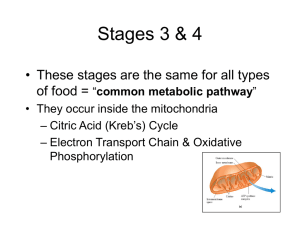
1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
Electron transport chain-2
... electron transport chain. • The Chemiosmotic theory proposes that after proton have transferred to the cytosolic side of inner mitochondrial membrane, they can re-enter the matrix by passing through the proton channel in the ATPase (F0), resulting in the synthesis of ATP in (F1) subunit. ...
... electron transport chain. • The Chemiosmotic theory proposes that after proton have transferred to the cytosolic side of inner mitochondrial membrane, they can re-enter the matrix by passing through the proton channel in the ATPase (F0), resulting in the synthesis of ATP in (F1) subunit. ...
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... Membrane proteins composed of redox molecules. Fixed enzyme Complex #1 (entrance of NADH): Step #1: FMN (Flavin mononucleotide) and Step #2: FeSP (iron sulphur protein) Step #3: Mobile enzyme: CoQ (Coenzyme Q) (entrance of FADH2) ...
... Membrane proteins composed of redox molecules. Fixed enzyme Complex #1 (entrance of NADH): Step #1: FMN (Flavin mononucleotide) and Step #2: FeSP (iron sulphur protein) Step #3: Mobile enzyme: CoQ (Coenzyme Q) (entrance of FADH2) ...
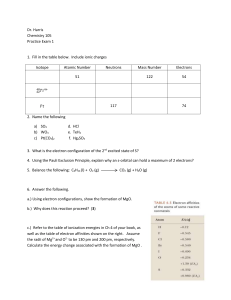
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... Energy is quantized. Emission is due to specific transitions between ground and excited states. 18. Refer to the activity series in chapter 10. For the single replacement reactions below, write the half reactions. Label the reducing and oxidizing agents. Show the net ionic equation. If no reaction o ...
... Energy is quantized. Emission is due to specific transitions between ground and excited states. 18. Refer to the activity series in chapter 10. For the single replacement reactions below, write the half reactions. Label the reducing and oxidizing agents. Show the net ionic equation. If no reaction o ...
Electron Transport Chain
... ATP is made through oxidative phosphorylation, powered by the free energy released from electron transfer from NADH to O2. a) Given the following reduction potentials, calculate the available standard free energy from this process. NAD+ + H+ + 2 e- NADH E’º = -0.32 V 1/2 O2 + 2 H+ + 2 e- H2O E’º ...
... ATP is made through oxidative phosphorylation, powered by the free energy released from electron transfer from NADH to O2. a) Given the following reduction potentials, calculate the available standard free energy from this process. NAD+ + H+ + 2 e- NADH E’º = -0.32 V 1/2 O2 + 2 H+ + 2 e- H2O E’º ...
Lesson
... ALCOHOL FERMENTATION Occurs in yeast, fungi, bacteria & plants Pyruvate becomes acetaldehyde Produces CO 2 ...
... ALCOHOL FERMENTATION Occurs in yeast, fungi, bacteria & plants Pyruvate becomes acetaldehyde Produces CO 2 ...
Study Guide
... Stepwise oxidation of glucose = catabolism of glucose Phases of Glycolysis, products of Glycolysis, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of NAD+, NADH, FAD, FADH2 as electron carriers (redox reactions) Pyruvate oxidation under aerobic conditions, pyruvate fermentation under anae ...
... Stepwise oxidation of glucose = catabolism of glucose Phases of Glycolysis, products of Glycolysis, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of NAD+, NADH, FAD, FADH2 as electron carriers (redox reactions) Pyruvate oxidation under aerobic conditions, pyruvate fermentation under anae ...
Exam 1 454 Study Guide
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
File
... A. The only order of cards that allowed the complete electron transfer transport is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 from the NADH end to the oxygen end. B. This investigation models the protein complexes in the electron transport chain as follows: The electrons are pulled in a direction toward molecules that are m ...
... A. The only order of cards that allowed the complete electron transfer transport is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 from the NADH end to the oxygen end. B. This investigation models the protein complexes in the electron transport chain as follows: The electrons are pulled in a direction toward molecules that are m ...
Protein and Lipid Catabolism
... – Not associated with any one phylogenetic group – Except methanogenesis ...
... – Not associated with any one phylogenetic group – Except methanogenesis ...
Respiration
... • As electrons are moved from carriers with high energy to carriers with low energy, energy is released • Some of this energy is used to move protons across the membrane (ATP synthase) to generate ATP • Net gain of 28-32 ATP ...
... • As electrons are moved from carriers with high energy to carriers with low energy, energy is released • Some of this energy is used to move protons across the membrane (ATP synthase) to generate ATP • Net gain of 28-32 ATP ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS – The anabolic reduction of CO2 to form sugar.
... Note: the force that is driving the ETC is the pull on electrons exerted by the very highly electronegative O2. thus, “oxidative phosphorylation.” * NUMBERS ARE PER GLUCOSE MOLECULE Chemiosmosis, or chemiosmotic phosphorylation operates in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and is referre ...
... Note: the force that is driving the ETC is the pull on electrons exerted by the very highly electronegative O2. thus, “oxidative phosphorylation.” * NUMBERS ARE PER GLUCOSE MOLECULE Chemiosmosis, or chemiosmotic phosphorylation operates in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and is referre ...
The Theme of Oxidative Phosphorylation in Glycolysis and Cellular
... The main point of oxidative phosphorylation is the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power ATP production. Similarly, the main purpose of playing arcade games is to win tickets for prizes (okay, and also maybe to have fun and earn high scores in the games). NADH is more often the electron ...
... The main point of oxidative phosphorylation is the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power ATP production. Similarly, the main purpose of playing arcade games is to win tickets for prizes (okay, and also maybe to have fun and earn high scores in the games). NADH is more often the electron ...
Chapter 14 - Part I
... • Resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane – also called respiratory chain • 15 proteins involved in the chain – grouped in 3 large respiratory enzyme complexes – NADH dehydrogenase complex – Cytochrome b-c1 complex – Cytochrome oxidase complex ...
... • Resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane – also called respiratory chain • 15 proteins involved in the chain – grouped in 3 large respiratory enzyme complexes – NADH dehydrogenase complex – Cytochrome b-c1 complex – Cytochrome oxidase complex ...
Metabolism_PartII Group work
... inside each of the following different chemoorganoheterotrophic bacteria using the different catabolic pathways in the table below. o Obligate aerobe o Facultative anaerobe o Obligate anaerobe Table of catabolic processes o The central metabolic pathways Glycolysis Pentose phosphate pathway ...
... inside each of the following different chemoorganoheterotrophic bacteria using the different catabolic pathways in the table below. o Obligate aerobe o Facultative anaerobe o Obligate anaerobe Table of catabolic processes o The central metabolic pathways Glycolysis Pentose phosphate pathway ...
Transport of molecules into a bacterial cell
... – If reduced NAD molecules are “poker chips”, they contain energy which needs to be “cashed in” to make ATP. – In order for glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to continue, NAD that gets reduced to NADH must get re-oxidized to NAD. – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron ...
... – If reduced NAD molecules are “poker chips”, they contain energy which needs to be “cashed in” to make ATP. – In order for glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to continue, NAD that gets reduced to NADH must get re-oxidized to NAD. – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.