* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jeopardy - SmittyWorld
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
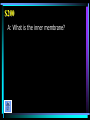
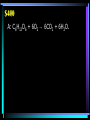
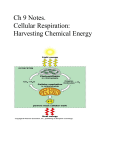
Cellular Respiration Edition Carbs Glycolysis Fermentation Kreb’s Cycle Electron Transport Chain Energy $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Biology $100 A: It is the literal translation of the name “carbohydrate”. $100 Q: What is “carbon water”? $200 A: Glucose, fructose, and galactose, all 3 are identified as this. $200 Q: What are monosacharides? $300 A: All carbohydrates, except monosacharides, are assembled into polymers by this reaction. $300 Q: What is a dehydration synthesis (or condensation) reaction? $400 A: A:When Whenaahydrolysis hydrolysisreaction reactionoccurs occurswith with starch, starch,this thismolecule moleculeisisproduced producedinin large largequantities. quantities. $400 Q: What is glucose? $500 A: Plants, specifically seeds and roots, but also stems and leaves. $500 Q: Where do carbohydrates come from? $100 A: The organic molecule glycolysis starts with. $100 Q: What is glucose? $200 A: Glycolysis occurs here. $200 Q: What is the cytosol/cytoplasm? $300 A: As a result of glycolysis, the carbon based molecule of glucose is changed to this carbon based molecule. $300 Q: What is pyruvic acid (pyruvate)? $400 A: As bonds in glucose are broken, free energy is transferred to the bonds of this molecule. $400 Q: What is ATP? $500 A: This molecule becomes available for use in alcoholic fermentation, or can be utilized by the Electron Transport Chain as part of aerobic respiration. $500 Q: What is NADH? $100 A: Fermentation occurs when this is not present. $100 Q: What is oxygen? $200 A: This waste product of fermentation is considered desirable by many adults in western civilization. $200 Q: What is ethyl alcohol (ethanol)? $300 A: For humans, this product of fermentation accumulates in muscle cells and interferes with normal muscle function. $300 Q: What is lactic acid? $400 A: It is what allows yeast to perform alcoholic fermentation, while humans cannot. $400 Q: What is an enzyme? $500 A: This commercial use of fermentation is the primary source of food around the world. $500 Q: What is bread making (baking)? $100 A: This is where the Kreb’s Cycle occurs. $100 Q: What is the mitochondrial matrix? $200 A: Liberated in large amounts, it is the key “product” of the Kreb’s Cycle. $200 Q: What are hydrogen atoms? $300 A: The number of times the Kreb’s Cycle functions for every molecule of glucose. $300 Q: What is twice? $400 A: This molecule is released by aerobic organisms as a result of performing the Kreb’s Cycle. $400 Q: What is Carbon Dioxide (CO2)? $500 A: It’ why the Kreb’s Cycle is referred to as a cycle. $500 Q: What is 4-carbon molecules are recycled to join with new Acetyl CoA forming new Citric Acid to start again $100 A: This is what “cascades” along the Electron Transport Chain, releasing free energy with each collision. $100 Q: What is electrons? $200 A: The part of the mitochondrion where the Electron Transport Chain occurs. $200 A: What is the inner membrane? $300 A: 36 ATP. $300 Q: What is the total number of ATP synthesized by the Electron Transport Chain? $400 A: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O. $400 Q: What is the balanced equation for aerobic respiration? $500 A: How the free energy released during the Electron Transport Chain is harnessed and used to synthesize ATP. $500 Q: What is chemiosmosis (ATP synthetase)? $100 A: The contestant on the far right would get the most efficient metabolism out of the lunch she ate by doing this? $100 Q: What is breathe oxygen? $200 A: This type of reaction always results in the use of a fuel to produce water and carbon dioxide. $200 Q: What is a combustion reaction? $300 A: Cellular Respiration would be represented by this type of energy curve. $300 Q: What is an exothermic energy curve? $400 A: This is how many times more efficient aerobic respiration is than anaerobic respiration. $400 Q: What is 19? $500 A: The radiant energy captured from the sun by plants can be found in the potential energy of this molecule in your cells. $500 Q: What is ATP?