Amygdala Modulation of Cerebellar Learning
... cerebellar anterior interpositus nucleus during acquisition and retention of eyeblink conditioning (Experiment 2). A very small proportion of cerebellar neurons responded to the conditioned stimulus (CS) during CeA inactivation. Finally, retrograde and anterograde tracing experiments identified the ...
... cerebellar anterior interpositus nucleus during acquisition and retention of eyeblink conditioning (Experiment 2). A very small proportion of cerebellar neurons responded to the conditioned stimulus (CS) during CeA inactivation. Finally, retrograde and anterograde tracing experiments identified the ...
conditioning - MsMcAnullaswiki
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
A learned reinforcer
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
... meaning they learn expectancy or awareness of a stimulus (Rescorla & Wagner, 1972). ...
Learning - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... unconditioned stimulus begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus ...
... unconditioned stimulus begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus ...
PDF (2_RMC_CH1_Introduction)
... reaction, such as salivation, to only the meaningful stimulus. Over time, the subject begins to respond to the previously neutral stimulus in the same way as the meaningful one. The subject has formed an association; he or she now begins salivating to the presence of the bell alone without food. In ...
... reaction, such as salivation, to only the meaningful stimulus. Over time, the subject begins to respond to the previously neutral stimulus in the same way as the meaningful one. The subject has formed an association; he or she now begins salivating to the presence of the bell alone without food. In ...
File - Ms.Carey`s Webpage!
... learning in his classic experiments on conditioning dogs. He noticed that they learned by association. It was his experiments that are called CLASSICAL CONDITIONING. Pavlov received a medical degree in Russia at the age of 33 and spent the next three decades focusing on learning and ...
... learning in his classic experiments on conditioning dogs. He noticed that they learned by association. It was his experiments that are called CLASSICAL CONDITIONING. Pavlov received a medical degree in Russia at the age of 33 and spent the next three decades focusing on learning and ...
File
... learning in his classic experiments on conditioning dogs. He noticed that they learned by association. It was his experiments that are called CLASSICAL CONDITIONING. Pavlov received a medical degree in Russia at the age of 33 and spent the next three decades focusing on learning and ...
... learning in his classic experiments on conditioning dogs. He noticed that they learned by association. It was his experiments that are called CLASSICAL CONDITIONING. Pavlov received a medical degree in Russia at the age of 33 and spent the next three decades focusing on learning and ...
d_Study Guide_Classical-Operant Conditioning - psy1
... Classical Conditioning: a simple form of learning in which one stimulus creates a response that is usually created by another stimulus ...
... Classical Conditioning: a simple form of learning in which one stimulus creates a response that is usually created by another stimulus ...
Exercise Sheet 6 - Machine Learning
... output neuron. Download the training pattern file from the course website and open it. Try different learning algorithms with different parameter settings and observe the results with the Error Graph View and the Projection View. (a) Use the Backpropagation learning algorithm to train a MLP for the ...
... output neuron. Download the training pattern file from the course website and open it. Try different learning algorithms with different parameter settings and observe the results with the Error Graph View and the Projection View. (a) Use the Backpropagation learning algorithm to train a MLP for the ...
Learning
... In Watson’s experiment, Little Albert associated a frightening loud noise (US) with a white rat (CS) to elicit fear (CR). ...
... In Watson’s experiment, Little Albert associated a frightening loud noise (US) with a white rat (CS) to elicit fear (CR). ...
Chapter 2 LEARNING: Principals and Applications
... timing and frequency of reinforcement • Partial schedule- when positive reinforcement occurs immediately but not every time • Skinner learned of the effectiveness of partial reinforcement when the “Skinner Box” broke • it is generally a more stable and longer lasting behavior ...
... timing and frequency of reinforcement • Partial schedule- when positive reinforcement occurs immediately but not every time • Skinner learned of the effectiveness of partial reinforcement when the “Skinner Box” broke • it is generally a more stable and longer lasting behavior ...
Classical Conditioning - Cedar Bluffs Public Schools
... timing and frequency of reinforcement • Partial schedule- when positive reinforcement occurs immediately but not every time • Skinner learned of the effectiveness of partial reinforcement when the “Skinner Box” broke • it is generally a more stable and longer lasting behavior ...
... timing and frequency of reinforcement • Partial schedule- when positive reinforcement occurs immediately but not every time • Skinner learned of the effectiveness of partial reinforcement when the “Skinner Box” broke • it is generally a more stable and longer lasting behavior ...
Central Nervous ppt
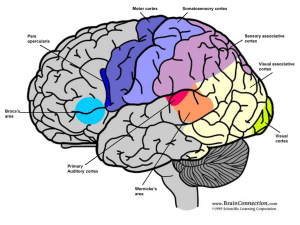
... 2- Sensory areas - provide for conscious awareness of sensation 3- Association areas - integrate all other information Each hemisphere is concerned with the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body ...
... 2- Sensory areas - provide for conscious awareness of sensation 3- Association areas - integrate all other information Each hemisphere is concerned with the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body ...
Chapter 5 - Learning
... behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – is any stimulus event that increases the likelihood that the behavior it follows will be repeated. Skinner coined the term operant conditioning to describe the process of learning by which responses are strengthened through manipulating the effe ...
... behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – is any stimulus event that increases the likelihood that the behavior it follows will be repeated. Skinner coined the term operant conditioning to describe the process of learning by which responses are strengthened through manipulating the effe ...
Striate cortex April 2009
... 'responsible' for processing a stimulus of a given size, as a function of visual field location. In the center of the visual field, corresponding to the fovea of the retina, a very large number of neurons process information from a small region of the visual field. If the same stimulus is seen in th ...
... 'responsible' for processing a stimulus of a given size, as a function of visual field location. In the center of the visual field, corresponding to the fovea of the retina, a very large number of neurons process information from a small region of the visual field. If the same stimulus is seen in th ...
Part1
... Synapses may be excitatory or inhibitory They may turn on or turn off at different rates ...
... Synapses may be excitatory or inhibitory They may turn on or turn off at different rates ...
Reticular Activating System
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
Glossary
... Conditioned A learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of response (CR) previous conditioning. Conditioned A previously neutral stimulus that has, through conditioning, stimulus (CS) acquired the capacity to evoke a conditioned response. ...
... Conditioned A learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of response (CR) previous conditioning. Conditioned A previously neutral stimulus that has, through conditioning, stimulus (CS) acquired the capacity to evoke a conditioned response. ...
multiple choice
... A) psychological pain. B) attacks on character. C) penalties, such as loss of privileges. D) intense physical pain. E) delayed and inconsistent consequences. 17) The factor that makes a food aversion different from most types of classical conditioning is that 17) ______ A) there can be a long time d ...
... A) psychological pain. B) attacks on character. C) penalties, such as loss of privileges. D) intense physical pain. E) delayed and inconsistent consequences. 17) The factor that makes a food aversion different from most types of classical conditioning is that 17) ______ A) there can be a long time d ...
Conditioning
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
PSYC 305
... Research on learning has been influenced by this approach to psychology that emphasizes the study of observable behavior and the role of the environment as a determinant of behavior. ...
... Research on learning has been influenced by this approach to psychology that emphasizes the study of observable behavior and the role of the environment as a determinant of behavior. ...
Bernstein_06_Learning
... • Signals what is inappropriate behavior but does not specify correct alternative behavior. ...
... • Signals what is inappropriate behavior but does not specify correct alternative behavior. ...
Chapter Six
... • Signals what is inappropriate behavior but does not specify correct alternative behavior. ...
... • Signals what is inappropriate behavior but does not specify correct alternative behavior. ...
t2u-powerpoint-learning-theory
... 1) Have they explained the results of Harlow (1959) so that someone who doesn’t know this study would understand the outcome? 2) Have they explained why Harlow’s research undermines the learning theory effectively? ...
... 1) Have they explained the results of Harlow (1959) so that someone who doesn’t know this study would understand the outcome? 2) Have they explained why Harlow’s research undermines the learning theory effectively? ...