Cell Cycle & Cell Division
... Meiosis II produces gametes with one copy of each chromosome and thus one copy of each gene. ...
... Meiosis II produces gametes with one copy of each chromosome and thus one copy of each gene. ...
Define Chromatin: Histones: Sister chromatids: Centromere
... Kinetochore: Interphase: Prophase: Prometaphase: Metaphase: Anaphase: Telophase: Cytokinesis: Binary Fission: Metastisis: ...
... Kinetochore: Interphase: Prophase: Prometaphase: Metaphase: Anaphase: Telophase: Cytokinesis: Binary Fission: Metastisis: ...
Exam 3 Questions for Monday Feb 4th
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
... image should be a set of bullets describing what is happening in that image. MAKE SURE YOU INDICATE THE PLOIDY OF EVERY IMAGE. You need only label a structure once. The starting cell will have a haploid number of 3 (this could change…be prepared for anything). (The following terms should be included ...
Chromosomes and Cell Division!
... has equal genetic input into offspring Good for when you need genetic variability Happens in sex cells (haploid + haploid = diploid) ...
... has equal genetic input into offspring Good for when you need genetic variability Happens in sex cells (haploid + haploid = diploid) ...
Reproduction
... • Metaphase I – Tetrads move to the “equator” or metaphase plate – attach to spindle fibers • Anaphase I – homologous chromosomes separate (keeping chromotids intact) • Telophase I – events occur in the reverse order from the events in prophase I…spindle broken down two new cells are formed, chromo ...
... • Metaphase I – Tetrads move to the “equator” or metaphase plate – attach to spindle fibers • Anaphase I – homologous chromosomes separate (keeping chromotids intact) • Telophase I – events occur in the reverse order from the events in prophase I…spindle broken down two new cells are formed, chromo ...
Cell Division Homework #3
... What event occurs in prophase I of meiosis that did not occur in prophase of mitosis? ...
... What event occurs in prophase I of meiosis that did not occur in prophase of mitosis? ...
Meiosis II
... appearance of the chromosomes, the development of the spindle apparatus, and the breakdown of the nuclear membrane (envelope). Although this drawing from the text shows the chromosomes pairs in close association, including the chiasmata or points of contact of the arms of adjacent chromosomes, this ...
... appearance of the chromosomes, the development of the spindle apparatus, and the breakdown of the nuclear membrane (envelope). Although this drawing from the text shows the chromosomes pairs in close association, including the chiasmata or points of contact of the arms of adjacent chromosomes, this ...
Mitosis Notes
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
... Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) Centrioles (or poles) appear and begin to move ...
Meiosis and Variation Guided Notes
... Why don’t your siblings look EXACTLY like you? Why don’t you look EXACTLY like your parents? ...
... Why don’t your siblings look EXACTLY like you? Why don’t you look EXACTLY like your parents? ...
Anatomy and Physiology - Effingham County Schools
... • Divisions result in 4 daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent. (Haploid = n) • Meiosis 1 separates the homologous chromosomes (2 copies of each chromosome-1 from mom & 1 from dad) and Meiosis 2 ...
... • Divisions result in 4 daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent. (Haploid = n) • Meiosis 1 separates the homologous chromosomes (2 copies of each chromosome-1 from mom & 1 from dad) and Meiosis 2 ...
WINK Meiosis and Genetics
... Theme: Sex cells are formed by a process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is halved after replication. With the exception of sex chromosomes, for each chromosome in the body cells of a multicellular organism, there is a second similar, but not identical, chromosome. Altho ...
... Theme: Sex cells are formed by a process of cell division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is halved after replication. With the exception of sex chromosomes, for each chromosome in the body cells of a multicellular organism, there is a second similar, but not identical, chromosome. Altho ...
Reviewing Concepts - Canvas by Instructure
... a. The genetic material is duplicated. b. A cell grows in size. c. The number of organelles increases. d. The cytoplasm is divided in two. 3. The cytoplasm is divided into two daughter cells during a. metaphase. b. prophase. c. cytokinesis. d. anaphase. 4. Which of the following steps occurs during ...
... a. The genetic material is duplicated. b. A cell grows in size. c. The number of organelles increases. d. The cytoplasm is divided in two. 3. The cytoplasm is divided into two daughter cells during a. metaphase. b. prophase. c. cytokinesis. d. anaphase. 4. Which of the following steps occurs during ...
File
... of one another during meiosis. Pairs of chromosomes line up randomly during metaphase resulting in gene pairs separating into different cells. ...
... of one another during meiosis. Pairs of chromosomes line up randomly during metaphase resulting in gene pairs separating into different cells. ...
DATE - MrD-Home
... Copyright © 2007, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. ...
... Copyright © 2007, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited, a subsidiary of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. This page may be reproduced for classroom use by the purchaser of this book without the written permission of the publisher. ...
Meiosis I and II
... 2d~ students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization) 2e~ students know why approximately half of an individual’s DNA sequence comes from each parent ...
... 2d~ students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization) 2e~ students know why approximately half of an individual’s DNA sequence comes from each parent ...
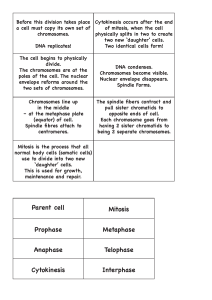
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
... Before this division takes place Cytokinesis occurs after the end a cell must copy its own set of of mitosis, when the cell chromosomes. physically splits in two to create two new ‘daughter’ cells. DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at ...
Intro to Meiosis - Solon City Schools
... Each pair is similar, but not exactly alike…we call them ...
... Each pair is similar, but not exactly alike…we call them ...
Unit 2. Cell Cycle Review Guide
... 7. For each of the following stages, record the main event that happens. • Metaphase • Prophase • Telophase • Anaphase 8. Is meiosis an example of asexual or sexual reproduction? Explain your answer. ...
... 7. For each of the following stages, record the main event that happens. • Metaphase • Prophase • Telophase • Anaphase 8. Is meiosis an example of asexual or sexual reproduction? Explain your answer. ...
Reproduction
... • During Meiosis I – an abnormality that can happen is that one pair of tetrads doesn’t separate so both chromosomes go to one side while the other side doesn’t get a copy of that chromosome at all – this is the cause of down’s syndrome. • non disjunction animation ...
... • During Meiosis I – an abnormality that can happen is that one pair of tetrads doesn’t separate so both chromosomes go to one side while the other side doesn’t get a copy of that chromosome at all – this is the cause of down’s syndrome. • non disjunction animation ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.