Modelling Cerebellar Function in Saccadic Adaptation
... • Same basic circuit repeated many times (hence “neuronal machine”) • Important: half the cells in the entire brain are in the cerebellum ...
... • Same basic circuit repeated many times (hence “neuronal machine”) • Important: half the cells in the entire brain are in the cerebellum ...
Classical Conditioning
... In classical conditioning, antecedent events become associated with one another. We see learning when the new stimulus will also bring forth a response. ...
... In classical conditioning, antecedent events become associated with one another. We see learning when the new stimulus will also bring forth a response. ...
Chap2
... Spontaneous recovery occurs after extinction has been learned, but a break in exposure to the stimulus occurs. After spontaneous recovery, extinction returns. ...
... Spontaneous recovery occurs after extinction has been learned, but a break in exposure to the stimulus occurs. After spontaneous recovery, extinction returns. ...
Learning - Psychological Sciences
... US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
... US (food) are paired, resulting in salivation (UR). After conditioning, the neutral stimulus (now Conditioned Stimulus, CS) elicits salivation (now Conditioned Response, CR) ...
Learning
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
Affiliates Day Poster Joseph Young
... SFC measures synchronization between single neuron and local population as a function of frequency ...
... SFC measures synchronization between single neuron and local population as a function of frequency ...
Slide ()
... limb of the diagonal band; DR, dorsal raphe; FX, fornix; IC, inferior colliculus; LC, locus ceruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; MCP, middle cerebellar peduncle; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MR, median raphe; MS, medial septum; MTT, mammillothalamic tract; NTS, nucleus tractus solitariu ...
... limb of the diagonal band; DR, dorsal raphe; FX, fornix; IC, inferior colliculus; LC, locus ceruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; MCP, middle cerebellar peduncle; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MR, median raphe; MS, medial septum; MTT, mammillothalamic tract; NTS, nucleus tractus solitariu ...
Slide ()
... limb of the diagonal band; DR, dorsal raphe; FX, fornix; IC, inferior colliculus; LC, locus ceruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; MCP, middle cerebellar peduncle; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MR, median raphe; MS, medial septum; MTT, mammillothalamic tract; NTS, nucleus tractus solitariu ...
... limb of the diagonal band; DR, dorsal raphe; FX, fornix; IC, inferior colliculus; LC, locus ceruleus; LDT, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; MCP, middle cerebellar peduncle; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; MR, median raphe; MS, medial septum; MTT, mammillothalamic tract; NTS, nucleus tractus solitariu ...
Chapter 8 Vocabulary
... In ____________________ ____________________, organisms learn that certain events occur together. Two variations of associative learning are classical conditioning and operant conditioning. (p. 288) ______________________ is the school of thought maintaining that psychology should be an objective sc ...
... In ____________________ ____________________, organisms learn that certain events occur together. Two variations of associative learning are classical conditioning and operant conditioning. (p. 288) ______________________ is the school of thought maintaining that psychology should be an objective sc ...
Intro to Learning
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
... • Acquisition: the stage when the CS and US are paired together. • Generalization: when the CR occurs even if the CS is slightly different • Discrimination: the capacity to distinguish between similar but distinct stimuli. • Extinction: the gradual elimination of a learned response that occurs when ...
Oct. 17, 2007
... – Responses are learned rather than innate – Learning is adaptive – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
... – Responses are learned rather than innate – Learning is adaptive – Our experiments can uncover the laws of learning • These laws will apply to animals and to humans ...
Classical Conditioning
... the school to safety. In November, the beeping alarm went off again, and the students again hurried out fearfully. However, this time it was only a fire drill, so there was no fire. Then for 10 days straight in December, the alarm malfunctioned and went off daily. Now no one paid any attention to it ...
... the school to safety. In November, the beeping alarm went off again, and the students again hurried out fearfully. However, this time it was only a fire drill, so there was no fire. Then for 10 days straight in December, the alarm malfunctioned and went off daily. Now no one paid any attention to it ...
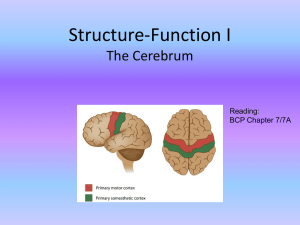
Structure-Function I
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
No Slide Title - people.vcu.edu
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
... FROM THE MOTOR CORTEX CORTICOSPINAL PATHWAY CORTICOBULBAR PATHWAY PYRAMIDAL TRACT LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL TRACT ...
BehNeuro11#2 (2) - Biology Courses Server
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
... What primary roles do the PV and LH play in regulating body weight i.e., what do they do? ...
RAPID REVIEW Learning is the process that allows us to adapt to
... point, the NS is called a conditioned stimulus (CS) and the response is called a conditioned, or learned, response (CR). The repeated pairing of the NS and UCS is known as acquisition. In order for classical conditioning to occur, the CS must occur before the UCS, the CS and UCS must occur close tog ...
... point, the NS is called a conditioned stimulus (CS) and the response is called a conditioned, or learned, response (CR). The repeated pairing of the NS and UCS is known as acquisition. In order for classical conditioning to occur, the CS must occur before the UCS, the CS and UCS must occur close tog ...
Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
... • Connect cerebrum to lower brain and cord centers • Internal capsule – dense band of tracts between thalamus and basal nuclei • Corona radiata – fanning out of band ...
... • Connect cerebrum to lower brain and cord centers • Internal capsule – dense band of tracts between thalamus and basal nuclei • Corona radiata – fanning out of band ...
Chapter 8
... the initial stage in classical conditioning the phase associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a conditioned response in operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response ...
... the initial stage in classical conditioning the phase associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a conditioned response in operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response ...
AP PSYCHOLOGY-Period 4 CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
... Extinction- the process of unlearning a behavior (when CS no longer causes the CR) Generalization- the tendency to respond to a similar CS (dogs respond to all types of bells, not just the one they were trained/conditioned with) Discrimination- when the subject is trained to tell the difference betw ...
... Extinction- the process of unlearning a behavior (when CS no longer causes the CR) Generalization- the tendency to respond to a similar CS (dogs respond to all types of bells, not just the one they were trained/conditioned with) Discrimination- when the subject is trained to tell the difference betw ...
review sheet (CC/OC)
... 16. Below are everyday situations in which some form of operant behavior is occurring. After reading each scenario, indicate whether it is an instance of generalization or discrimination. a. We stop our vehicles when the traffic light is red, but continue through the light when it is green. b. We s ...
... 16. Below are everyday situations in which some form of operant behavior is occurring. After reading each scenario, indicate whether it is an instance of generalization or discrimination. a. We stop our vehicles when the traffic light is red, but continue through the light when it is green. b. We s ...
physio unit 9 [4-20
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
Chapter Seven Part One - K-Dub
... 2.by using language to acquire information about events experienced by others. ...
... 2.by using language to acquire information about events experienced by others. ...
stimulus - K-Dub
... 2. by using language to acquire information about events experienced by others. ...
... 2. by using language to acquire information about events experienced by others. ...