* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
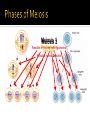
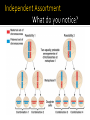
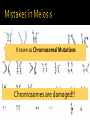
The great chromosome reducer! from diploid to haploid…. What are the two types of sex cells in humans? Where are gametes located in males and females? Testes and Ovaries How do sex cells (gametes) divide? Meiosis!! Why do gametes divide? To reduce the chromosome number from 2n to n (so that fertilization can occur) Meiosis results in 4 gametes that are haploid (n) So…what does the n mean??? Why do gametes have only 23 chromosomes? So n= 23 Gametes areFertilization haploid (n) Occurs! Gametes have 23 Chromosomes Gamete (egg) 23 Chromosomes + Gamete (Sperm) 23 Chromosomes 46 Chromosomes (chromosome number restored with newly formed zygote) Meiosis Meiosis 12 Replicates Results DNA in four n cells (gametes) Cells Divide Results in two 2n cells Meiosis Video Genetic Variation! What is genetic variation? Why is it important? How does this occur? No set determination Random Fertilizationon which sperm will fertilize the ovum (egg)! Independent Assortment (in Meiosis) Crossing Over (in Meiosis) How does this happen? How does it increase genetic variation? Alleles of different genes separate independently of one another during meiosis. Pairs of chromosomes line up randomly during metaphase resulting in gene pairs separating into different cells. What is it? How does it increase Genetic Variation? The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes Known as Chromosomal Mutations Chromosomes are damaged!! This is called Nondisjunction What does n mean again??? Chromosomes did not separate correctly Deletion Chromosome fragment was lost Duplication Chromosome fragment inserted twice Inversion Chromosome fragment inserted backward Translocation Chromosome fragment moves from one chromosome to another