2. Mendel’s principles require two things: Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from its _______________________ When an organism produces its own ____________________________, those sets must be separat ...
... 1. Genes are located on _________________________________ in the cell nucleus. 2. Mendel’s principles require two things: Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from its _______________________ When an organism produces its own ____________________________, those sets must be separat ...
Meiosis
... •Meiosis is the type of cell division by which sex cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. •Meiosis involves a reduction in the amount of genetic material. •A.K.A. reduction division To maintain normal chromosome number once fertilization occurs ...
... •Meiosis is the type of cell division by which sex cells (eggs and sperm) are produced. •Meiosis involves a reduction in the amount of genetic material. •A.K.A. reduction division To maintain normal chromosome number once fertilization occurs ...
Biology H/Pre-IB
... 5. What is cytokinesis? How does cytokinesis differ in animal and plant cells? 6. What is the function of a metaphase plate? 7. What is the function of centrioles? 8. During which phase does nuclear membrane break down and nucleus disappear? Why does that happen? 9. What is the purpose of meiosis? 1 ...
... 5. What is cytokinesis? How does cytokinesis differ in animal and plant cells? 6. What is the function of a metaphase plate? 7. What is the function of centrioles? 8. During which phase does nuclear membrane break down and nucleus disappear? Why does that happen? 9. What is the purpose of meiosis? 1 ...
Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome
... Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome number by half sex cell division gametes = sperm & egg (ovum) (plural = ova) results in 4 haploid cells sperm (23) + egg (23) zygote (46) = fertilized egg you have exactly ½ of your Dad’s chromosomes and ½ of your Mom’s puberty = stage ...
... Meiosis = nuclear division that reduces chromosome number by half sex cell division gametes = sperm & egg (ovum) (plural = ova) results in 4 haploid cells sperm (23) + egg (23) zygote (46) = fertilized egg you have exactly ½ of your Dad’s chromosomes and ½ of your Mom’s puberty = stage ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.