CHAPTER 6
... Succinate-CoQ Reductase Also called succinate dehydrogenase or flavoprotein 2 (FP2) - FAD covalently bound four subunits, including 2 Fe-S proteins Three types of Fe-S cluster: 4Fe-4S, 3Fe-4S, 2Fe-2S Path: Succinate → FADH2 → 2Fe2+ → CoQH2 Net reaction: succinate + CoQ → fumarate + CoQH2 ΔEo'= 0.029 ...
... Succinate-CoQ Reductase Also called succinate dehydrogenase or flavoprotein 2 (FP2) - FAD covalently bound four subunits, including 2 Fe-S proteins Three types of Fe-S cluster: 4Fe-4S, 3Fe-4S, 2Fe-2S Path: Succinate → FADH2 → 2Fe2+ → CoQH2 Net reaction: succinate + CoQ → fumarate + CoQH2 ΔEo'= 0.029 ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... <8 valence electrons exceptions: Be=4, B=6 (formal charge) >8 valence electrons: 3rd row elements and below Consider formal charges in evaluating structures When to draw resonance structures, and how many (resonance = average) VSEPR structures predict 3‐dimensional arrangement of elect ...
... <8 valence electrons exceptions: Be=4, B=6 (formal charge) >8 valence electrons: 3rd row elements and below Consider formal charges in evaluating structures When to draw resonance structures, and how many (resonance = average) VSEPR structures predict 3‐dimensional arrangement of elect ...
Formation of pyruvic acid (P
... 3-The cycle involves a sequence of compounds inter-related by oxidationreduction and other reactions which finally produces [CO2 and H2O]. 4- It is the final common pathway of breakdown or catabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. 5-Acetyl CoA derived mainly from oxidation of either glucose or ...
... 3-The cycle involves a sequence of compounds inter-related by oxidationreduction and other reactions which finally produces [CO2 and H2O]. 4- It is the final common pathway of breakdown or catabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. 5-Acetyl CoA derived mainly from oxidation of either glucose or ...
electron transport
... P/O ratio is the number of molecules of ATP formed per two electrons through the chain • The number of H+ pass through the ATP synthase to synthesize an ATP, depending on the number of the c-subunit in the F0 • The number of c-subunit in ATP synthase ranges from 8-15, depending on the organism • The ...
... P/O ratio is the number of molecules of ATP formed per two electrons through the chain • The number of H+ pass through the ATP synthase to synthesize an ATP, depending on the number of the c-subunit in the F0 • The number of c-subunit in ATP synthase ranges from 8-15, depending on the organism • The ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation - Biology E
... In the third stage of respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ...
... In the third stage of respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ...
Test Review Guide ch. 7, 9, 10
... 10. The first chemical reaction in the Krebs cycle is ____ 11. The final energy products (and number) of each turn of the Krebs Cycle. 12.How many NADHS, FADH2, ATP are produced in the Krebs cycle? 13. Where is phosphorylation reaction substrate level or oxidative? 15. List three characteristics of ...
... 10. The first chemical reaction in the Krebs cycle is ____ 11. The final energy products (and number) of each turn of the Krebs Cycle. 12.How many NADHS, FADH2, ATP are produced in the Krebs cycle? 13. Where is phosphorylation reaction substrate level or oxidative? 15. List three characteristics of ...
Document
... both the acid and base forms of DNP are hydrophobic enough to dissolve in the membrane. ...
... both the acid and base forms of DNP are hydrophobic enough to dissolve in the membrane. ...
i. introduction to metabolism and catabolism
... (2) The is often referred to as an electrochemical gradient, as protons have positive charges (electro) and are chemicals b) The proton gradient is a form of stored energy (1) Both due to diffusion and electrical attraction, the protons would like to reenter the mitochondrial matrix (2) Protons are ...
... (2) The is often referred to as an electrochemical gradient, as protons have positive charges (electro) and are chemicals b) The proton gradient is a form of stored energy (1) Both due to diffusion and electrical attraction, the protons would like to reenter the mitochondrial matrix (2) Protons are ...
Cellular Respiration Overview
... down NADH and FADH2 by pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
... down NADH and FADH2 by pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient ...
Describe and discuss the process of chemiosmosis in eukaryotic
... D. Chloroplasts and Mitochondria both utilize the process of chemiosmosis. Compare and contrast the process of chemiosmosis as it occurs in a chloroplast and a mitochondrion by describing 3 similarities and 3 differences between the two. ...
... D. Chloroplasts and Mitochondria both utilize the process of chemiosmosis. Compare and contrast the process of chemiosmosis as it occurs in a chloroplast and a mitochondrion by describing 3 similarities and 3 differences between the two. ...
A. glycolysis
... 3. acetyl – CoA changes shape and then joins with a four carbon compound to make citric acid (release a CO2 molecule) ...
... 3. acetyl – CoA changes shape and then joins with a four carbon compound to make citric acid (release a CO2 molecule) ...
Document
... Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mechanism • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein, ATP synthase. • ATP synthase uses the exergonic ...
... Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mechanism • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein, ATP synthase. • ATP synthase uses the exergonic ...
Question
... a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron transport chain d. Transporting CO2 into the mitochondria e. Acting as a terminal electron acceptor ...
... a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron transport chain d. Transporting CO2 into the mitochondria e. Acting as a terminal electron acceptor ...
2-4_EnergyProd_FabinyiB
... It not just generates ATP but also provides precursor for creating amino acids. As glycolysis, CAC also regulated in several ways for energy preserving. The created NADHs transfers electrons to the electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the pH gradient and electrical potential that ...
... It not just generates ATP but also provides precursor for creating amino acids. As glycolysis, CAC also regulated in several ways for energy preserving. The created NADHs transfers electrons to the electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the pH gradient and electrical potential that ...
chapter 7 – cyu
... 3. Crookes put an iron cross in the middle. The cross blocked the rays coming from the cathode end. The shadow on the one end (anode) allowed him to see where the electrons were coming from. Crookes also had another experiment using a pinwheel in which electric currents, when switched on, would caus ...
... 3. Crookes put an iron cross in the middle. The cross blocked the rays coming from the cathode end. The shadow on the one end (anode) allowed him to see where the electrons were coming from. Crookes also had another experiment using a pinwheel in which electric currents, when switched on, would caus ...
Chapter 5 Quiz: Cellular respiration and fermentation Mark your
... It provides the cell with a mechanism to regenerate the oxidized form of electron carriers, allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
... It provides the cell with a mechanism to regenerate the oxidized form of electron carriers, allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
Jeopardy - SmittyWorld
... A: This molecule becomes available for use in alcoholic fermentation, or can be utilized by the Electron Transport Chain as part of aerobic respiration. ...
... A: This molecule becomes available for use in alcoholic fermentation, or can be utilized by the Electron Transport Chain as part of aerobic respiration. ...
Biochemistry 6/e
... passed to cytochrome c1 and the other transferred to heme bH and then to heme bH. In this latter half of the Q cycle, however, the bH electron is transferred to the semiquinone anion, UQ×- at the Qn site. With the addition of two H+ from the mitochondrial matrix, this produces a molecule of UQH2, wh ...
... passed to cytochrome c1 and the other transferred to heme bH and then to heme bH. In this latter half of the Q cycle, however, the bH electron is transferred to the semiquinone anion, UQ×- at the Qn site. With the addition of two H+ from the mitochondrial matrix, this produces a molecule of UQH2, wh ...
The Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis
... Enzyme Complexes Involved in Electron Transport Oxidation/reduction enzymes: 1. NADH dehydrogenase 2. Flavoproteins (FAD) 3. Iron-sulfur proteins 4. Cytochromes 5. Quinones (lipid-soluble) ...
... Enzyme Complexes Involved in Electron Transport Oxidation/reduction enzymes: 1. NADH dehydrogenase 2. Flavoproteins (FAD) 3. Iron-sulfur proteins 4. Cytochromes 5. Quinones (lipid-soluble) ...
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP
... Electrons are carried from Complex III to Complex IV by cytochrome c, a small hydrophilic peripheral membrane protein located on the cytosolic or P side of the IMM. Complex II (Succinate-UQ oxidoreductase) is membrane bound and contains the FADH2 as a prosthetic group . So electrons from FADH2 feed ...
... Electrons are carried from Complex III to Complex IV by cytochrome c, a small hydrophilic peripheral membrane protein located on the cytosolic or P side of the IMM. Complex II (Succinate-UQ oxidoreductase) is membrane bound and contains the FADH2 as a prosthetic group . So electrons from FADH2 feed ...
Quiz8ch8.doc
... a. mitochondria, cytoplasm b. cytoplasm, mitochondria c. cytoplasm, chloroplasts d. chloroplasts, mitochondria 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the CO2 molecules in this equation come from __________ during reactions ...
... a. mitochondria, cytoplasm b. cytoplasm, mitochondria c. cytoplasm, chloroplasts d. chloroplasts, mitochondria 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the CO2 molecules in this equation come from __________ during reactions ...
Bioenergetics and Mitosis Review Sheet
... 1. Be able to identify the oxidizing and the reducing agent in a chemical reaction. 2. What is the chemical structure of ATP? 3. What portion of the ATP molecule is high in energy? Why? 4. What happens in glycolysis? 5. What are the 3 products of glycolysis? 6. Through what method are the ATP molecu ...
... 1. Be able to identify the oxidizing and the reducing agent in a chemical reaction. 2. What is the chemical structure of ATP? 3. What portion of the ATP molecule is high in energy? Why? 4. What happens in glycolysis? 5. What are the 3 products of glycolysis? 6. Through what method are the ATP molecu ...
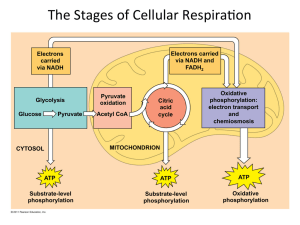
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.