* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Quiz: Cellular respiration and fermentation Mark your
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
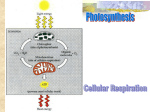
Chapter 5 Quiz: Cellular respiration and fermentation Mark your answers on the scantron answer sheet. 1) Why is ATP used in the preparatory stage of glycolysis? a. It is needed to produce water from the energy-conserving stage. b. ATP is needed to allow the cell to move toward a carbon source. c. It is needed to reduce NAD+ to NADH. d. It makes the process of converting glucose into two 3-carbon molecules easier. 2) Circle each of the following that are products of glycolysis? a. ATP b. pyruvic acid c. glucose d. NADH e. NAD+ 3) Where does the energy come from to make ATP during glycolysis? a. pyruvic acid b. NADH c. glucose d. water 4) What is the NET ATP produced from one molecule of glucose in glycolysis? a. 1 ATP b. 2 ATP c. 4 ATP d. 6 ATP 5) The process of moving a phosphate from metabolic products to ADP to form ATP is called __________. a. reduction. b. substrate-level phosphorylation. c. glycolysis. d. oxidative phosphorylation. 6) Which of the following are products remaining after glycolysis has occurred for a single molecule of glucose? a. two molecules of pyruvic acid b. four net ATP c. two NADH d. two NAD+ 7) Another name for the Krebs cycle is ____________. a. the acetyl CoA cycle. b. the bridge cycle. c. the transition cycle. d. the citric acid cycle. 8) The overall purpose of the Krebs cycle is ________. a. to extract the energy from pyruvate molecules enzymatically. b. to produce carbon dioxide and water. c. to produce molecules of the energy carrier GTP. d. to convert pvruvic acid into acetyl CoA. 9) Which of the following is an electron carrier used in the Krebs cycle? a. NADH b. FADH2 c. both of these 10) Are carbon dioxide molecules produced in the Krebs cycle? d. neither of these A. Yes b. No 11) NADH is converted to ATP in a process known as ___________________. a. oxidation b. reduction c. decarboxylation d. oxidative phosphorylation 12) The primary role of electron transport chains in many organisms is to ___________________. a. generate usable energy in the form of ATP. b. allow water to flow from regions of high concentrations to low concentrations. c. transfer electrons along a cell membrane. d. pump hydrogen ions outside of a membrane. 13) Chemiosmosis ____________________________. a. occurs along the cell membrane of eukaryotes. b. is the process of using an electron gradient to produce ATP. c. is the name given to membrane-bound proteins involved in electron transport. d. is the process of using a proton gradient to generate ATP. 14) How do the protons flow in an electron transport system in a prokaryote? a. from regions of high concentration to low concentrations along a mitochondrial membrane b. from regions of low concentration to high concentrations along a cell membrane c. from regions of low concentration to high concentrations along a mitochondrial membrane d. from regions of high concentration to low concentrations along a cell membrane 15) Which compound provides the electrons at the start of the electron transport system in the animation? a. O2 b. NADH c. ATP d. H2O 16) What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of aerobic bacteria? a. water b. FADH2 c. oxygen d. NADH 17) Cyanide poisoning _______________________. a. diverts the energy from the proton gradient to other cell functions. b. allows for ATP production without using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. c. blocks cytochrome a3. d. acts in a manner similar to oxygen deprivation. 18) What effect does oxygen deprivation have on an aerobic cell? a. makes the cell unable to maintain a proton gradient b. keeps cytochrome a3 in the reduced state c. increases the amount of thermogenin d. an increase in the amount of heat generated by the ETC 19) What is the primary function of fermentation? a. It is a metabolic pathway used to produce organic acids, like lactic acid. b. It is an alternative way for a cell to produce carbon dioxide. c. It provides the cell with a mechanism to regenerate the oxidized form of electron carriers, allowing glycolysis to continue. d. It enables the electron transport chain to continue functioning in the absence of oxygen. 20) During fermentation, which compound is the substrate to be reduced with the electrons from NADH? a. glucose b. pyruvic acid c. oxygen d. ATP 21) Which of the following is a product of alcohol fermentation? a. carbon dioxide b. ethanol c. NAD+ d. b and c e. all of these 22) Which of the following is the organic acid produced by fermentation in human muscle cells? a. butyric acid b. lactic acid c. pyruvic acid d. succinic acid e. formic acid 23) The process on the left would occur n which part of the cell? a) mitochondria b) cytoplasm c) plasma membrane d) capsule e) cristae 24) ATP is being _______ in this process. a) used b) produced 25) Your cells go through this process during both aerobic respiration and fermentation. a) true b) false