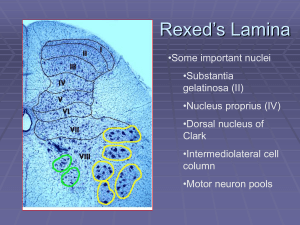
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
BOX 31.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE VESTIBULAR AND
... Phylogenetically, the vestibular and fastigial (medial) cerebellar nuclei predate the interpositus and dentate. Perhaps as a result, the vestibular and fastigial cerebellar circuits exhibit some distinctive properties compared to their relatively younger neighbors: 1. Unipolar brush cells are presen ...
... Phylogenetically, the vestibular and fastigial (medial) cerebellar nuclei predate the interpositus and dentate. Perhaps as a result, the vestibular and fastigial cerebellar circuits exhibit some distinctive properties compared to their relatively younger neighbors: 1. Unipolar brush cells are presen ...
Slide ()
... The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Similar pathways connect the anterior and posterior canals to the vertical recti and oblique muscles. A. Leftward head rotation excites hair cells in the left horizontal canal, thus exciting neurons that evoke rightward eye movement. The vestibular nuclei incl ...
... The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Similar pathways connect the anterior and posterior canals to the vertical recti and oblique muscles. A. Leftward head rotation excites hair cells in the left horizontal canal, thus exciting neurons that evoke rightward eye movement. The vestibular nuclei incl ...
Learning
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
side
... 2- Sensory areas - provide for conscious awareness of sensation 3- Association areas - integrate all other information Each hemisphere is concerned with the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body ...
... 2- Sensory areas - provide for conscious awareness of sensation 3- Association areas - integrate all other information Each hemisphere is concerned with the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body ...
Tourette-handout
... – Involved in planning and executing movements (Association Cortex) – Neurons are connected to various parts of the body (Motor Cortex) ...
... – Involved in planning and executing movements (Association Cortex) – Neurons are connected to various parts of the body (Motor Cortex) ...
179 - Edmund Rolls
... simulation neuronal learning is bounded by normalisation of each cell’s dendritic weight vector. An alternative, more biologically relevant implementation, using a local weight bounding operation, has in part been explored using a version of the Oja update rule (Oja 1982; Iiohonen 1984). ...
... simulation neuronal learning is bounded by normalisation of each cell’s dendritic weight vector. An alternative, more biologically relevant implementation, using a local weight bounding operation, has in part been explored using a version of the Oja update rule (Oja 1982; Iiohonen 1984). ...
Redalyc.Effects of aversive classical conditioning on habituation of
... this UR (conditioned diminution) when presented with the CS-US sequence (Fanselow, 1980; Fanselow and Baackes, 1982; Paletta and Wagner, 1986; etc.). Paletta y Wagner (1986) suggested that the relationship between CR and UR hypothesized by SOP was exemplified in the case of conditioned activity chan ...
... this UR (conditioned diminution) when presented with the CS-US sequence (Fanselow, 1980; Fanselow and Baackes, 1982; Paletta and Wagner, 1986; etc.). Paletta y Wagner (1986) suggested that the relationship between CR and UR hypothesized by SOP was exemplified in the case of conditioned activity chan ...
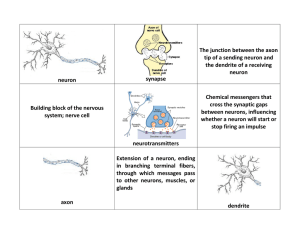
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands axon ...
... Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands axon ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
... description that emerge due to rules followed at a lower level of description. • Neural network modellers hope that we can understand behaviour by creating models of networks of artificial neurons. ...
1 - U-System
... fields, and more complex properties - destruction of primary somatosensory cortex causes a somatosensory deficit, but not a total loss; this is true because there is parallel processing occurring (thalamic info goes to both primary and association areas, which can function by themselves) - there are ...
... fields, and more complex properties - destruction of primary somatosensory cortex causes a somatosensory deficit, but not a total loss; this is true because there is parallel processing occurring (thalamic info goes to both primary and association areas, which can function by themselves) - there are ...
Learning Supplementary Handout
... SIMULTANEOUS CONDITIONING: CS (bell) and UCS (food) are presented at the same time. BACKWARD CONDITIONING: UCS (food) is presented first and is followed by the CS (bell) – definitely NOT the most effective method. ...
... SIMULTANEOUS CONDITIONING: CS (bell) and UCS (food) are presented at the same time. BACKWARD CONDITIONING: UCS (food) is presented first and is followed by the CS (bell) – definitely NOT the most effective method. ...
Chapter_8-Learning
... (unconditionally) triggers a dog’s salivary reflex. 2. What is the unconditional stimulus? The food 3. What is the conditioned response? Salvation in response to the tone. The salvation in response to the tone was CONDITIONAL upon the dog’s learning the association between the tone and the food. 4. ...
... (unconditionally) triggers a dog’s salivary reflex. 2. What is the unconditional stimulus? The food 3. What is the conditioned response? Salvation in response to the tone. The salvation in response to the tone was CONDITIONAL upon the dog’s learning the association between the tone and the food. 4. ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... Which of the following statements about brain development is true? a. At birth, the brain is nearly 70 percent of its adult weight. b. By age 2, the brain is approximately 50 percent of its adult weight. c. Brain growth is especially rapid in the first year, when the brain more than doubles in size. ...
... Which of the following statements about brain development is true? a. At birth, the brain is nearly 70 percent of its adult weight. b. By age 2, the brain is approximately 50 percent of its adult weight. c. Brain growth is especially rapid in the first year, when the brain more than doubles in size. ...
Learning - ThaparNotes
... • As the cat moved about in the box, trying to escape, sooner or later it would accidentally pull the string, and the door would open. • When the cat was put into the box again, the time between it being put in and finally pulling the string would gradually get shorter, until eventually the cat woul ...
... • As the cat moved about in the box, trying to escape, sooner or later it would accidentally pull the string, and the door would open. • When the cat was put into the box again, the time between it being put in and finally pulling the string would gradually get shorter, until eventually the cat woul ...
2015 Midterm Exam
... 39. Association to other areas of ipsilateral hemisphere. 40. Commissure to like areas of contralateral hemisphere. 41. Reciprocal modulator (READ) of thalamic input. 42. Same as the “granular layer”. 43. Subcortical target & non-reciprocal driver (WRITE) of higher-order thalamic relays. 44-50. Visi ...
... 39. Association to other areas of ipsilateral hemisphere. 40. Commissure to like areas of contralateral hemisphere. 41. Reciprocal modulator (READ) of thalamic input. 42. Same as the “granular layer”. 43. Subcortical target & non-reciprocal driver (WRITE) of higher-order thalamic relays. 44-50. Visi ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... After a rest period, an extinguished CR (salivation) spontaneously recovers, but if the CS (tone) persists alone, the CR becomes extinct again. ...
... After a rest period, an extinguished CR (salivation) spontaneously recovers, but if the CS (tone) persists alone, the CR becomes extinct again. ...
Academic Misconduct/ Cheating policy
... Less impediment from other cells & blood vessels One to one communication with bipolar cells & ganglion cells You really do have a blind spot ...
... Less impediment from other cells & blood vessels One to one communication with bipolar cells & ganglion cells You really do have a blind spot ...
Higher brain functions
... • After intense stimulation of the presynaptic neuron, the amplitude of the post-synaptic neuron’s response increases. • The stimulus applied is generally of short duration (less than 1 second) but high frequency • In the postsynaptic neuron, this stimulus causes sufficient depolarization to evacua ...
... • After intense stimulation of the presynaptic neuron, the amplitude of the post-synaptic neuron’s response increases. • The stimulus applied is generally of short duration (less than 1 second) but high frequency • In the postsynaptic neuron, this stimulus causes sufficient depolarization to evacua ...
Powerpoint version
... Steroid and thyroid hormones activate genes Diffuse freely into and out of cells Receptor proteins are in cytoplasm. Hormone binds and moves inside nucleus ...
... Steroid and thyroid hormones activate genes Diffuse freely into and out of cells Receptor proteins are in cytoplasm. Hormone binds and moves inside nucleus ...
Chapter 8 pt. 1: Learning and Classical Conditioning
... Studies proved that subjects attitudes did matter when attempting to create conditioned responses in them. Ex: ½ told that being conditioned was wise, sensible, and intelligent while other half was told the reverse….positive instructions assisted conditioning while negative instructions undermined ...
... Studies proved that subjects attitudes did matter when attempting to create conditioned responses in them. Ex: ½ told that being conditioned was wise, sensible, and intelligent while other half was told the reverse….positive instructions assisted conditioning while negative instructions undermined ...
File
... organism comes to associate two stimuli a neutral stimulus (NS) that signals an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) begins to produce a response (UCR) that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) With your partner or trio, relate this description to one of your previous examples of as ...
... organism comes to associate two stimuli a neutral stimulus (NS) that signals an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) begins to produce a response (UCR) that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) With your partner or trio, relate this description to one of your previous examples of as ...
PSYC 2500-02 LEARNING: QUIZ 2 NAME: Spring 2017 Read each
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...
... Clark Hull's 1943 equation for learning was revised in 1952 to add K (incentive motivation). The addition of K was from the results of the Crespi-Zeaman Effect. Which of the following statements describes this effect accurately? a) Changing the number of reinforcements had an unexpected sudden effec ...